Top Strategies for Managing Leg Cellulitis Effectively
Learn how to effectively manage and treat leg cellulitis, a bacterial skin infection that requires prompt medical attention. Key treatments include antibiotics, leg elevation, skin care, and maintaining hygiene to prevent recurrence. Early intervention can lead to quick recovery, typically within 10 days, but severe cases may take longer. Always consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plans to ensure complete healing and reduce complications.
Sponsored
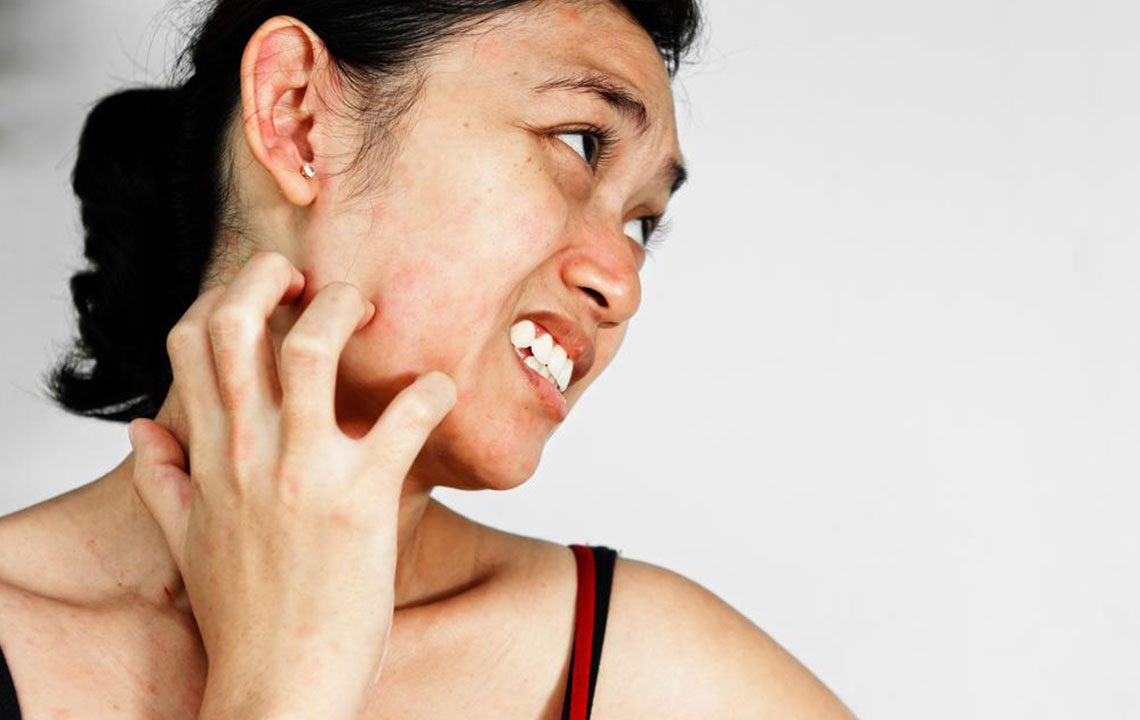
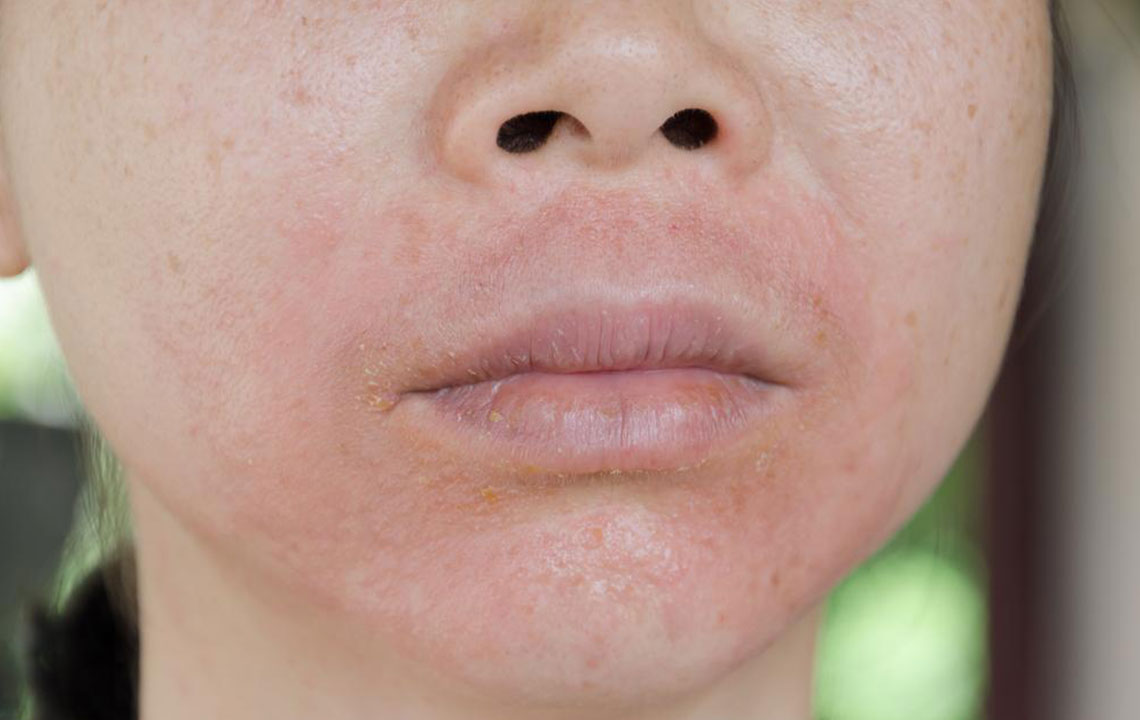
Cellulitis is a prevalent bacterial skin infection that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area. It is primarily caused by bacteria like staphylococcus or streptococcus entering through skin cracks. While it often appears on the lower legs, it can also occur on the arms, face, or other body regions. Without prompt treatment, cellulitis can spread into the bloodstream, posing serious health risks. Symptoms include rapid skin redness, inflamed large patches, tenderness, tight skin, and fever.
How to treat leg cellulitis effectively?
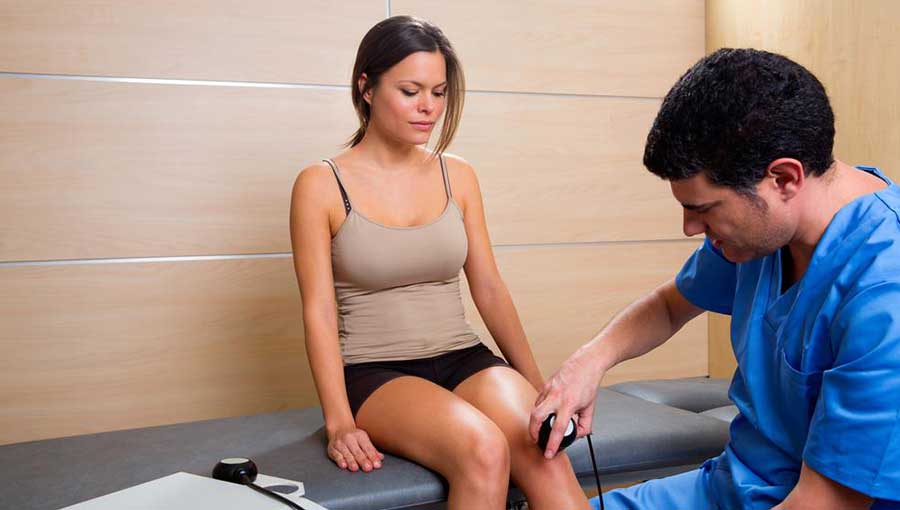
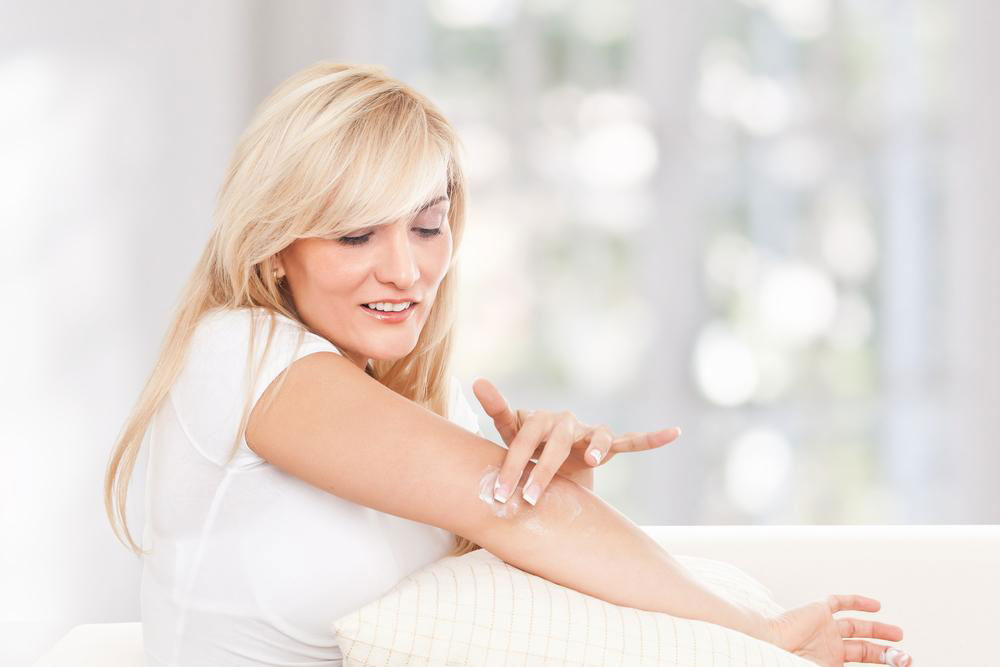
Managing this painful infection involves early medical intervention and proper care. Consulting a healthcare professional promptly is essential, and medications can help alleviate discomfort. Staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water aids recovery. Elevating your legs while resting reduces swelling, and staying active helps prevent stiffness. Avoid tight clothing until the infection clears up. Additionally, maintaining clean and moisturized skin reduces recurrence risk.
If cuts or wounds are present on your leg, clean them regularly with antiseptic creams and keep them covered, changing dressings periodically.
What are common treatments for leg cellulitis?
Typically, a 10 to 21-day course of prescribed oral antibiotics is recommended; the exact duration depends on infection severity. Symptoms may improve quickly, but completing the full course is crucial. Discontinuing medication early can lead to relapse. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek immediate medical attention. Fever or lack of response to medication warrants prompt consultation.
Proper treatment usually cures leg cellulitis within about ten days, though severe or chronic cases may take longer, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.