Understanding Vertebral Compression Fractures: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Learn about vertebral compression fractures, including their symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options. Early detection and proper care are key to recovery from this common spinal injury, which often results from osteoporosis or weakened bones. Non-invasive treatments and home remedies can aid healing, while surgical interventions may be necessary for severe cases. Understanding these aspects helps in preventing complications and ensuring effective recovery.
Sponsored

A vertebral compression fracture happens when a vertebral bone in the spine collapses, often creating a wedge shape with the vertebra shrinking and deforming. Multiple fractures can lead to kyphosis, a spinal curve that reduces height. Most fractures occur in the middle or lower back, causing significant discomfort.
Recognizing Symptoms
Symptoms may include back pain, stiffness, and weakness or numbness in limbs, though signs vary. Sudden pain is common, and the discomfort tends to worsen over time.Causes and Risk Factors
Fragile bones, osteoporosis, and weakening conditions are primary causes, especially in women over 50. Heavy lifting or falls can trigger fractures. Increased risk is linked to osteoporosis, certain cancers like lymphoma or myeloma, and racial factors, with Asian and Caucasian women being more susceptible.Diagnostic Methods
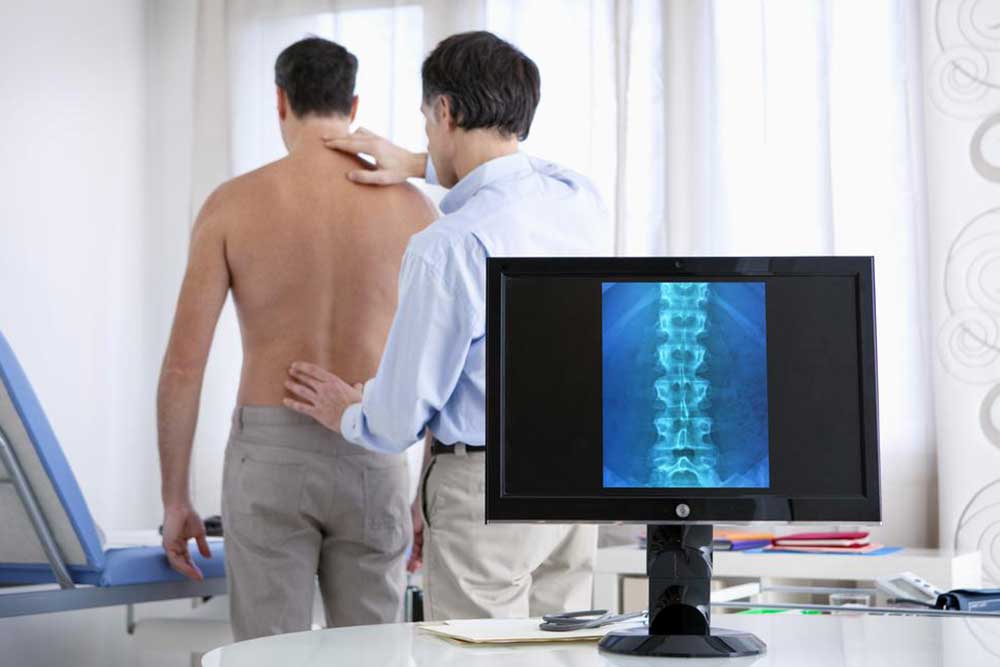
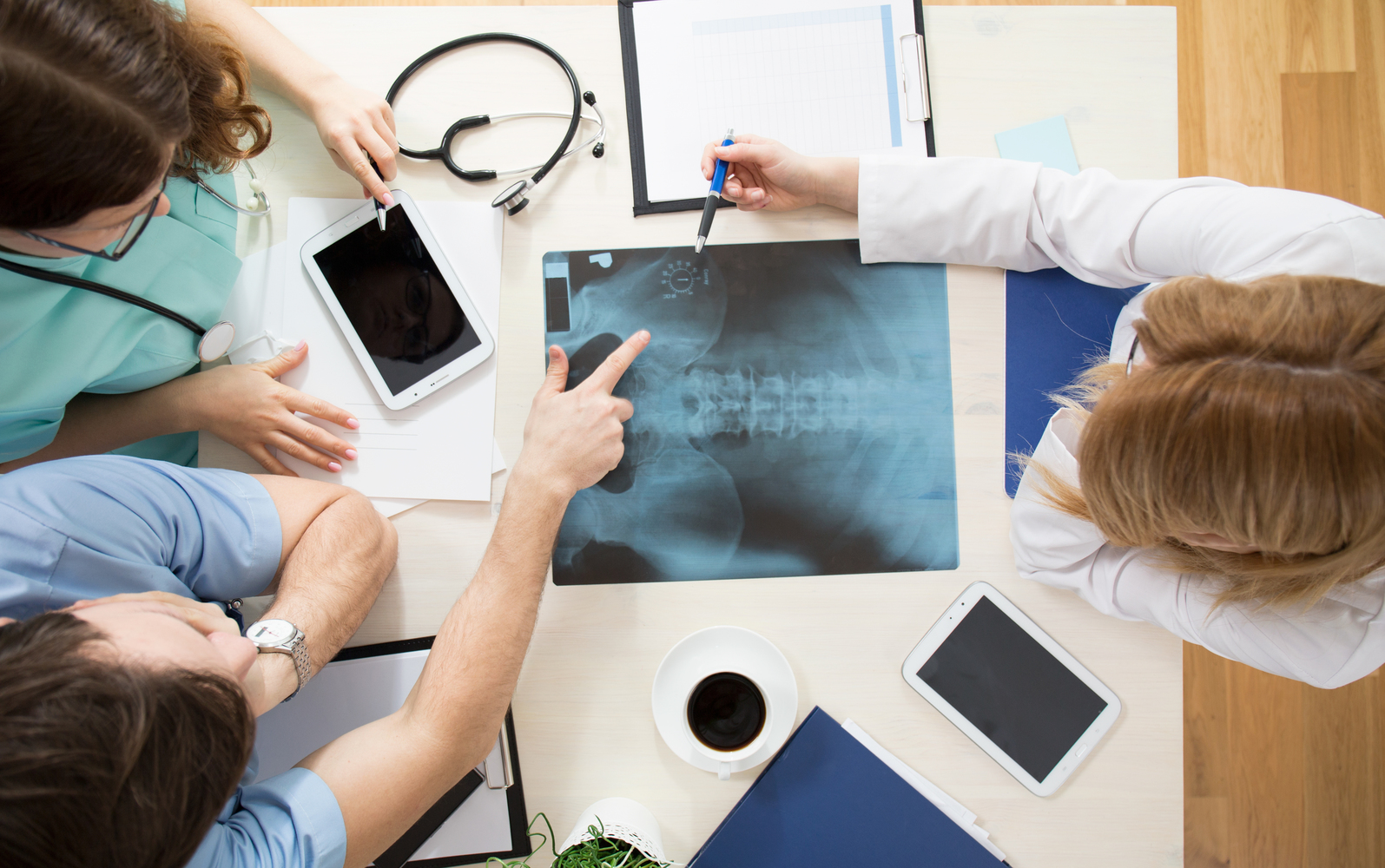
Doctors evaluate medical history and conduct physical assessments. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, CT scans, and bone scans are vital for confirmation of a fracture.Treatment Strategies
Non-surgical options include pain management, bracing, and calcium or vitamin D supplements. Surgery, like kyphoplasty or vertebroplasty, may be necessary for unstable fractures. Rehabilitation focuses on gradual activity resumption.Home Care Recommendations
Applying ice reduces swelling, and bed rest helps during recovery. Eating calcium- and vitamin D-rich foods strengthens bones. Early consultation is crucial for effective healing, which typically takes three to six months.