Effective Strategies for Managing and Treating Leg Cellulitis
Leg cellulitis is a bacterial infection marked by redness, swelling, and warmth. Early treatment with antibiotics and supportive measures like elevation and compression are vital to prevent complications. Recognizing symptoms early ensures prompt care and effective recovery.
Sponsored

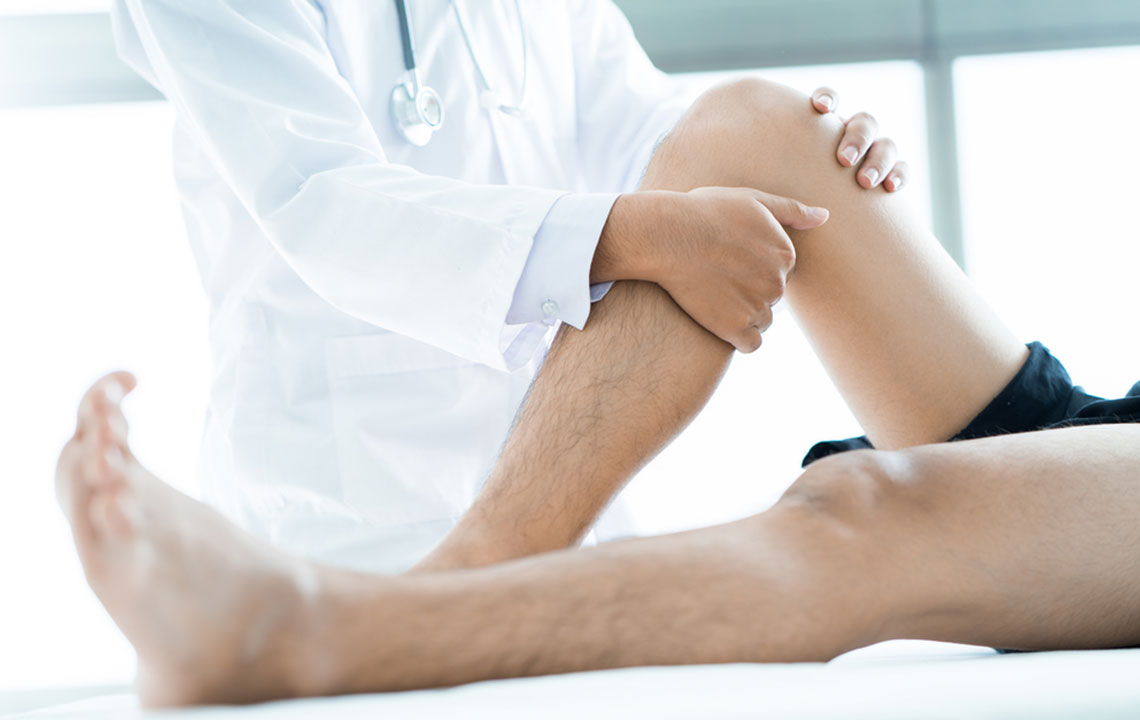
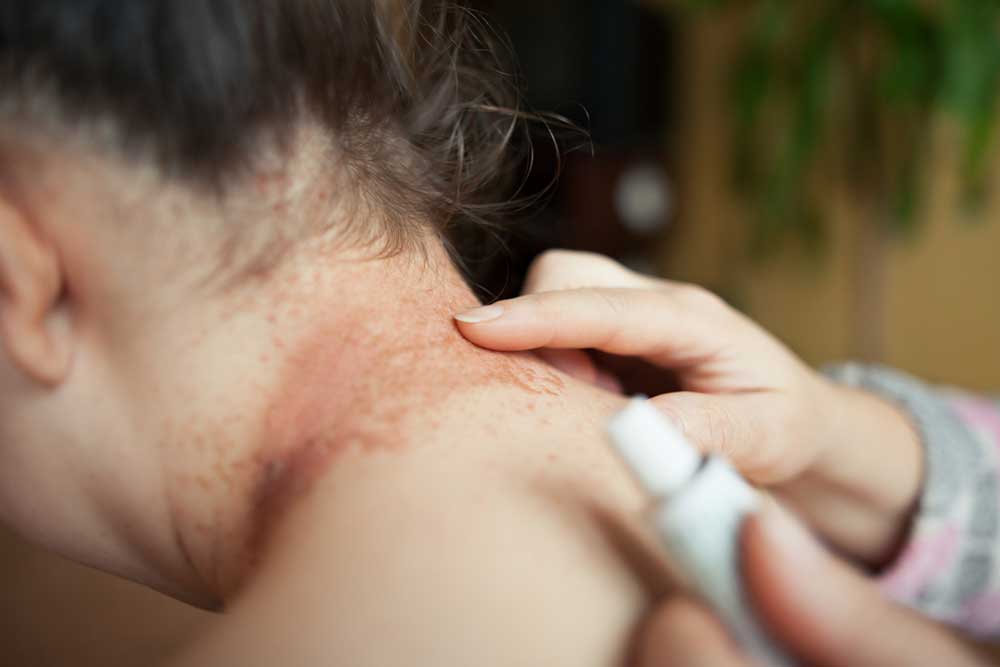
Leg cellulitis is a serious bacterial infection affecting the skin, causing redness, swelling, and tenderness. The affected area feels warm and may be painful. Although it's not contagious, the condition can be life-threatening if neglected. Typically impacting the lower legs, it can also occur on arms, face, or other regions. A minor skin break or tear provides a pathway for bacteria to invade. If untreated, the infection can spread quickly to lymph nodes and bloodstream, risking severe complications.
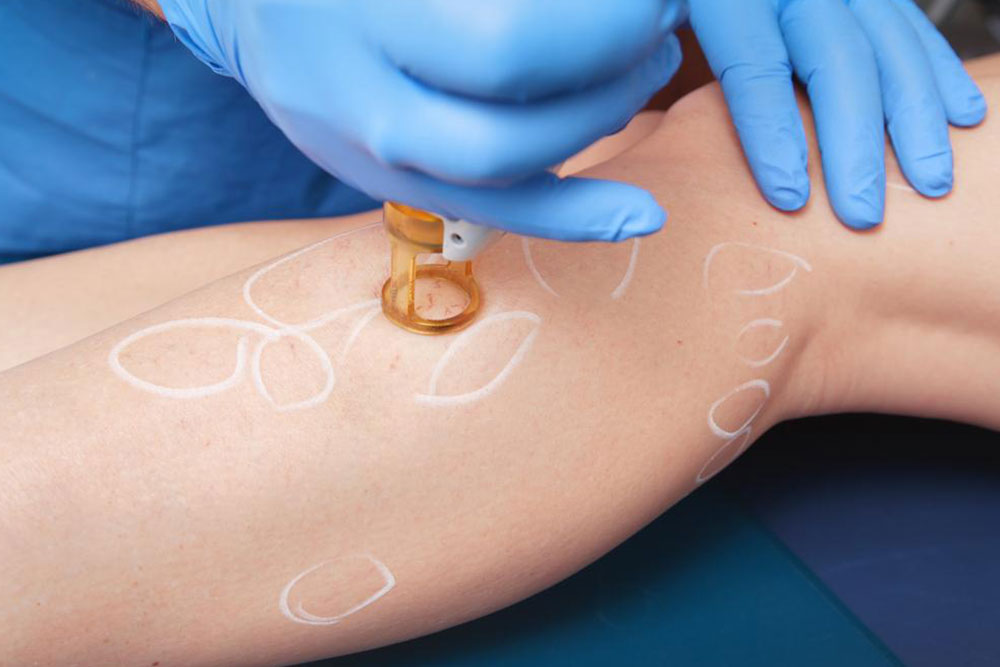
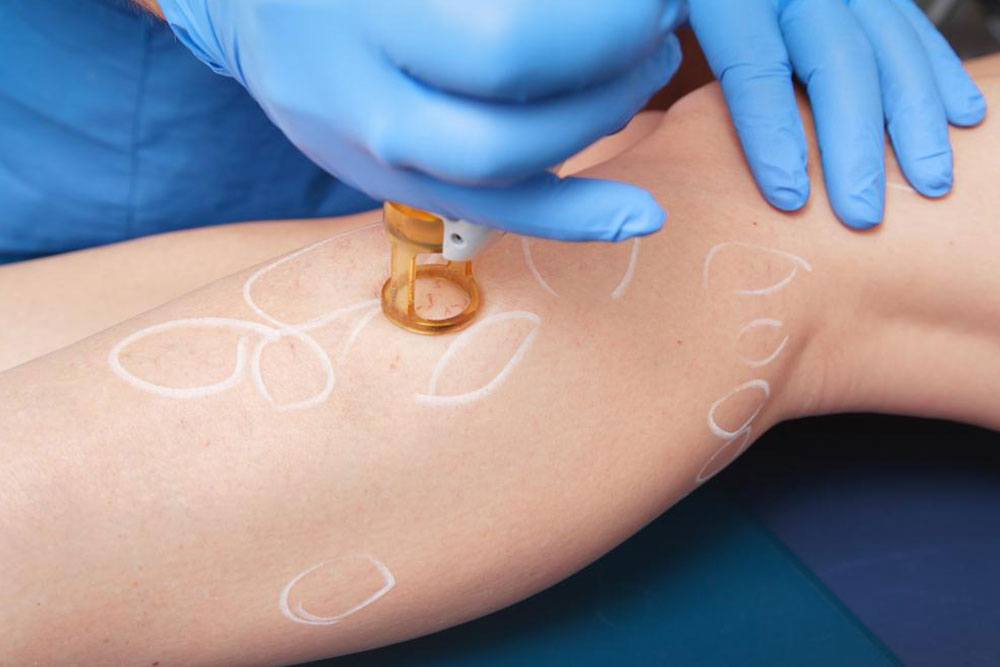
Prompt treatment is essential. The primary treatment involves oral antibiotics, with effectiveness monitored after three days. The course generally lasts five to ten days, but may extend up to two weeks if needed. Symptoms may improve within days, but severe cases with high fever, persistent symptoms, or lack of response to oral medication may require hospital intravenous antibiotics. Completing the full medication course is vital, even when symptoms improve. Elevating the affected limb and consulting your doctor are recommended to promote healing.
To reduce swelling and relieve pain, consider applying cold compresses, taking over-the-counter painkillers, elevating the limb, or using compression stockings. Symptoms like swelling, redness, warmth, fever, spots, blisters, and skin dimpling signal infection. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent rapid progression and complications. If you notice these signs, seek medical advice immediately for effective intervention and recovery.