Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Gout Pain and Preventing Attacks
Discover effective ways to treat and prevent gout, including medication options and lifestyle changes. Learn how drugs like NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids help manage symptoms, while preventive measures focus on lowering uric acid levels. Incorporate dietary tips, lifestyle modifications, and explore alternative therapies under medical guidance to control gout and reduce attacks effectively.
Sponsored
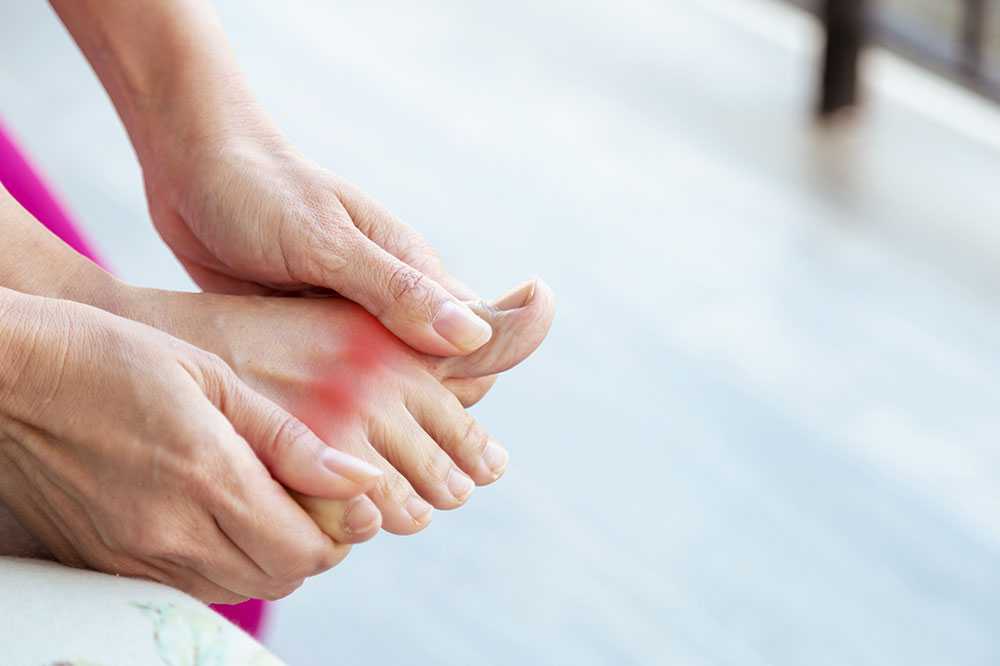
Approaches to Alleviating Gout Discomfort and Avoiding Future Flare-ups
Effective gout management often relies on medication choices tailored to your health status and personal preferences. These treatments aim to relieve acute pain episodes and prevent recurring attacks, while also minimizing complications like tophi formation due to uric acid crystal build-up.
Medications for Gout Management
Common drugs include:
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): Over-the-counter options such as ibuprofen and naproxen, along with prescription medicines like celecoxib and indomethacin, are used to reduce inflammation. Doctors may prescribe higher doses during attacks and lower doses for ongoing prevention.
It’s vital to note NSAIDs can cause stomach issues, including ulcers and bleeding.
Colchicine: This medication can effectively diminish gout pain but may cause side effects like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. After an attack, a daily low dose might help prevent future episodes.
Corticosteroids: Prednisone can manage pain and swelling when other medications are unsuitable. This drug may raise blood sugar, influence mood, or elevate blood pressure, so medical supervision is essential.
Preventive Medications to Reduce Gout-Related Risks
If gout attacks are frequent or less painful, doctors might recommend medications to lower uric acid levels:
Uric Acid Production Blockers: Drugs like allopurinol and febuxostat inhibit uric acid synthesis, decreasing attack risk but might cause rash, low blood counts, or liver issues.
Uric Acid Excretion Enhancers: Probenecid improves kidney removal of uric acid but can increase the likelihood of kidney stones and cause stomach or allergic reactions.
Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
While medications are primary, lifestyle and home remedies can support gout management. Suggestions include:
Reducing alcohol intake and sugary beverages, especially those with fructose.
Avoiding purine-rich foods like organ meats, red meat, and seafood.
Engaging in regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight to lower flare-up risks.
Consult your healthcare provider before trying alternative therapies, and be aware of their benefits and potential interactions with existing treatments. Some foods like cherries, vitamin C, and coffee have shown promise in reducing uric acid, but more research is necessary to confirm their effectiveness and safety.
Other complementary approaches such as relaxation techniques and homeopathic remedies may also aid in managing gout.