Understanding Constipation: Causes, Risks, and Prevention Strategies
Constipation is a widespread condition caused by diet, hydration, nerve, and muscle issues, affecting bowel habits and causing discomfort. Recognizing causes like poor diet, dehydration, and neurological factors helps prevent complications. Maintaining a fiber-rich diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding caffeine can support regular bowel movements and overall digestive health.
Sponsored

Constipation is a common digestive issue characterized by infrequent or hard stools. It affects people of all ages and is usually not a serious health concern. Typically, normal bowel movements vary from thrice daily to once every few days. When bowel movements are delayed beyond three days, stool becomes harder and more difficult to pass, leading to discomfort.
Symptoms include difficulty passing stool, infrequent bowel movements, bloating, abdominal pain, and dry or hard stools. Causes often relate to diet, fluid intake, and bowel habits.
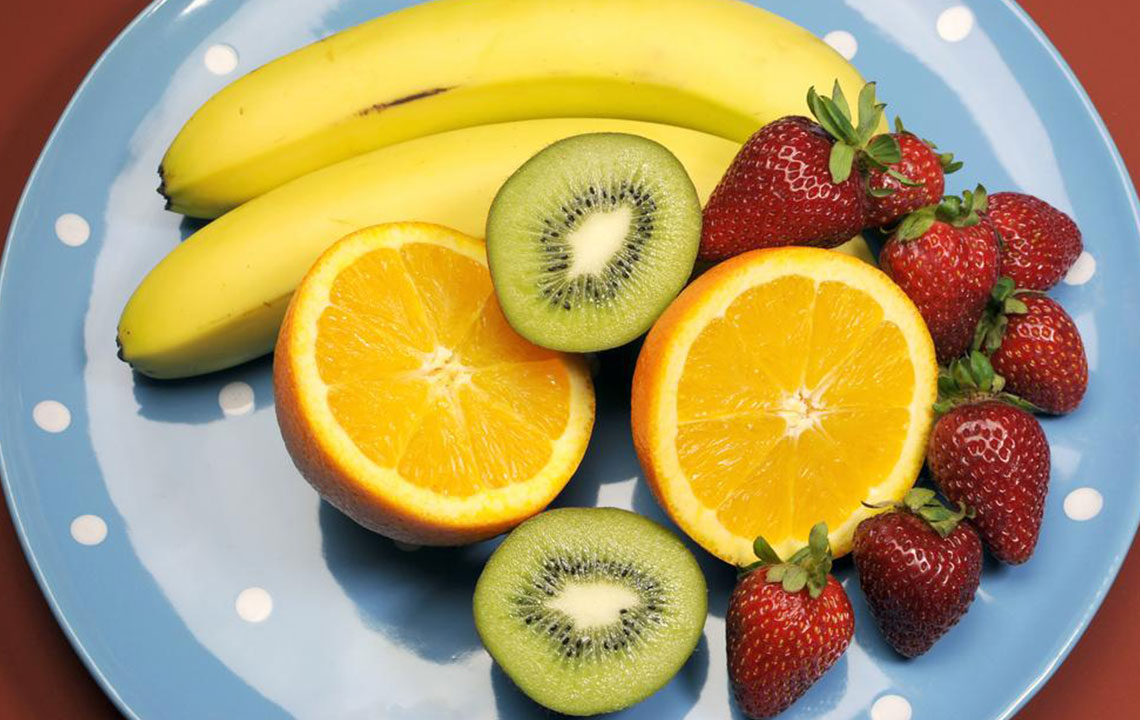
The primary contributors to constipation include poor dietary choices, insufficient hydration, and lifestyle factors. Eating foods high in animal fats and refined sugars, along with low fiber intake, hampers digestion and stool softness. Dehydration from inadequate fluid consumption dries out stools, making passage challenging. Excessive caffeine or alcohol intake can further dehydrate the body, worsening the condition.
Obstructions like anal fissures, bowel obstructions, or tumors can block stool movement. Nervous system issues such as neuropathy or neurological diseases like Parkinson’s affect nerve signals, disrupting bowel movement. Pelvic muscle dysfunctions, including weakness or uncoordinated contractions, also contribute to constipation.
Hormonal imbalances from conditions like thyroid disorders, diabetes, or pregnancy can disturb bowel function. Risk factors encompass dehydration, poor diet, physical inactivity, certain medications, and mental health conditions. Chronic constipation may lead to complications such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, rectal prolapse, and fecal impaction. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fiber, staying well-hydrated, and avoiding excessive caffeine can help prevent constipation and its complications.