Comprehensive Guide to Diabetic-Friendly Food Choices
This comprehensive guide offers essential advice on selecting the best and worst foods for diabetes management. Learn how to incorporate healthy proteins, grains, fruits, vegetables, and fats into your diet. Discover tips to avoid foods that may spike blood sugar levels and embrace lifestyle changes for better health. Perfect for diabetics seeking practical dietary guidance to maintain stable blood glucose and enhance overall wellness.
Sponsored

Guide to Managing Diabetes Through Food
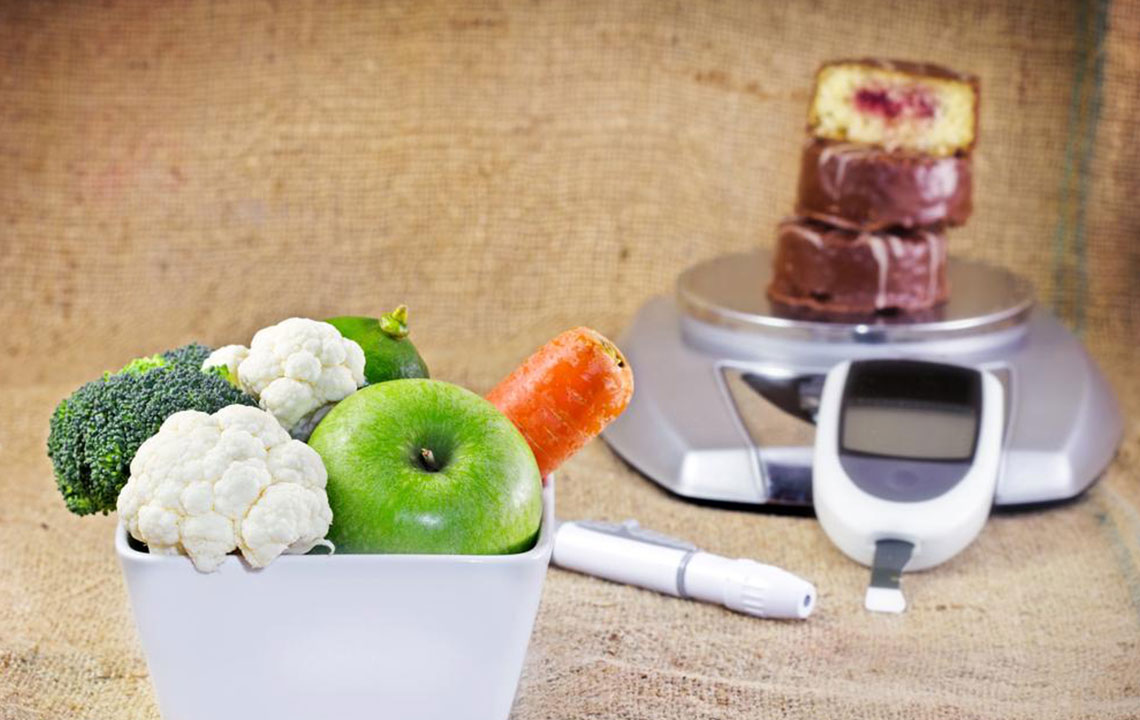
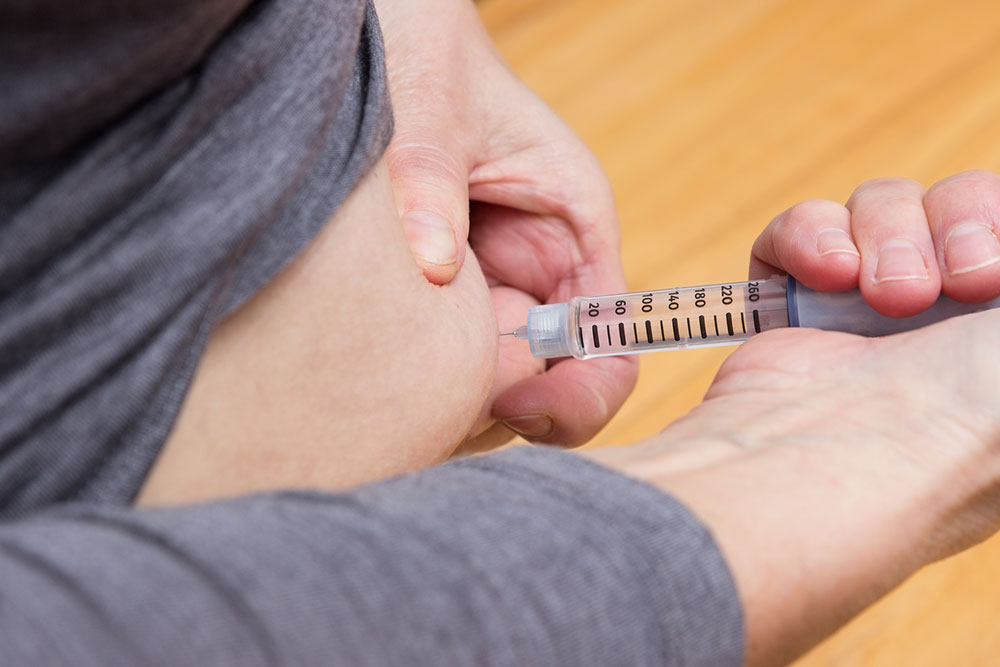
Diabetes, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, is a prevalent health concern in the United States. Rapid lifestyle changes and dietary habits contribute to the rising number of diagnosed individuals. Once diagnosed, managing blood sugar becomes a lifelong necessity, often requiring dietary adjustments. Luckily, a balanced diet doesn't have to be dull. Knowing the best and worst food options helps create an enjoyable, healthy meal plan suitable for diabetics, making it easier to maintain optimal health.
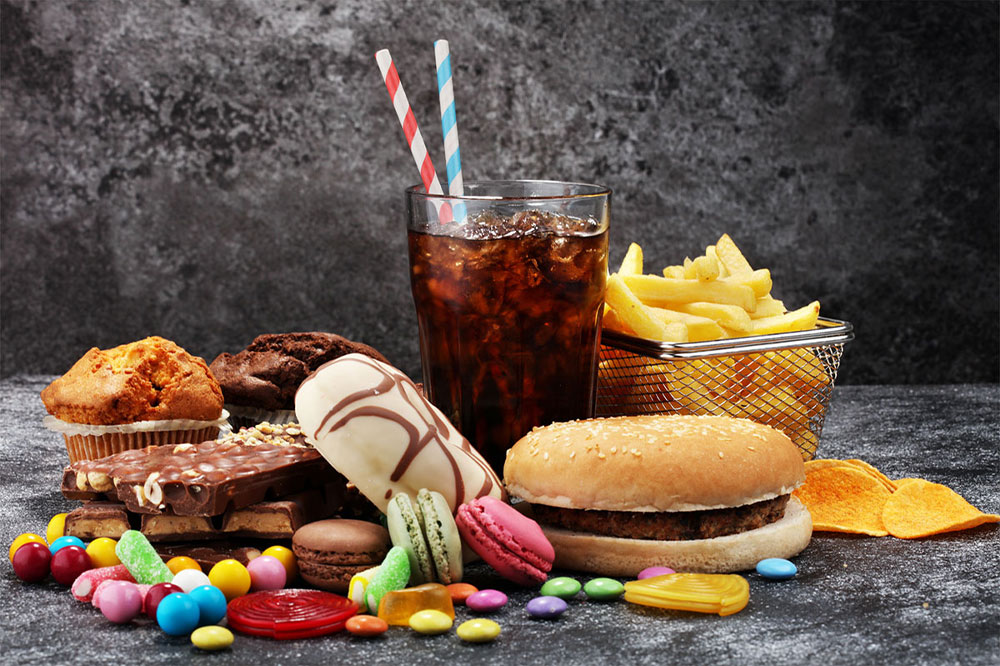
Choosing the Right Proteins According to the American Diabetes Association, protein intake is vital for diabetics, but the focus should be on lean sources like fish and poultry. Incorporate options like salmon and turkey several times weekly. Vegetarians can opt for beans and nuts, which are rich in healthy protein. Conversely, processed meats such as hot dogs and red meats are discouraged because they can spike blood sugar and harm cardiovascular health.
Milk and Dairy Selections Greek yogurt without artificial sweeteners is excellent for diabetics, suitable for breakfast or snacks. Opt for low-fat dairy options to control blood sugar levels. Avoid sugary desserts like chocolates and ice creams, which are high in fats, and steer clear of dairy products with added sugars or artificial flavors.
Whole vs. Processed Grains Whole grains like oats, quinoa, and wild rice are beneficial, helping regulate blood sugar and providing essential nutrients. On the other hand, refined grains from white flour—such as white bread, pastries, and many breakfast cereals—should be avoided, along with white rice and pasta, to prevent blood sugar spikes.
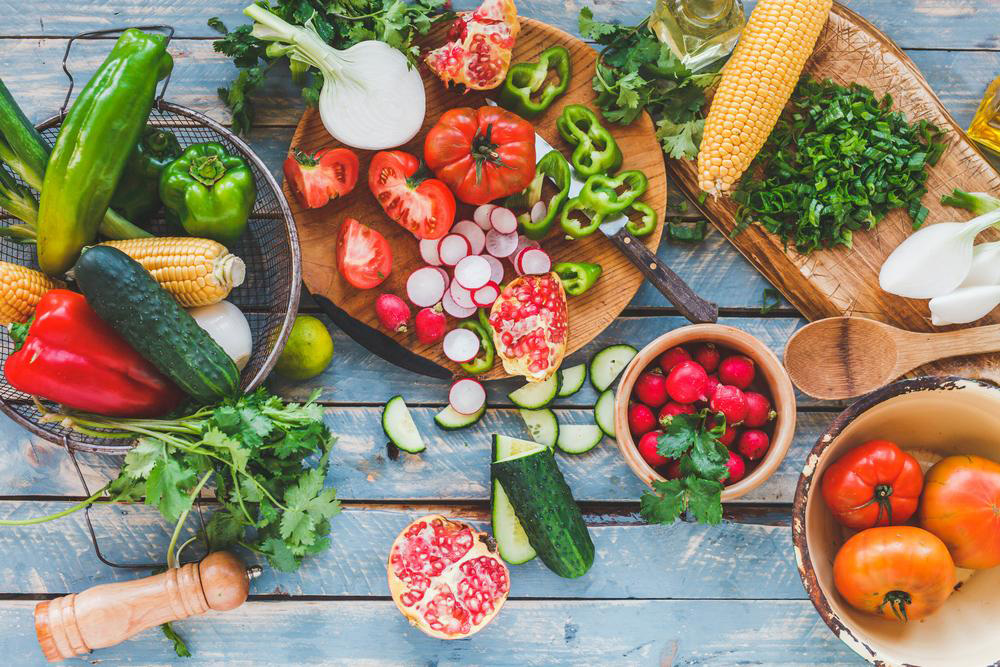
Fruit Choices and Precautions Fresh berries are excellent due to their fiber and antioxidant content. Other good options include guava, lemon, and cucumber. Dry fruits and high-sugar fruits should be consumed sparingly, as they can raise blood glucose levels. Packaged fruit juices are best avoided due to added preservatives and sugars.
Vegetables for Blood Sugar Control Prioritize high-fiber, low-carb vegetables such as carrots, broccoli, cauliflower, and leafy greens. Limit starchy vegetables like potatoes, peas, and corn, and consume them occasionally. These choices help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Healthy Fats and Their Role Incorporate beneficial fats like avocados, nuts (almonds, pecans), and oils rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Limit unhealthy fats found in fried foods, cheese, butter, and processed processed meats, which can exacerbate insulin resistance and cholesterol issues.
To effectively manage diabetes, focus on portion control and balanced carbohydrate intake. Knowledge of which foods to include or avoid, along with portion sizes, plays a crucial role. Adopting a healthy lifestyle with balanced diet and regular physical activity can help control blood sugar levels and improve overall well-being.