Understanding Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
This article provides a comprehensive overview of diabetic peripheral neuropathy, highlighting its causes, common symptoms like leg weakness and skin discoloration, risk factors, and effective management strategies. Emphasizing early detection and lifestyle modifications, it offers guidance on preventing nerve damage related to diabetes for improved health and mobility.
Sponsored
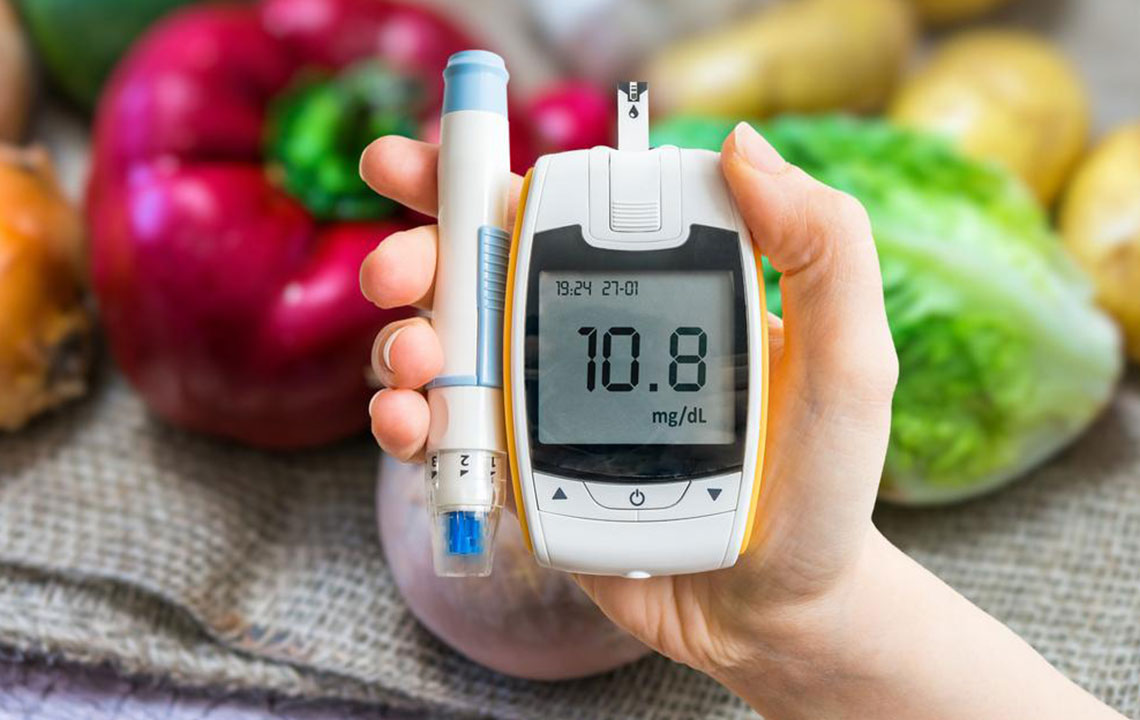
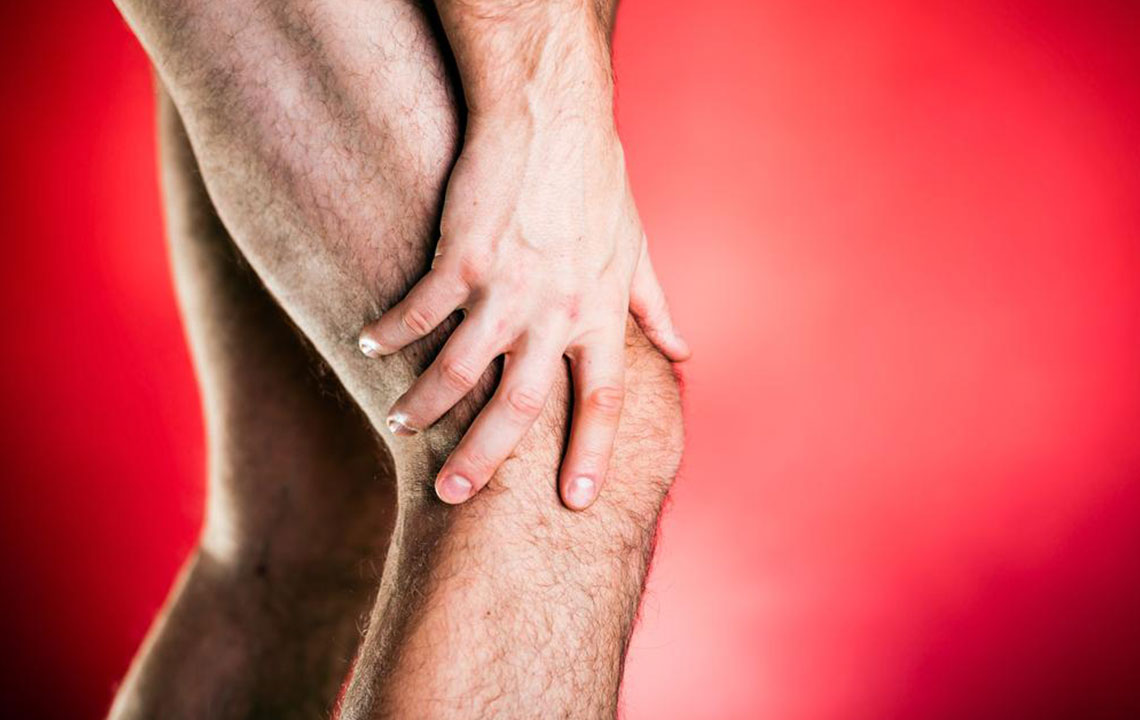
Diabetes is a serious health condition that can lead to a range of complications, notably nerve damage known as diabetic peripheral neuropathy. This condition often begins subtly, with early signs like leg discomfort and cramps, progressing over time due to prolonged high blood sugar levels which harm nerve fibers. Many individuals remain unaware of neuropathy until symptoms intensify, sometimes only diagnosed after severe nerve impairment affects the limbs.
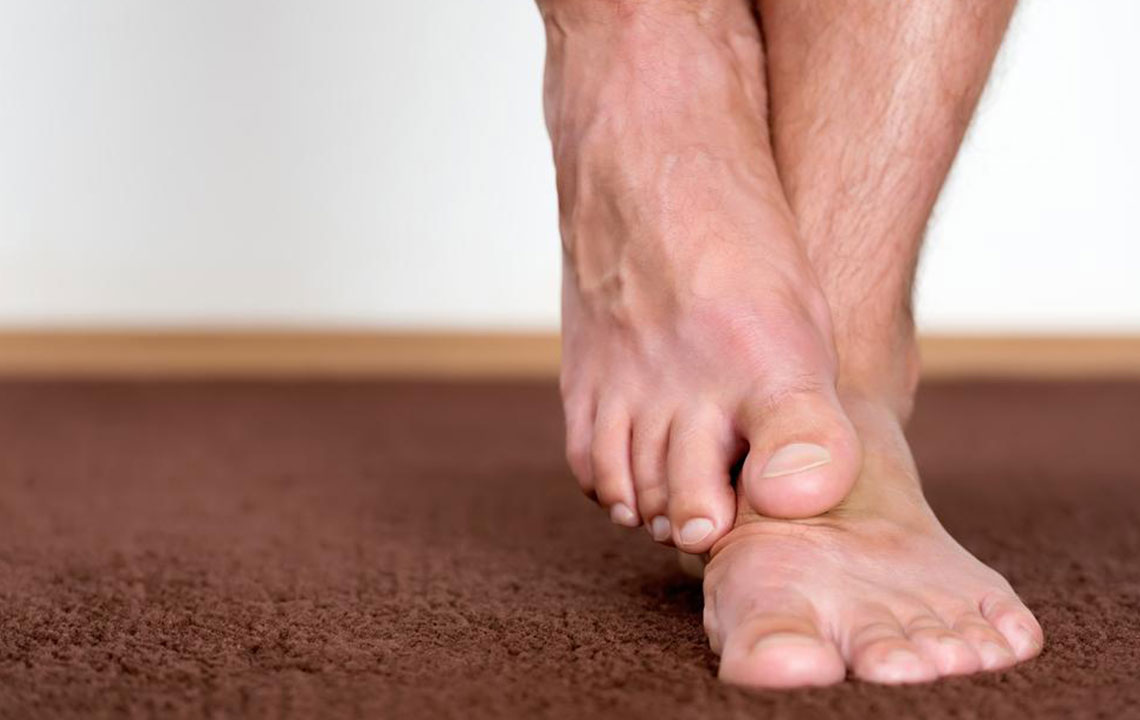
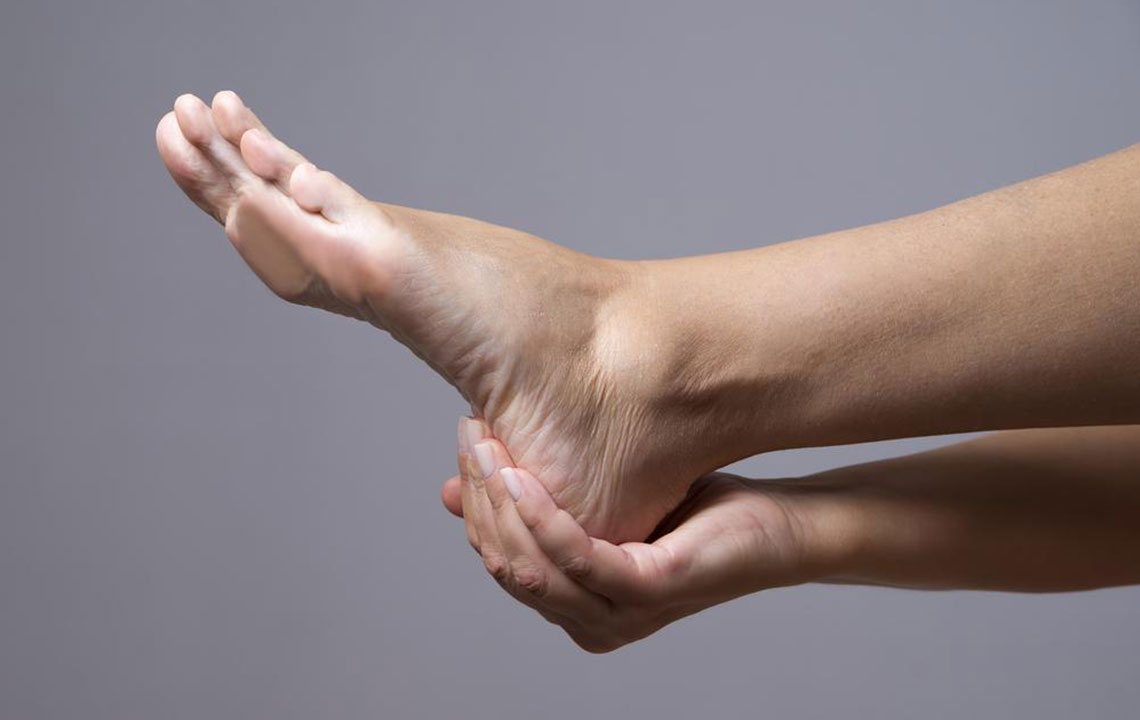
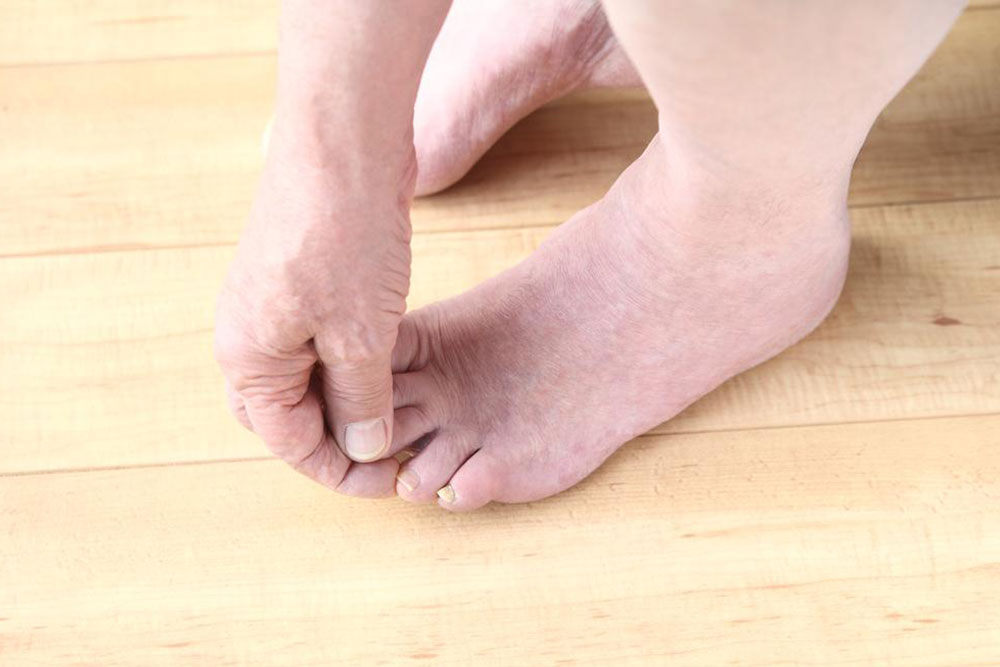
Diabetic neuropathy occurs when insulin production or effectiveness is compromised, impacting blood sugar regulation. Common signs include leg weakness, numbness, and skin changes such as discoloration and hair loss. Risk factors contributing to uncontrolled glucose include alcohol use, infections, autoimmune conditions, nutritional deficiencies, and repetitive nerve strain.
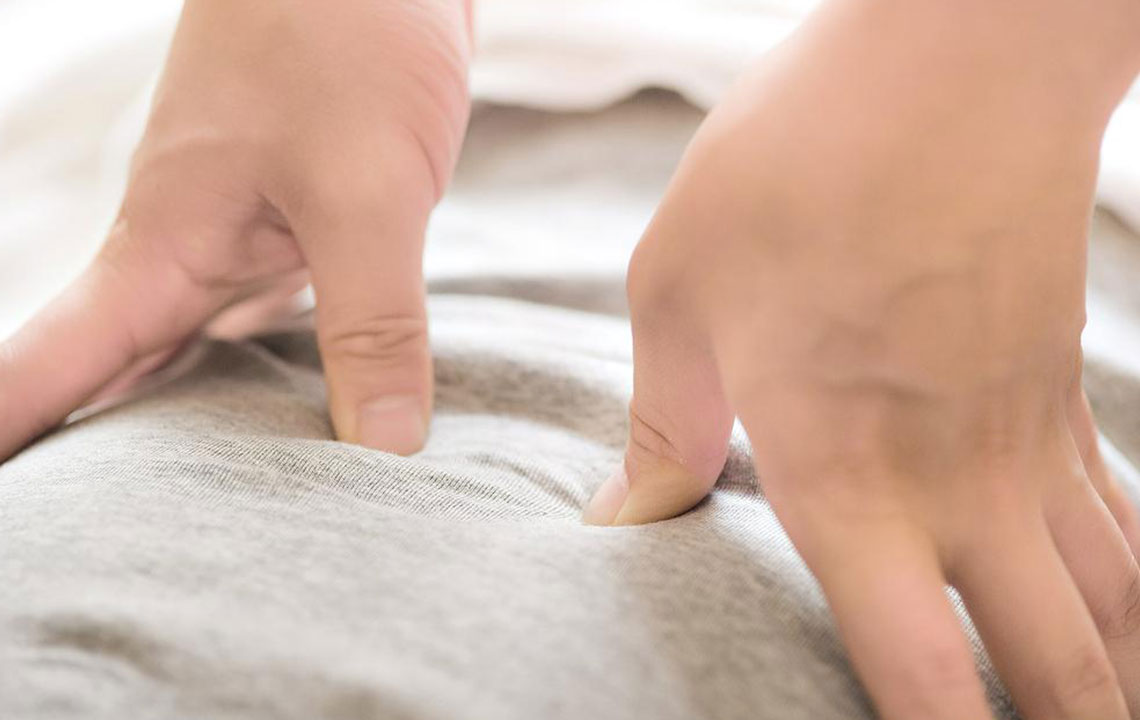
Symptoms like tingling, numbness, and changing skin color indicate nerve trouble, which could result from circulatory issues and nerve fiber damage. To prevent complications, adopting healthy lifestyle habits like a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and medical management is crucial. Early detection and treatment help maintain nerve health and prevent severe disability.
Managing diabetic neuropathy entails controlling blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, alongside consulting healthcare professionals. Recognizing early warning signs and taking proactive measures can significantly improve quality of life and prevent progression of nerve damage.