Comprehensive Guide to Ear Infection Remedies and Management
This comprehensive guide covers symptoms, causes, and treatment options for different types of ear infections, including outer, middle, and inner ear issues. Understanding these conditions helps in timely management and recovery. Key treatments involve medications, ear cleaning, and surgical options when necessary. Consulting healthcare providers ensures proper care. Protect your ears by avoiding excess moisture, irritants, and promptly addressing symptoms for effective relief and healing.
Sponsored
Ear infections are widespread conditions often linked to colds or other illnesses. They can occur in the outer, middle, or inner ear, each presenting unique symptoms. Understanding these differences helps in timely treatment and recovery.
Outer ear infections / Swimmer’s ear
This infection affects the ear canal's outer layer, commonly caused by prolonged moisture exposure, such as swimming or bathing. Bacteria or fungi infect the skin lining when it’s damaged or irritated.
Causes of outer ear infections
Breaks in the skin, excessive moisture, scratching, or inserting objects like cotton swabs can introduce bacteria, fungi, or irritants, leading to swimmer’s ear. Chemical irritants and certain skin conditions may also contribute.
Symptoms often develop gradually and worsen over a couple of days, including pain when touching or chewing, redness, swelling, discharge (white, yellow, clear, bloody, or foul-smelling), crusting at the ear canal opening, hearing difficulties, ringing, and facial or neck discomfort. Swollen lymph nodes may also occur.
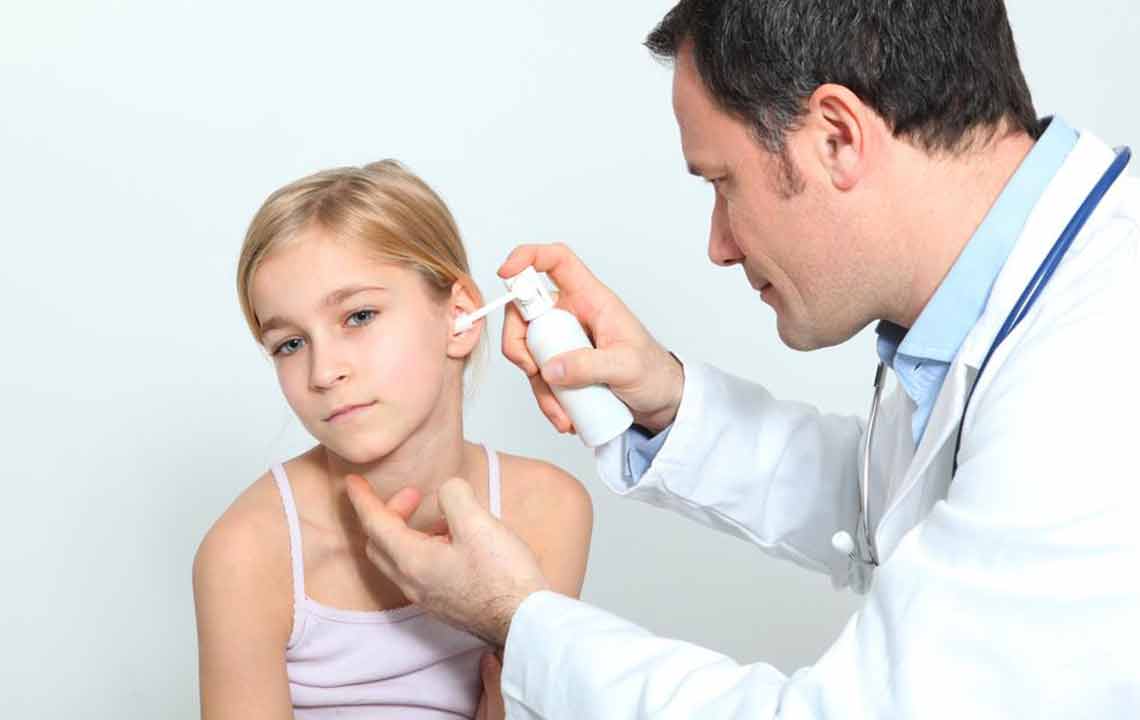
Outer ear infection management
Protect the ears by avoiding water exposure. Treatment involves pain relievers, antibiotics, ear cleaning, and soothing heat applications. Vinegar rinses can help restore pH balance and reduce swelling.
Middle ear infections
Often caused by bacteria or viruses, these infections stem from respiratory illnesses affecting the eustachian tubes, which become blocked or swollen. Fluid accumulates, leading to bacterial or viral growth.
Symptoms of middle ear infections
Presentations include ear pain, fever, thick or bloody ear discharge, nausea, appetite loss, irritability, and sleep disturbances, typically appearing within a week of respiratory symptoms.
Managing middle ear infections
Treatment focuses on alleviating pain with medications, antibiotics, and possibly surgical interventions like ear tubes or removal of adenoids and tonsils for recurrent cases.
Inner ear infections / Labyrinthitis
Involving inflammation of the inner ear, primarily the labyrinth, which helps control balance. Virus or bacteria infections, often linked to respiratory illnesses, trigger swelling.
Signs of inner ear infections
Symptoms develop quickly and are intense, including dizziness, nausea, hearing loss, vertigo, tinnitus (ringing or buzzing), and trouble focusing.
Inner ear infection treatment
Management includes medications such as antibiotics, corticosteroids, antihistamines, and sedatives to control symptoms.
Ruptured eardrum
Elevated pressure from fluid buildup may cause the eardrum to tear, resulting in fluid discharge (brown, yellow, or white). Pain often reduces upon rupture as pressure alleviates.
Symptoms of a ruptured eardrum
Sudden relief or sharp pain
Clear or bloody fluid drainage
Hearing loss
Buzzing or ringing sounds
Dizziness or facial weakness
Treatment of ruptured eardrum
Most heal naturally within weeks. Severe cases may require surgical repair, using tissue grafts to restore the eardrum. Antibiotics and pain relievers assist recovery, but medical supervision is essential.
Overall, timely diagnosis and treatment are vital for ear infections. Consultation with healthcare professionals ensures proper care and quicker recovery. Always seek medical advice for persistent or severe symptoms.