Effective Strategies for Managing Blood Glucose Levels in Diabetes
Discover comprehensive strategies to control blood sugar levels in diabetes. From regular monitoring and carbohydrate management to exercise and blood pressure control, learn effective approaches to improve your overall health. Support from healthcare professionals and support groups can enhance your efforts, helping you lead a healthier life with diabetes.
Sponsored
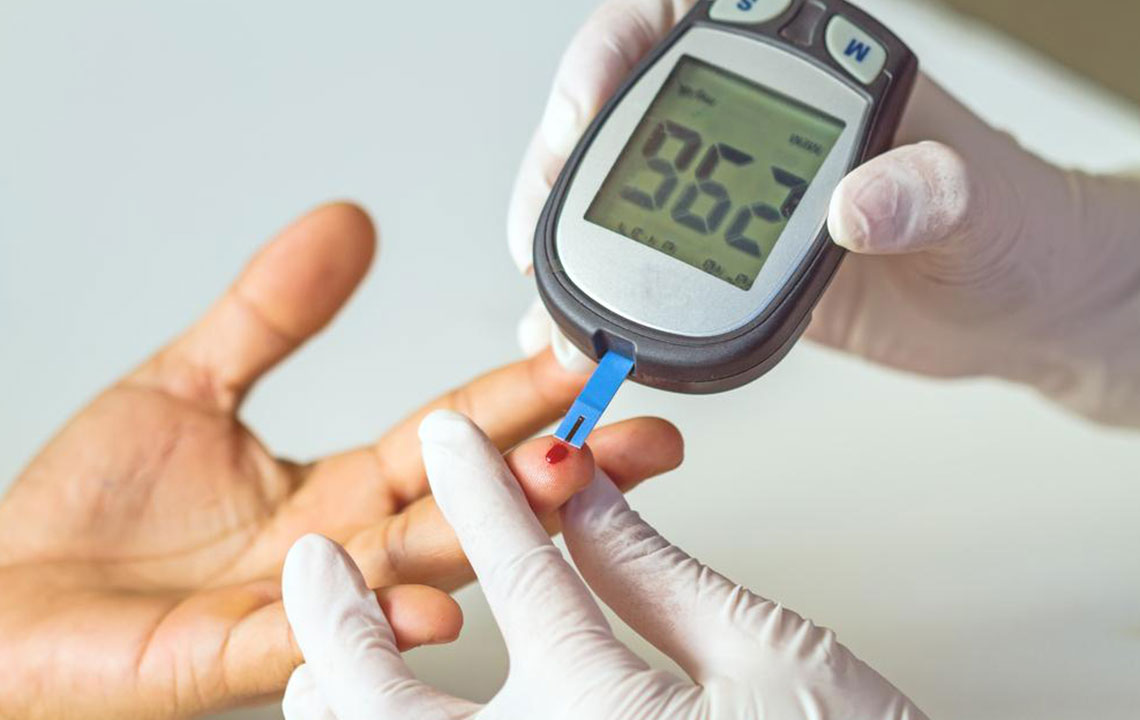
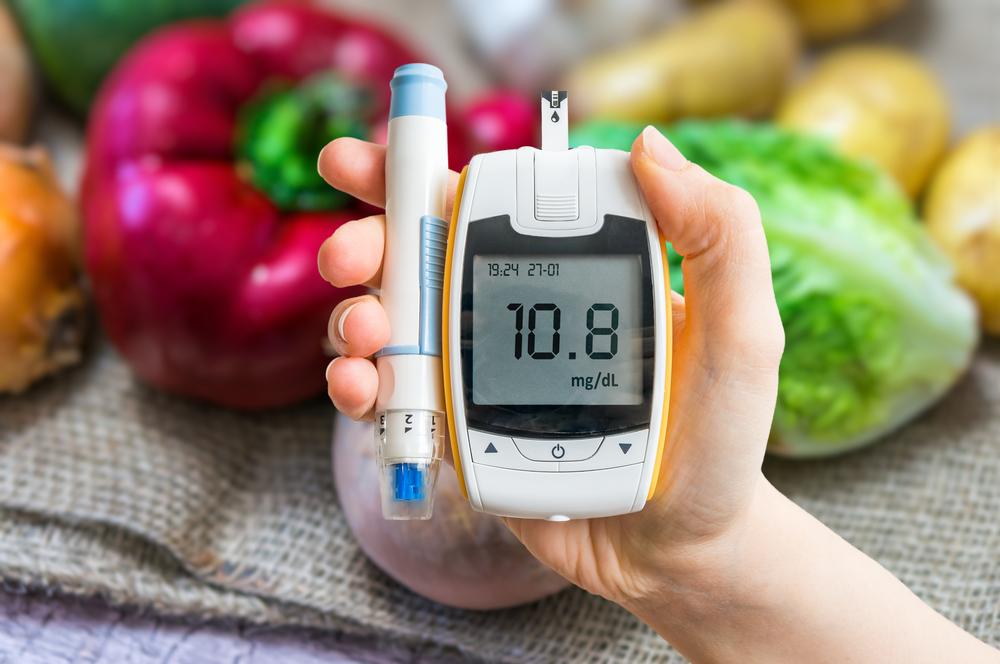
Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
One cornerstone of diabetes management is frequent blood sugar testing. Your healthcare provider may suggest specific times for testing, such as fasting and post-meal. You can also perform additional checks at home without prior notice. This approach offers real-time insights into your condition, enabling you to make informed adjustments in diet and activity levels to maintain stability.
Imagine managing a team where unpredictability hampers performance; similarly, consistent monitoring helps keep your blood sugar levels within desired ranges, allowing better control over your health.
Managing Carbohydrate Consumption
Carbohydrates greatly influence blood sugar spikes, making their regulation crucial. Women typically need about 40-45 grams per meal, while men require 45-60 grams. For context, a small serving of rice or pasta contains approximately 45 grams of carbs. Pairing carbohydrates with proteins like meats and nuts or choosing high-fiber foods such as vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can slow digestion and prevent blood sugar surges. Prioritizing fiber-rich foods and minimizing added sugars are essential steps in managing diabetes effectively.
Incorporating foods like sweet potatoes, whole wheat bread, beans, pumpkins, and gourds supports better blood sugar management and vascular health. Beware of processed "sugar-free" products, as they may contain high-carb additives detrimental to your health.
Physical Activity as a Therapeutic Tool
Engaging in regular exercise helps significantly lower blood glucose levels. Consistency is key; aim for at least 150 minutes of activity weekly, divided into manageable 30-minute sessions. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are excellent options. Always consult a healthcare professional before initiating a new exercise routine. Exercise releases endorphins, improving mood and motivation, which further supports your health efforts.
Monitoring Blood Pressure and Lipid Levels
Managing diabetes isn't just about blood sugar; controlling cholesterol and blood pressure is equally important. Regularly check cholesterol levels every five years or more frequently if needed. HbA1c tests, which reflect average blood sugar over time, should be performed at least twice annually. Blood pressure and weight should be routinely monitored during medical visits.
Effective diabetes management benefits from a collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals, family, and support groups. Education, peer encouragement, and understanding your condition enhance adherence to treatment plans. Participating in diabetes education classes and support networks can provide valuable insights and motivation for sustained health improvements.






