Comprehensive Guide to Eye Infections and How to Protect Your Vision
Learn everything about eye infections, including their symptoms, causes, and prevention strategies. Recognizing early signs and understanding risk factors can help protect your vision and ensure timely treatment. This guide emphasizes the importance of proper eye hygiene and prompt medical care to avoid severe complications and preserve eye health.
Sponsored
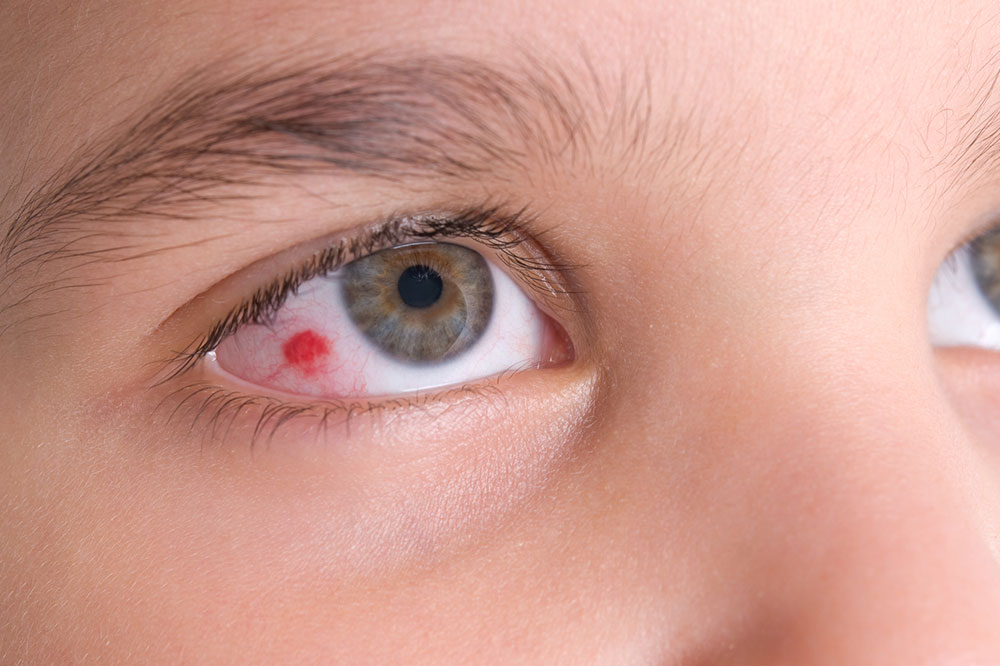
Understanding Eye Infections: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention
Eye infections can pose serious threats to your eye health if not addressed promptly. These infections occur when harmful microorganisms invade any part of the eye, often caused by bacteria or viruses, but sometimes influenced by other factors. Accurate diagnosis and treatment depend on identifying the specific type of infection. Being aware of the symptoms, causes, and potential risks is crucial for maintaining optimal eye health and preventing complications.
Common Signs of Eye Infections
While symptoms can differ depending on the infection, some typical signs include:
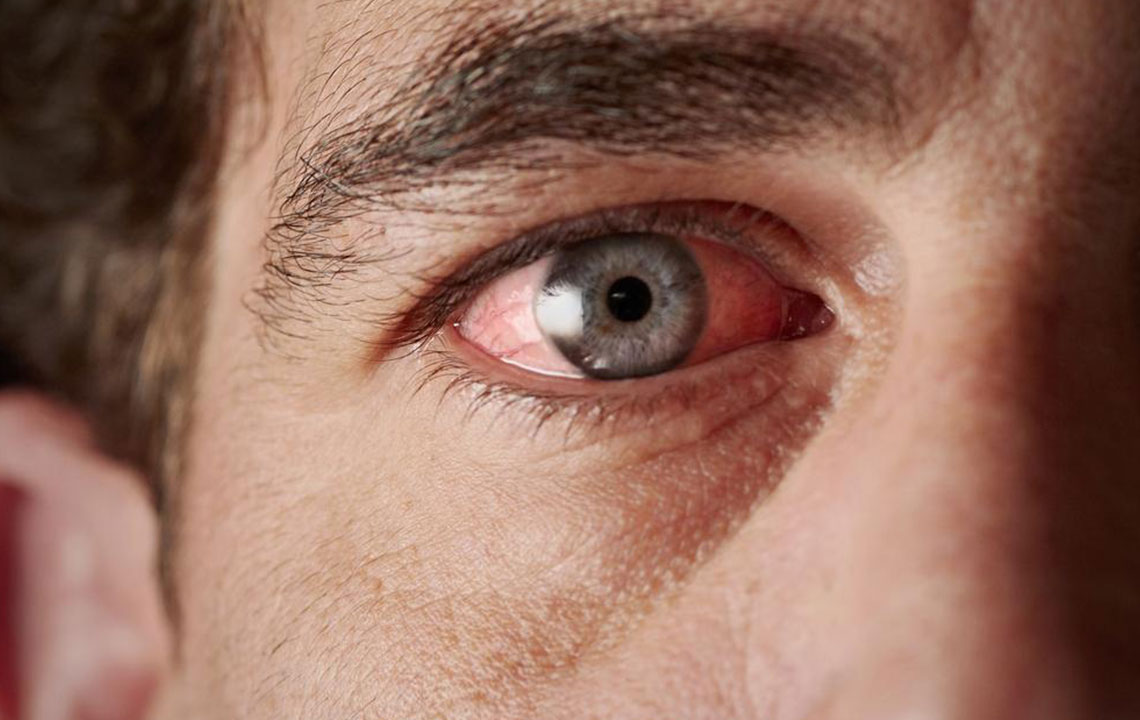
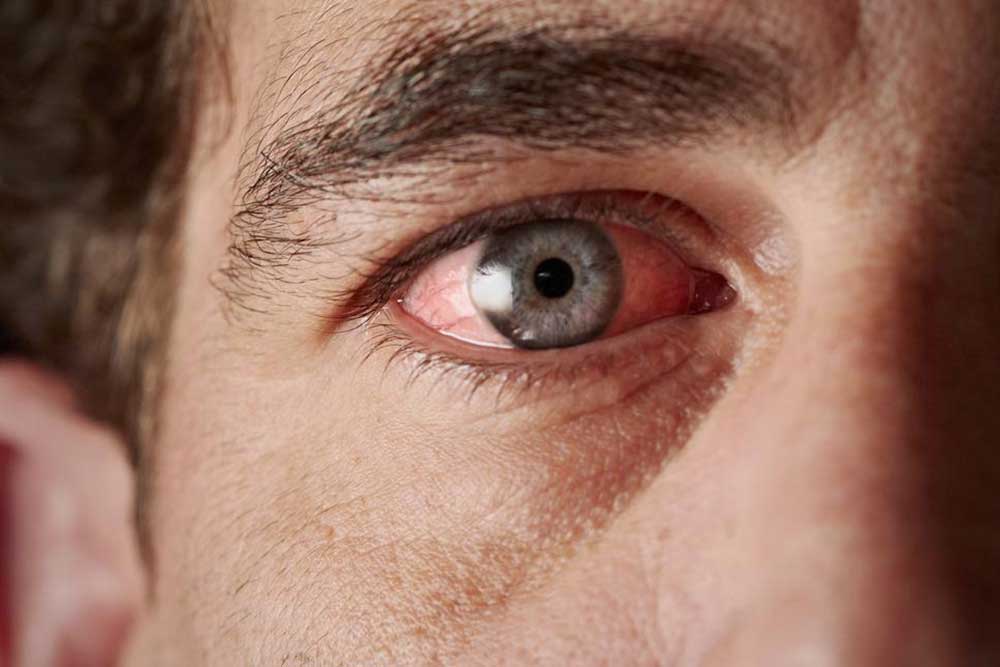
Redness
Pain or discomfort
Discharge from the eyes
Teary or watery eyes
Dryness
Sensitivity to light
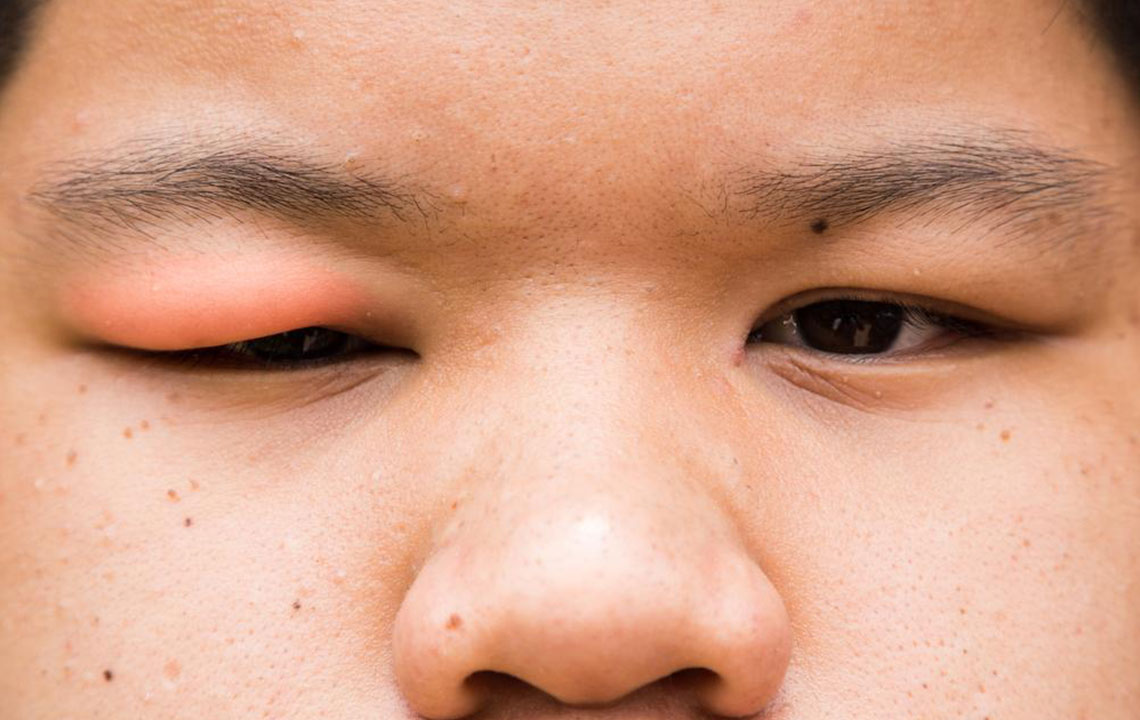
Swelling or inflammation
Itching
Blurred vision
Small, painful lumps under the eyelids
Eyelid tenderness
Crust formation on eyelashes after waking
Prompt medical attention is essential if you experience any of these symptoms. Avoid self-diagnosis or delaying treatment, as it can lead to severe eye damage or permanent vision loss.
Causes Behind Eye Infections
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): This highly contagious infection often affects children in crowded places like schools or daycare centers, caused mainly by viruses or bacteria.
Viral Keratitis: Viral infections such as ocular herpes caused by Herpes simplex virus can lead to viral keratitis.
Fungal Keratitis: Fungi like Fusarium, found in organic matter, can cause fungal keratitis, especially after eye injuries involving plant material.
Acanthamoeba Keratitis: Parasite-related infections, more common in contact lens users, can threaten vision if untreated.
Trachoma: This severe bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis is a leading cause of blindness worldwide.
Risk Factors for Eye Infections
Poor eye hygiene practices
Autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis
Contact lens usage
Previous eye injuries or trauma