Understanding Herniated Disc: Symptoms, Causes, and Relief Strategies
This article explores herniated disc symptoms, causes, preventive measures, and treatment options. It highlights the importance of early diagnosis, conservative approaches, and minimally invasive surgeries. Adopting healthy lifestyle choices can help prevent disc herniation and ensure spinal health, reducing pain and mobility issues caused by nerve compression. Essential for individuals experiencing back pain, this guide offers practical insight into maintaining a healthy spine and avoiding serious complications.
Sponsored
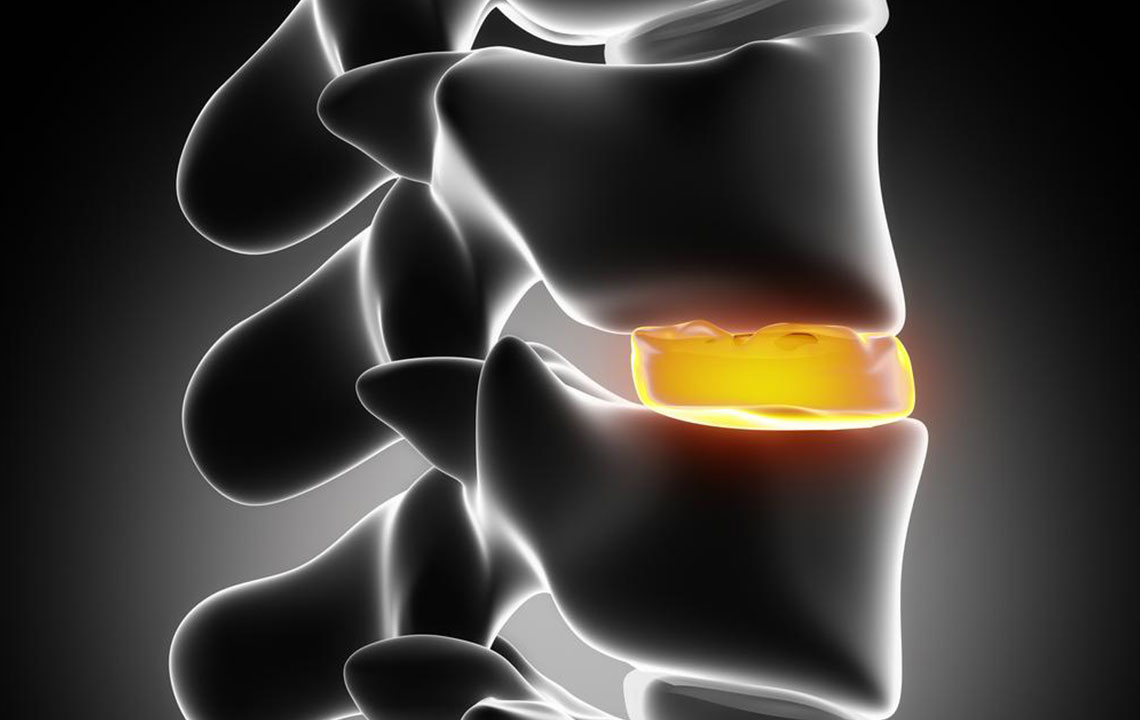
Herniated disc: Symptoms, causes, and treatment options
A herniated disc, often called a slipped or ruptured disc, frequently affects the lower back. It happens when the soft inner core of a spinal disc protrudes through the tough outer layer, putting pressure on nearby nerves. This gradual condition develops as the disc's structural integrity diminishes over time, often resulting from degeneration or injury. The displaced nucleus pushes against the weakened casing, causing pain and discomfort.
Early stages may show no noticeable symptoms, but as nerve irritation occurs, patients might experience sharp pain, numbness, or tingling. These symptoms surface when the herniation presses on nerve roots, leading to severe back pain and mobility issues.
Common causes of herniated disc
Age-related degeneration
As individuals age, spinal discs lose elasticity and water content, making them more prone to herniation and other issues.
Sudden impact or severe injuries can cause the disc to rupture or bulge, especially in high-impact accidents.
Chronic wear and tear from daily activities also contribute to disc herniation. Activities involving heavy lifting, poor posture, obesity, or repetitive jolts exert additional strain on the spine, increasing the risk. Occupations requiring prolonged sitting, standing, or lifting can accelerate this process. Participating in contact sports or having a family history of disc problems further raises susceptibility. Any activity stressing the back can trigger a herniated disc.
Recognizable symptoms of herniated disc
Symptoms are often subtle at first but can progress to significant pain and neurological issues. Key indicators include:
Pain, tingling, or numbness radiating to arms, hands, shoulders, or neck in cervical herniation
Upper back pain extending to the chest and torso in thoracic cases
Lower back pain, muscle spasms, and shooting pain down the leg (sciatica), especially if the nerve root is compressed in lumbar herniation
In severe cases, loss of bladder or bowel control if the nerve bundle is critically compressed
Non-invasive treatment options for herniated disc
Minimally invasive surgical options
Preventive measures for herniated disc