Top Strategies for Treating Red Eyes Effectively
Discover effective methods for treating red eyes, including home remedies like warm and cold compresses, appropriate use of eye drops, and when to seek medical attention. Learn how to identify causes such as infections, allergies, or blood vessel issues, and adopt long-term habits to prevent recurrence. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures safe and personalized treatment for red eye relief and eye health maintenance.
Sponsored
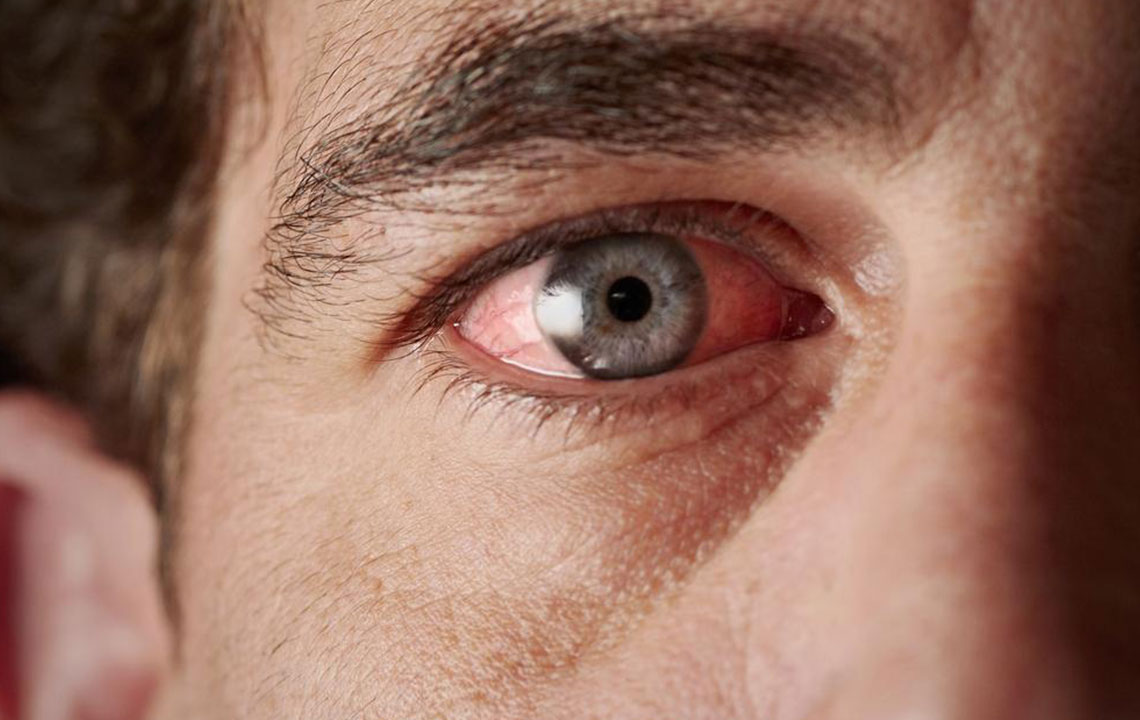
Eyes endure daily exposure to dust, weather changes, and harsh temperatures, which can lead to redness and irritation. Red eyes may result from infections, allergies, foreign objects, or broken blood vessels. Usually temporary, red-eye often clears up quickly, but understanding the underlying cause is essential for proper treatment.
Conditions like conjunctivitis (pink eye), allergies, blepharitis, or subconjunctival hemorrhage require specific approaches. Recognizing the cause helps determine the right treatment—whether home remedies or medical intervention.
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
An inflammation that appears in allergic, viral, or bacterial forms. It’s highly contagious, and diagnosis guides treatment.
Allergic Reactions
Common allergens like pollen, mold, and pet dander trigger histamine release, drying eyes and causing blood vessels to swell.
Blepharitis
An inflammation of the eyelid edges presenting with redness, burning, and itching.
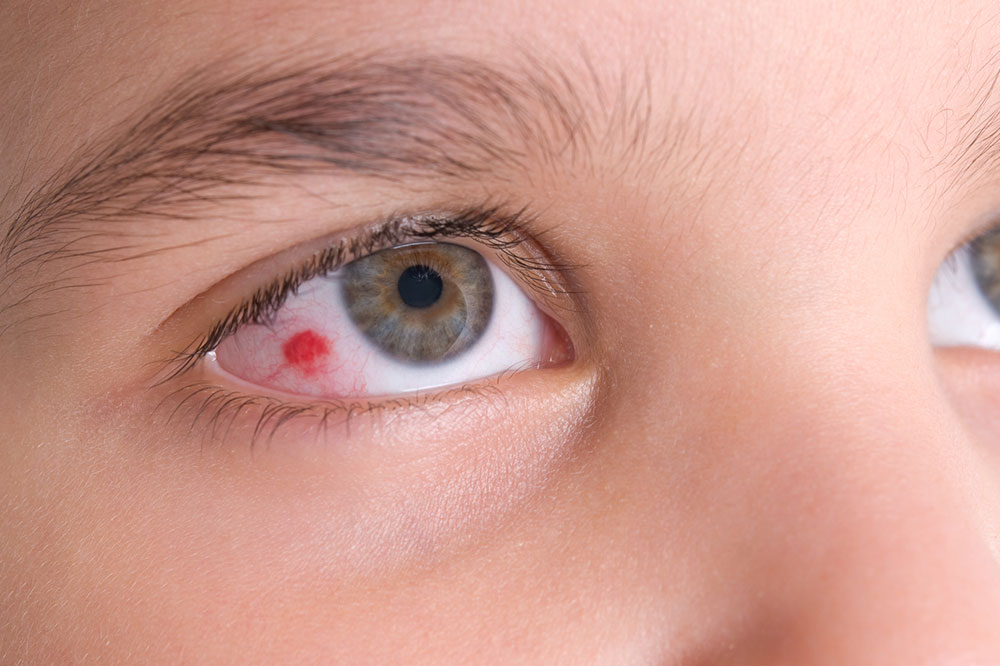
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
Looks like a small bruise in the eye caused by coughing, sneezing, or minor trauma, especially in individuals on blood thinners or with high blood pressure.
Red eye treatment varies based on the cause but often includes:
Warm Compress
Applying a warm, damp cloth for 10 minutes enhances blood flow, reduces inflammation, and promotes eyelid oil production. It’s particularly effective for blepharitis.
Cold Compress
Using a cool, damp cloth or ice wrapped in a cloth can help reduce swelling, itchiness, and inflamed blood vessels. It offers quick relief for allergic or viral conjunctivitis.
Eye Drops
Consultation with an eye specialist is essential. Antihistamine drops relieve allergy-related redness, while vasoconstrictor drops reduce blood vessel dilation. Avoid using eye drops with preservatives or for non-recommended conditions to prevent adverse effects.
Additional Treatments
For infections, antibiotics prescribed by a doctor are necessary. Long-term care involves changing contact solutions, maintaining a healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, avoiding environments with pollen or smoke, and seeking medical advice to prevent recurrent redness.