Signs and Symptoms Indicating a Spinal Compression Fracture
This article highlights key signs of spinal compression fractures, including back pain, hunchback posture, height loss, breathing issues, hip discomfort, and digestive problems. Recognizing these symptoms early, especially in at-risk groups like women over 50, can lead to timely medical intervention and prevent severe complications. Consulting healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment is essential. The article emphasizes understanding the effects of vertebral collapse and how it impacts overall health.
Sponsored
Indicators of a Spinal Compression Fracture
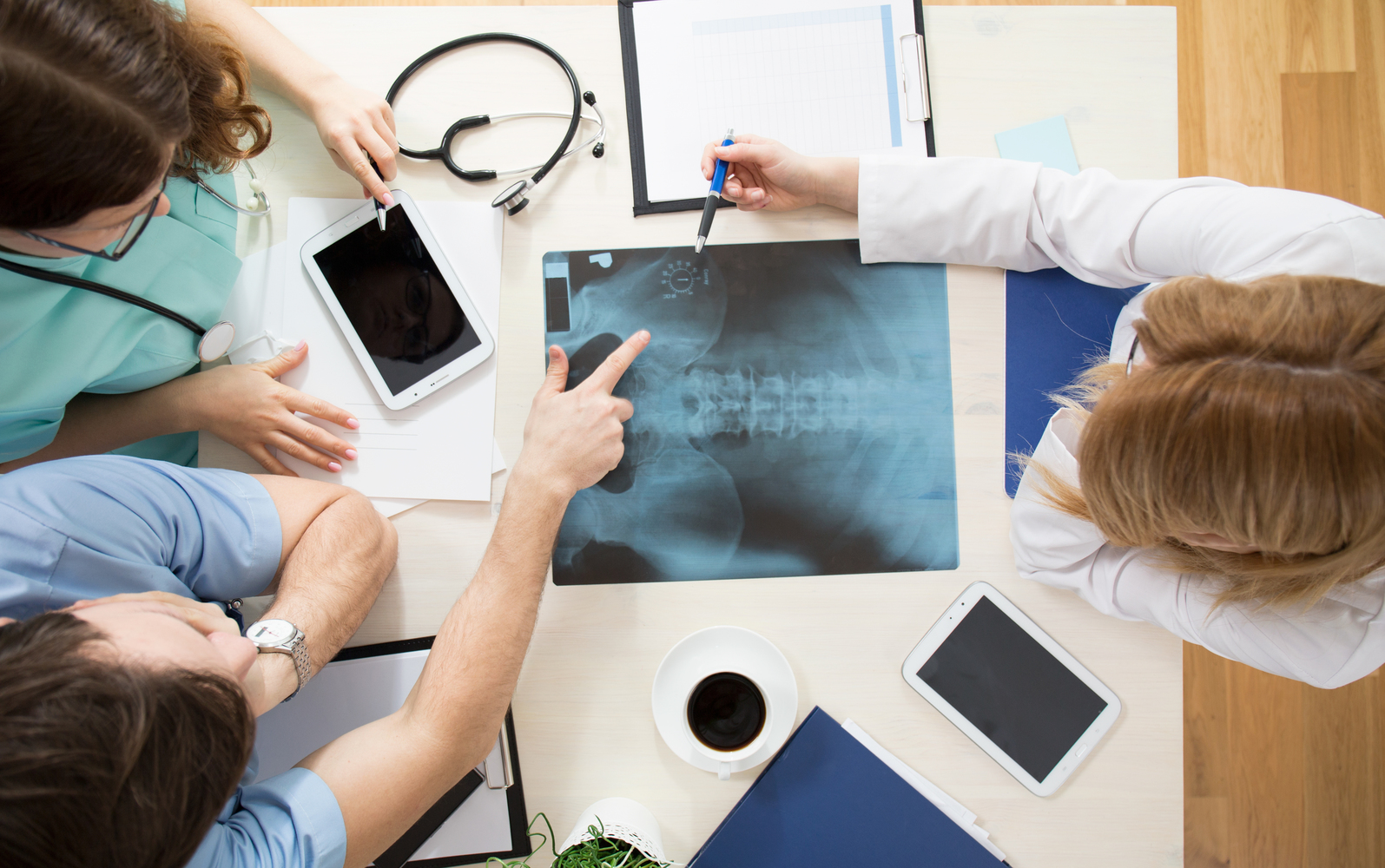
Back pain is a primary indicator of spinal compression fractures. The discomfort may appear suddenly or develop gradually, often worsening over time. Osteoporosis is a common cause, especially in women over 50. If you're in this age group, consulting a healthcare provider is vital to prevent further vertebral damage through early intervention. The fracture can cause the vertebrae to collapse, altering spinal stability and affecting overall bodily functions.
This collapse can lead to changes in posture and movement. The following symptoms may suggest a spinal compression fracture:
Back Hump or Kyphosis
As vertebrae collapse, the spine curves forward, creating a hunchback appearance and causing persistent back and neck pain as the body adjusts.
Reduction in Height
Multiple fractures cause the spine to shorten gradually, resulting in a noticeable loss of height over time.
Respiratory Difficulties
Severe spinal compression can impair lung function, leading to breathing issues.
Hip Discomfort
Vertebral collapse shortens the spine and brings ribs closer to the hips, causing friction and pain in the hip area.
Digestive Symptoms
Spinal shortening can exert pressure on the stomach, resulting in appetite loss, weight reduction, and constipation.
If you or someone you know experiences back pain with any of these symptoms, seeking medical advice is crucial. Early diagnosis can facilitate effective treatment and prevent complications.