Preventing Eye Infections from Contact Lens Misuse
This article highlights the risks of eye infections caused by improper contact lens usage and provides essential tips for safety. Proper cleaning, hygiene practices, and avoiding water contact can prevent serious eye conditions. Recognizing infection symptoms early and seeking medical attention is crucial for maintaining eye health. Following these guidelines helps contact lens wearers reduce infection risks and enjoy clear vision safely.
Sponsored
Individuals who wear contact lenses face a higher chance of developing eye infections. Poor hygiene practices, improper handling, and neglecting proper care can lead to mild discomfort or serious eye conditions that require urgent medical attention.
Types of Eye Infections Caused by Incorrect Contact Lens Use
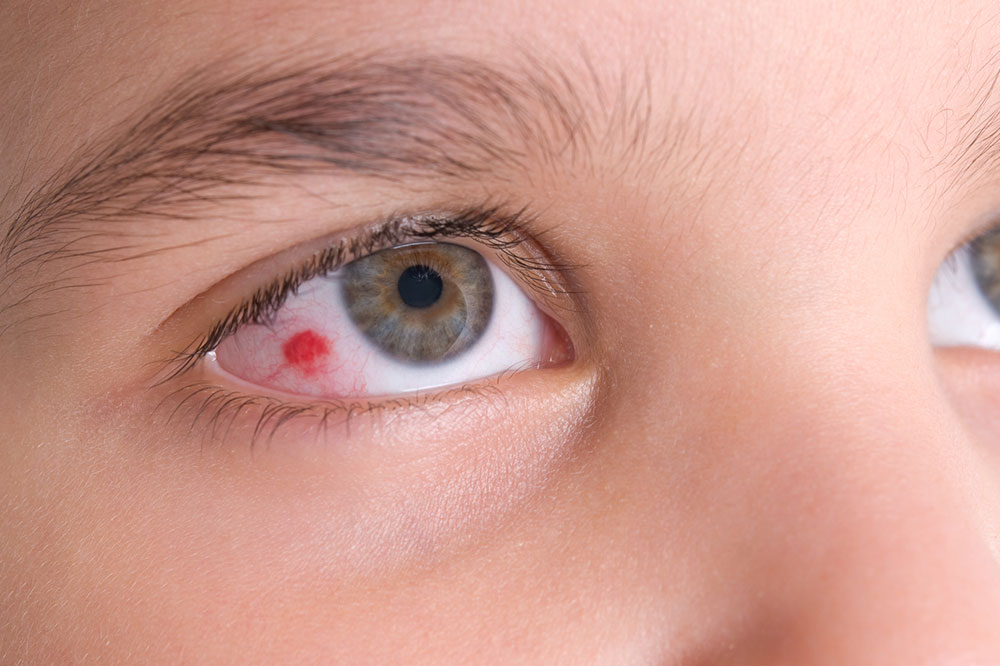
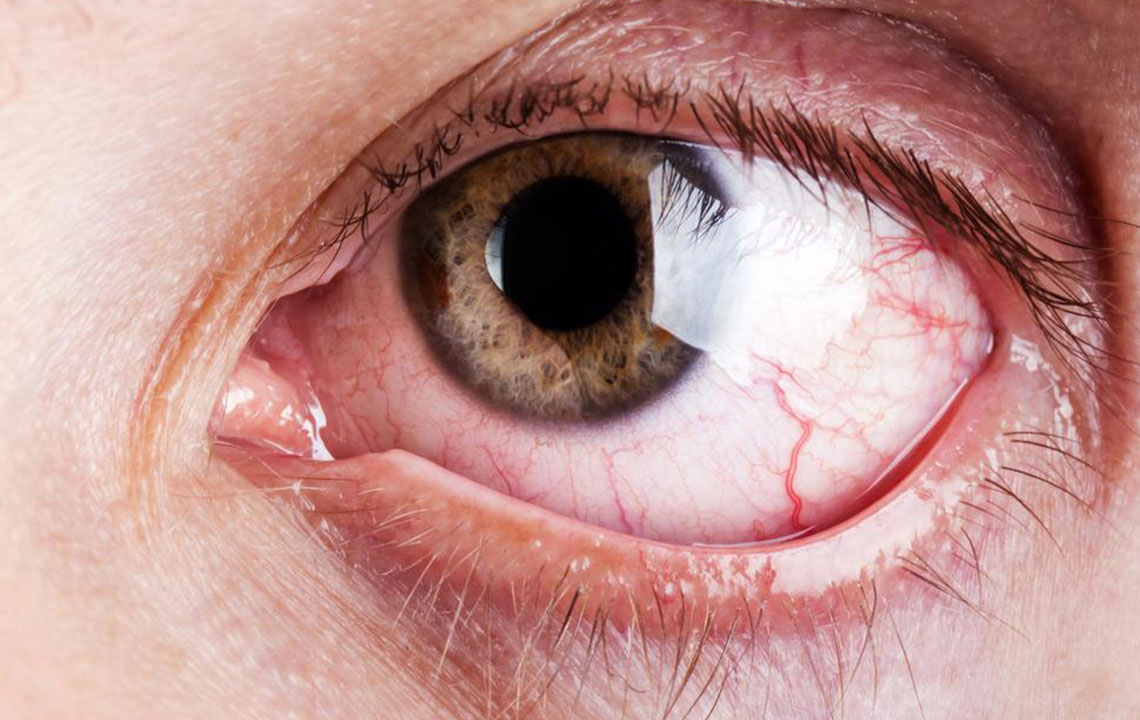
Several infections can result from not adhering to proper contact lens protocols. One prevalent issue is keratitis, affecting the cornea. It primarily stems from bacterial contamination but can also be caused by fungi or viruses.
Minor eye injuries, such as scratches from contact lens wear, can increase infection risk. Moreover, existing eye trauma can be worsened by contact lens use, leading to further complications.
Conjunctivitis is another common concern, often triggered by contamination. Recognizing infection symptoms early is crucial for proper treatment.
If you notice symptoms like redness, itching, pain, swelling, blurred vision, thick or sticky eye discharge, watery eyes, sensitivity to light, dry sensation, or general discomfort, seek medical advice promptly.
Preventive Measures for Contact Lens-Related Eye Infections
Wash your hands thoroughly with soap before handling lenses
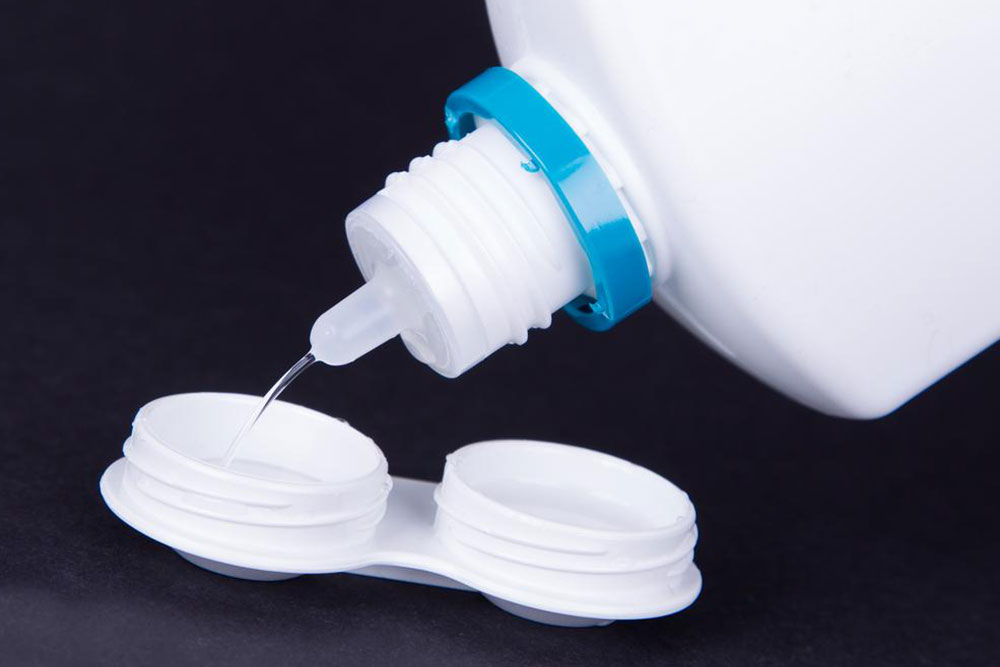
Disinfect lenses with a suitable solution each time you remove them
Always use fresh disinfectant, avoiding reusing solutions or topping up old ones
Clean lenses thoroughly before each use to remove debris
Regularly sanitize your lens case and replace it every few months
Remove lenses before sleeping to allow oxygen flow and prevent bacterial growth
Avoid water contact—do not wear lenses while swimming, showering, or bathing—to reduce contamination risk