Understanding Herniated Discs: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
This article explores herniated discs, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and lifestyle changes to manage and prevent nerve compression issues effectively. From physical therapy to surgical options, learn how to address this common spine condition.
Sponsored

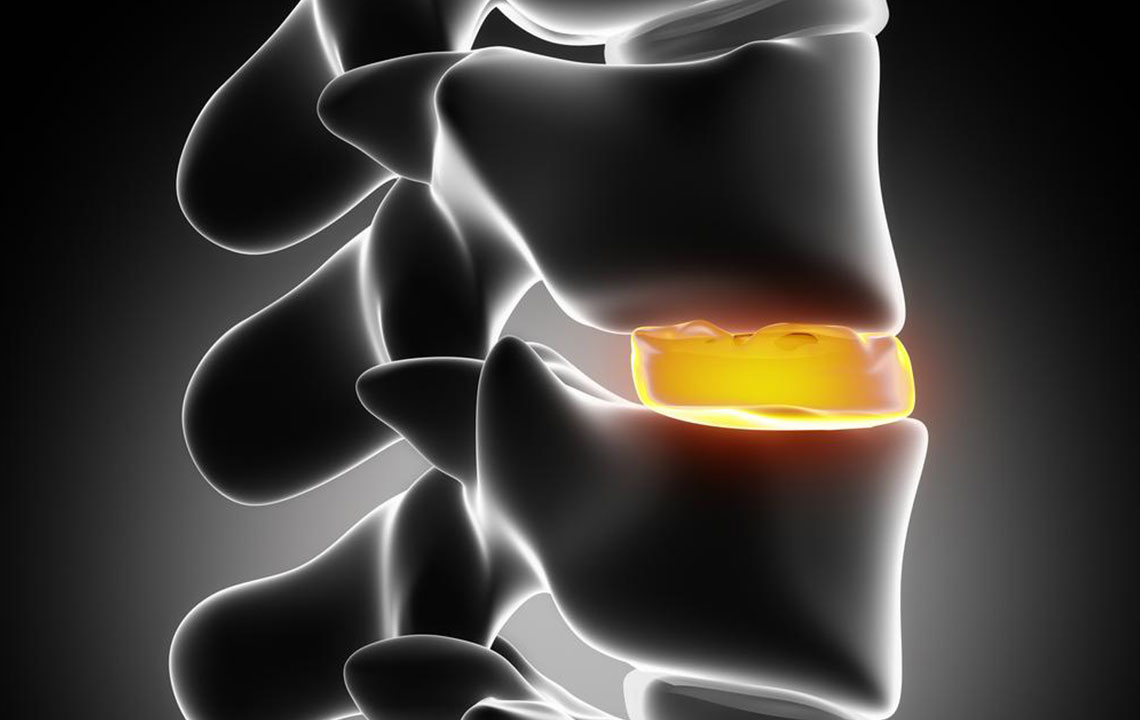
A herniated disc occurs when the cushioning pads between your vertebrae protrude beyond their normal boundaries. This happens due to weakening of the disc's outer layer, which can lead to nerve compression and pain. If untreated, a herniated disc may cause tears or more severe issues.
Causes of a Herniated Disc
Degenerative changes from aging are a primary cause, where discs lose water content and flexibility. Repeated stress, improper lifting, or sudden injuries can also contribute. Lifestyle factors like smoking, poor posture, and lack of exercise further increase risk.
Age-related degeneration causes discs to become brittle, making them prone to bulging or herniation. Excessive weight, poor ergonomic habits, and trauma from accidents or sports activities also play a role. Recognizing risk factors can aid in prevention and timely treatment.
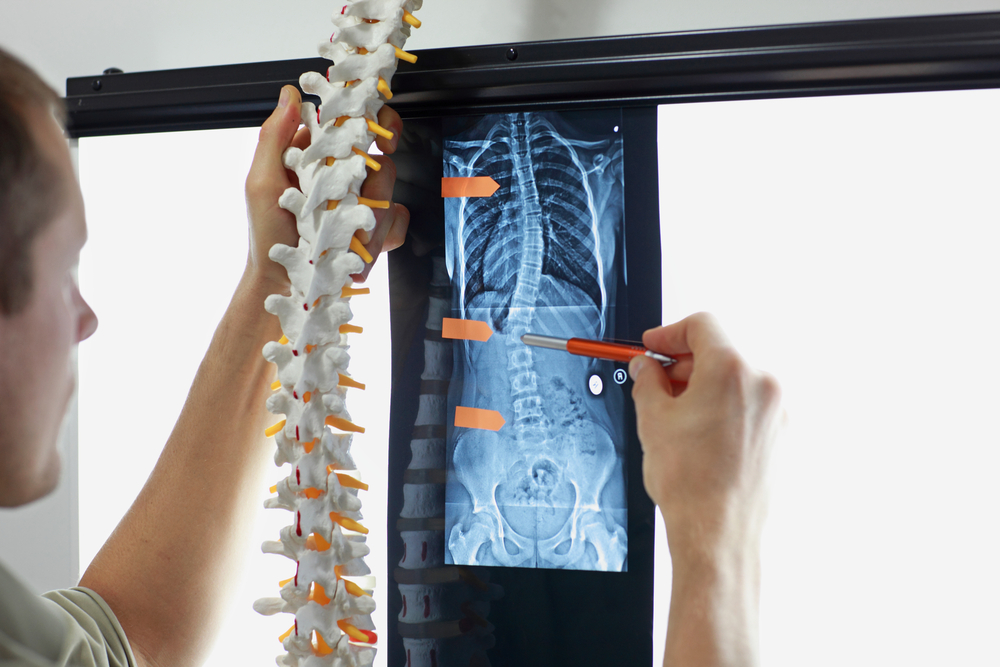
Symptoms depend on the herniation's location. In the cervical spine, discomfort and numbness may affect the neck, shoulders, arms, and hands. In the lumbar area, symptoms include pain, weakness, or numbness in the hips, legs, and feet. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans help diagnose the condition.
Treatments involve rest, medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Pain relievers like NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, and cold or hot compresses can alleviate symptoms. Physical therapy exercises strengthen back muscles, improve flexibility, and promote healing. In severe cases, epidural injections or surgery might be necessary if conservative measures fail.