Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Bulging Discs
Explore effective strategies for treating bulging discs, including symptoms, causes, and non-invasive management options. Learn how exercise, chiropractic care, and lifestyle changes can help alleviate pain and promote healing, avoiding unnecessary surgery.
Sponsored

Understanding Bulging Disc Treatment Options
The spine bears the brunt of physical activities, both passive and active. One common injury caused by excessive strain is a bulging disc, which requires timely intervention. It's crucial to recognize the symptoms and explore effective treatment strategies.
What Is a Bulging Disc?
A prevalent condition characterized by swelling in the discs situated between vertebrae.
This swelling can exert pressure on nerves and neighboring tissues, causing discomfort.
Typically affecting the cervical (neck) or lumbar (lower back) regions, it can occasionally appear in the thoracic (mid-back) area.
Causes of a Bulging Disc
Your lifestyle and daily activities influence spinal health. The following factors may lead to a bulging disc:
Aging: The natural degenerative process of discs as we grow older can cause bulging. Proper treatment can alleviate associated pain.
Work-related strain: Physically demanding jobs may increase the risk of disc injuries.
Unhealthy habits: Smoking or tobacco use can weaken spinal discs, making them more susceptible to bulging.
Signs and Symptoms of a Bulging Disc
Pain radiating down the legs or arms is common.
Numbness, tingling, and sensation loss may occur.
Back bulging discs often cause pain radiating through the lower back.
Neck bulges can result in shoulder, arm, and hand pain.
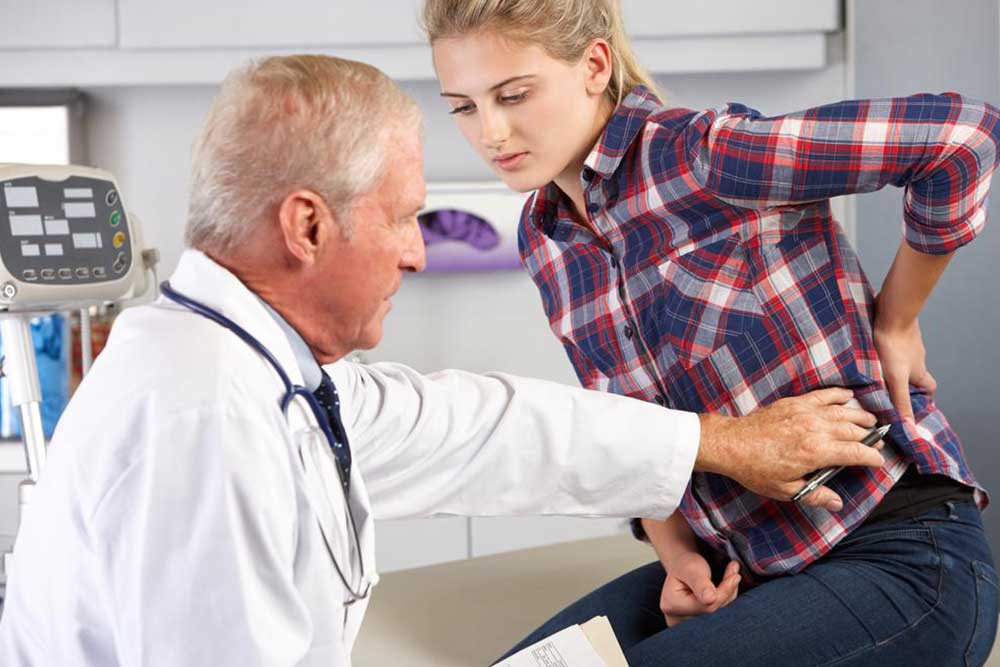
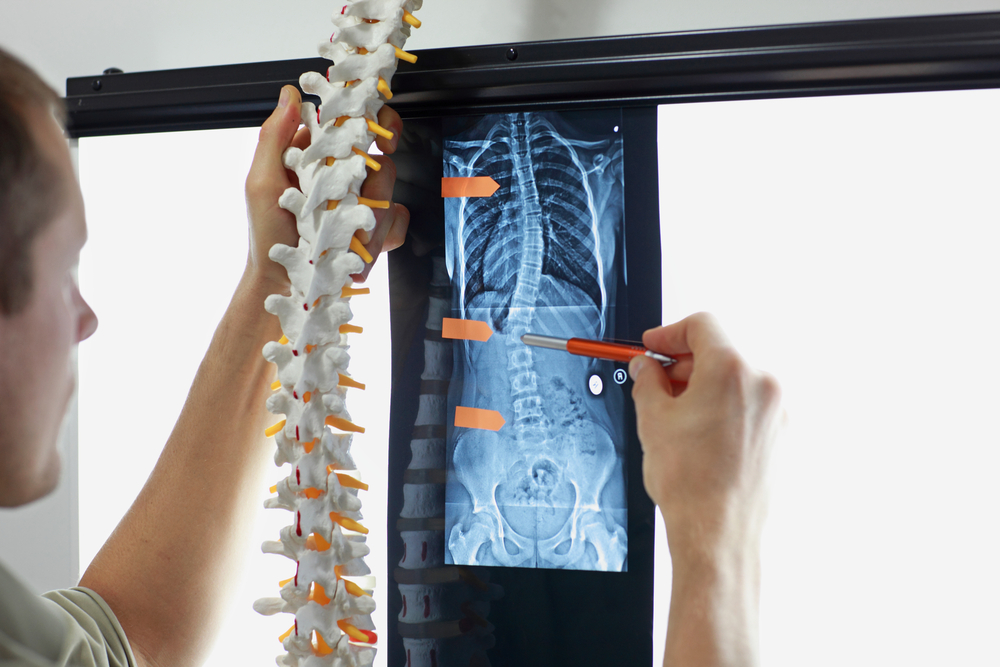
Diagnostic Procedures Before Treatment
Physicians evaluate symptoms through physical examination.
Imaging tests like MRI or CT scans are utilized for precise diagnosis.
Electromyography (EMG) may be conducted to assess nerve function.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Bulging Discs
Surgery is usually a last resort; most cases can be managed conservatively through various approaches.
Targeted stretches and exercises prescribed by physiotherapists can provide relief.
Applying heat or cold packs can reduce muscle soreness and inflammation respectively.
Maintaining an active lifestyle helps prevent worsening of symptoms.
Spinal adjustments by trained chiropractors may alleviate pressure and improve alignment.