Essential Guide to Managing Gout: Treatments and Prevention
This comprehensive guide explores effective gout treatments, including medications and lifestyle changes. It emphasizes the importance of managing uric acid levels through proper diet, medication, and healthy habits to prevent flare-ups and long-term joint damage.
Sponsored
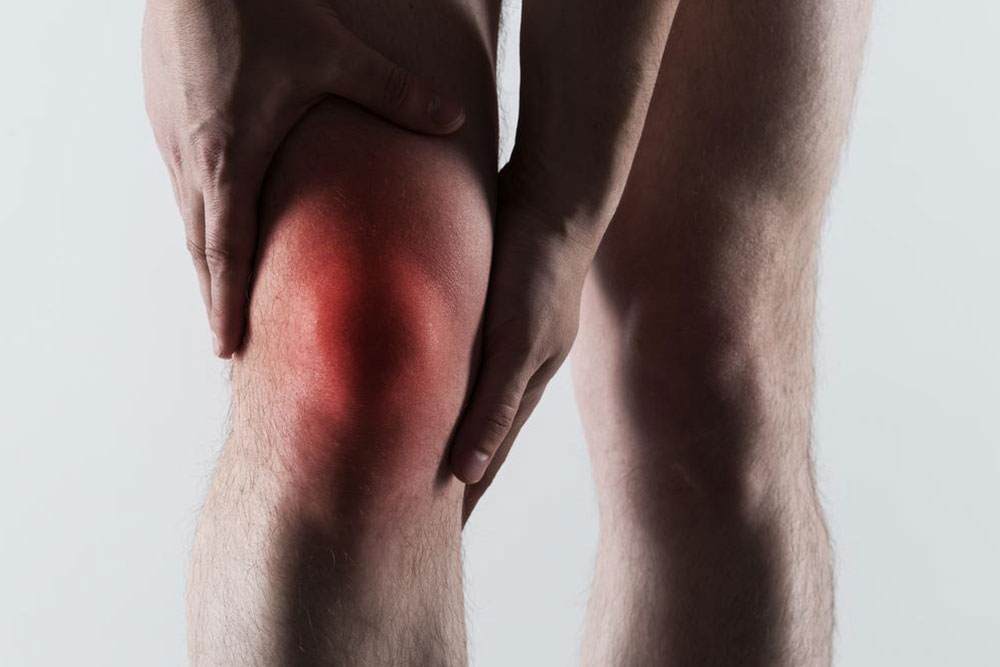
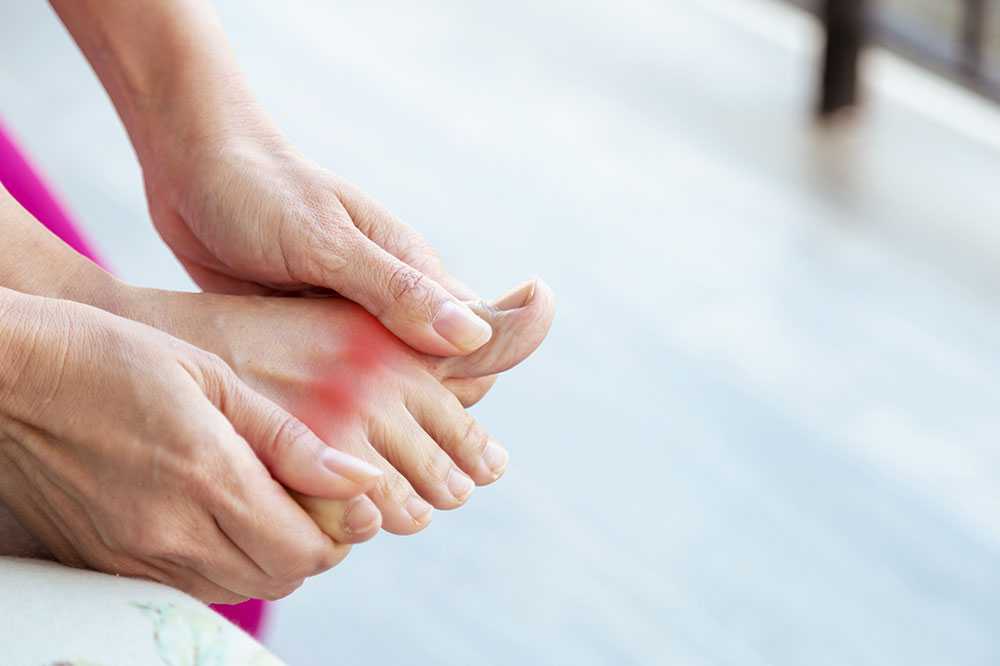
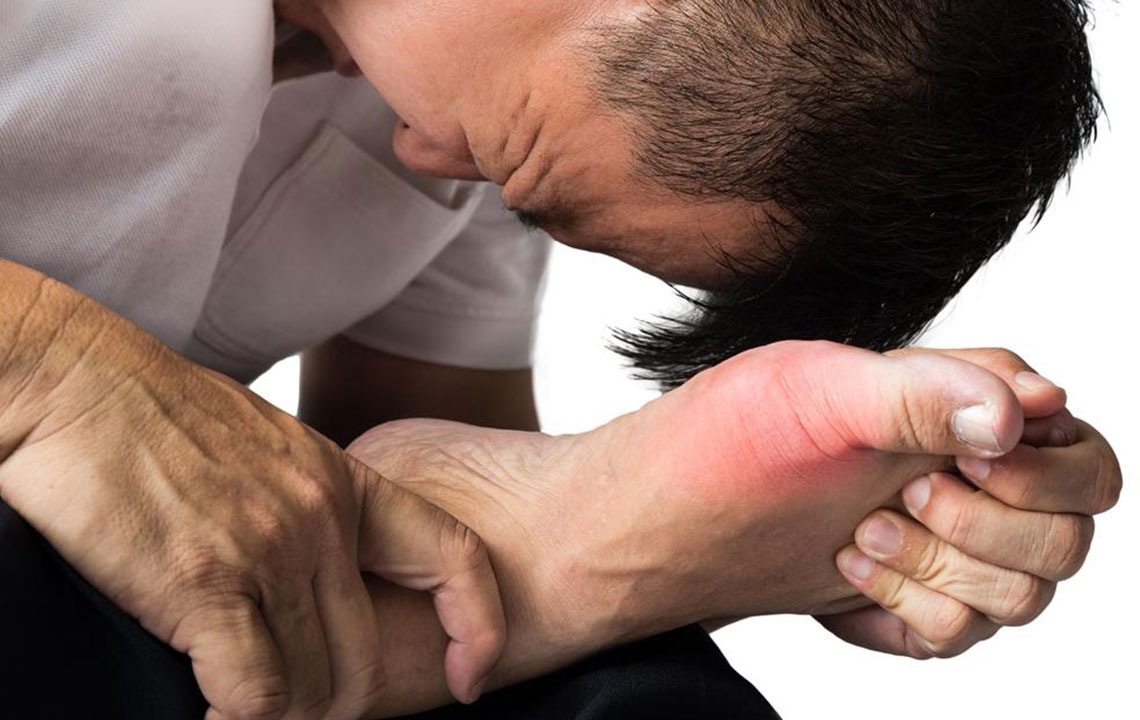
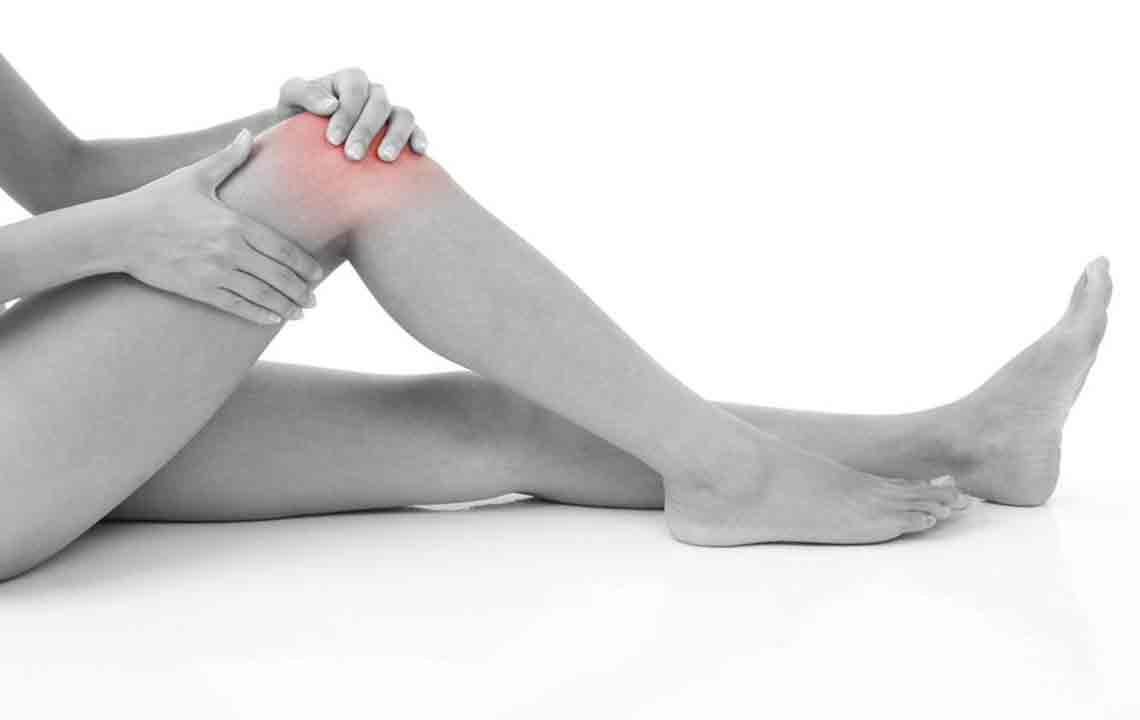
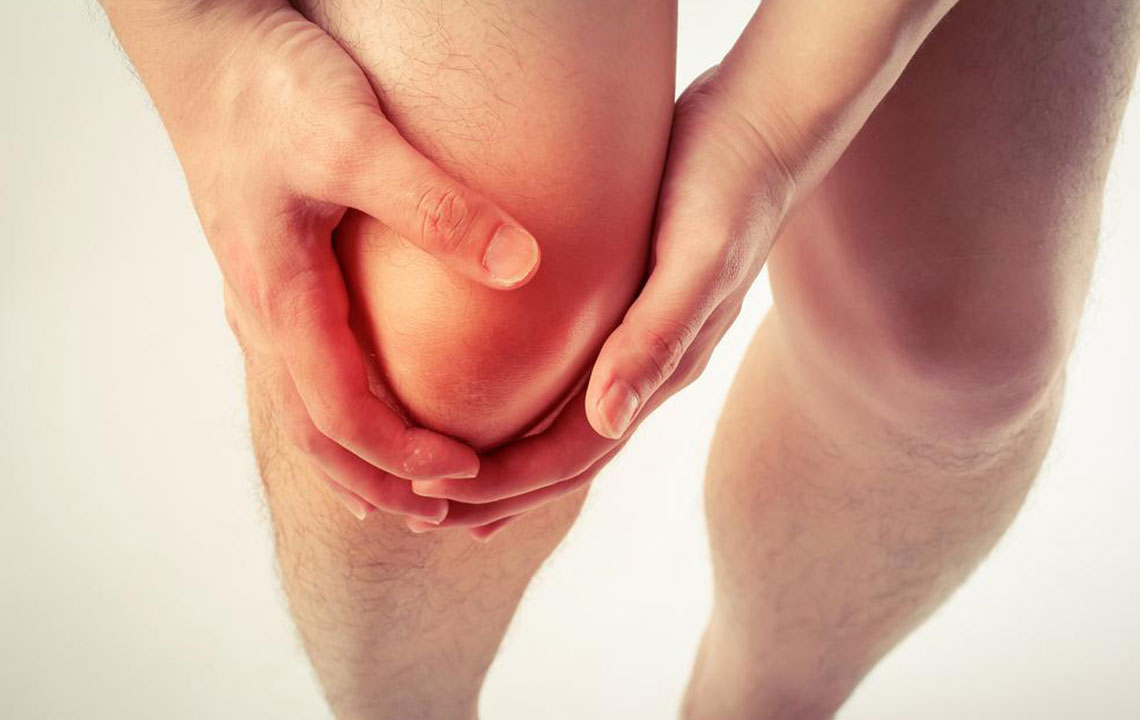
Gout is a painful form of arthritis characterized by sudden flare-ups causing joint redness, swelling, and tenderness. Understanding how to effectively treat this condition is crucial for relief and prevention.
Common symptoms include intense joint pain, inflammation, and warmth. Typically, these attacks happen abruptly, making joints feel burning and swollen.
Understanding Gout Causes
Gout results from the accumulation of urate crystals due to high uric acid levels in the blood. Elevated uric acid can be caused by obesity, excessive alcohol intake, and diets rich in purines—found in red meats, white bread, rice, pasta, and processed foods.
Effective Gout Treatments
Medications are the mainstay for managing gout. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, or celecoxib help reduce inflammation and pain. Colchicine is another effective option to alleviate pain and prevent uric acid crystal formation. Corticosteroids are prescribed to control inflammation when NSAIDs or colchicine are unsuitable.
To prevent future attacks, it's important to manage uric acid levels. Drugs like allopurinol and febuxostat inhibit uric acid production, while probenecid increases its excretion via urine. Lifestyle modifications, such as reducing alcohol and purine-rich foods, maintaining a healthy weight, and consuming vitamin C-rich foods like oranges, broccoli, and grapefruit, can significantly lower risks. Coffee consumption may also help reduce symptoms, though it doesn't cure gout.