Comprehensive Guide to Sun-Induced Skin Pigmentation
Explore comprehensive insights on skin pigmentation caused by sun exposure and aging. Learn about natural remedies and medical options like chemical peels, cryotherapy, laser treatments, and dermabrasion for effective removal of age spots. This guide emphasizes sun protection, skin care routines, and professional procedures to restore an even skin tone, enhancing your youthful appearance. Find out which treatments suit your skin type and how to maintain healthy, luminous skin with proper care and expert advice.
Sponsored

Understanding and Treating Skin Pigmentation from Sun Exposure
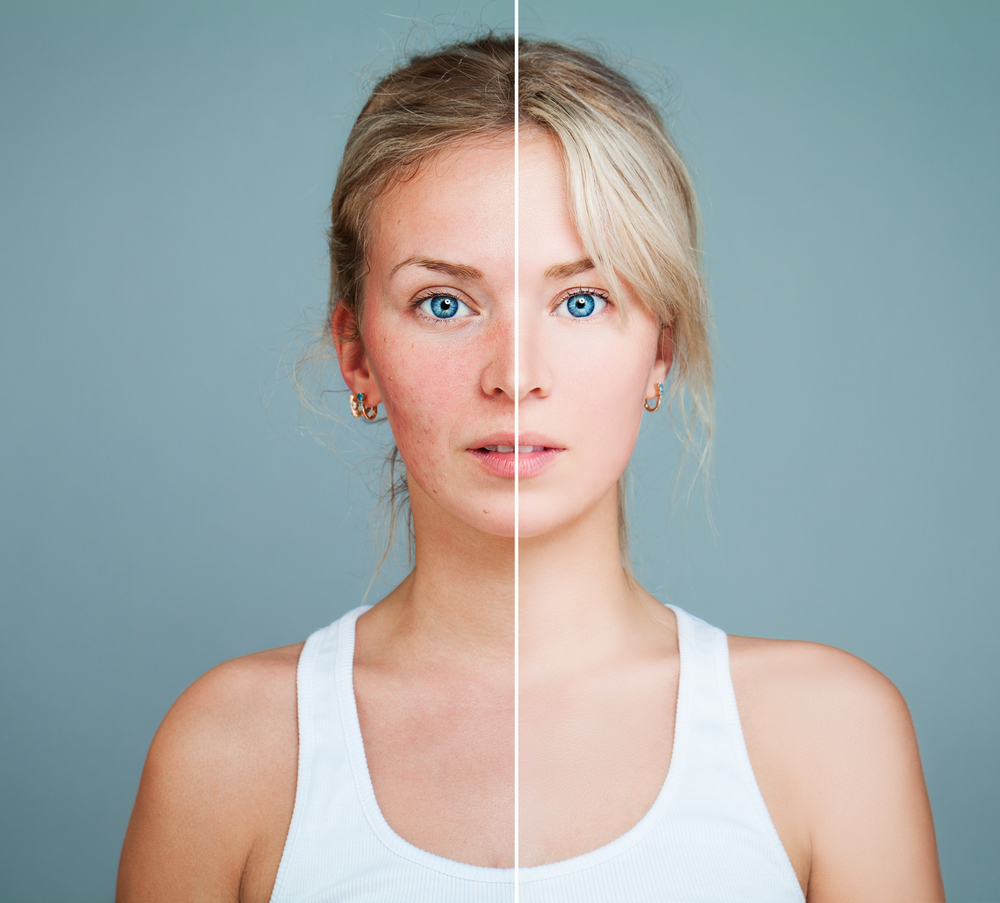
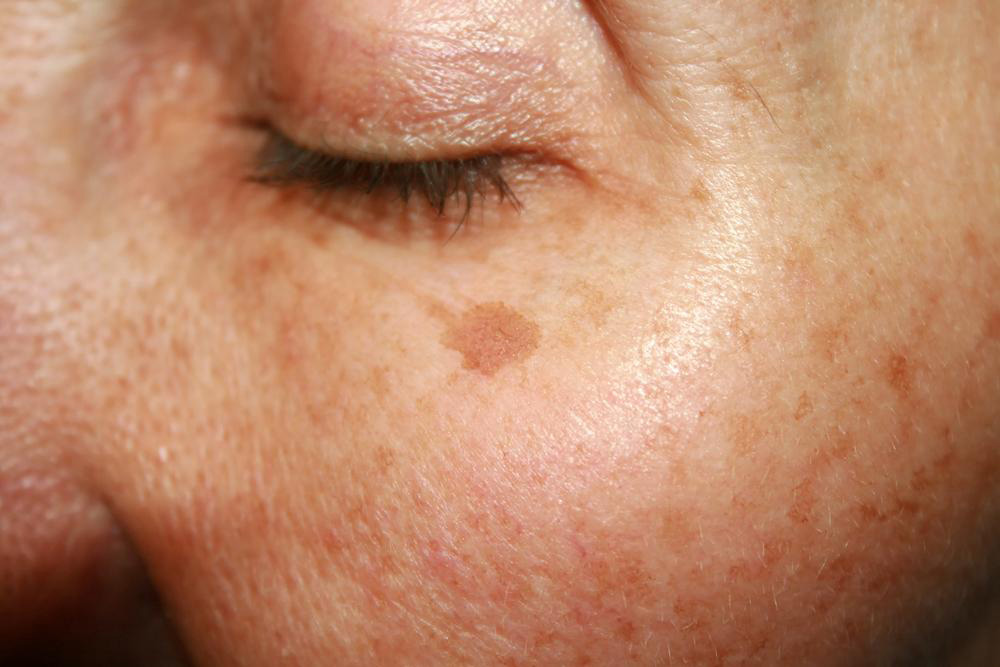
Skin pigmentation spots, commonly called age spots, liver spots, or sun spots, are patches that appear due to aging or prolonged sun exposure. These spots typically develop on areas like the hands, face, arms, neck, and shoulders, which are regularly exposed to sunlight. They range in color from light brown to dark brown, black, or red, giving a dull appearance. Recognizing the root causes is essential for effective treatment of these age-related skin changes.
Origins of Skin Pigmentation Spots
These pigmentation marks result primarily from sun exposure, which stimulates excess melanin production in skin cells. Aging naturally causes basal cells to produce lipofuscin, a pigmented residue that accumulates and forms spots. These cellular changes may be difficult to reverse. As UV rays hit the skin, melanin synthesis increases, leaving sun-exposed regions more prone to pigmentation. Addressing these spots involves targeted treatments to restore skin tone and brightness.
Through aging and sunlight, pigment-producing cells become hyperactive, leading to visible dark patches. In particular, sun-exposed areas accumulate more melanin, resulting in sunspots. Effective treatment options are diverse, ranging from home remedies to medical procedures, allowing individuals to choose the best approach for skin rejuvenation.
Natural Remedies for Pigmentation
• Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing and healing properties, aloe vera gel helps moisturize skin and reduce pigmentation. It contains anti-inflammatory compounds that promote healthy skin and diminish dark spots.
• Apple Cider Vinegar: Rich in alpha hydroxy acids, this vinegar acts as a natural exfoliant, helping to lighten dark patches when applied daily.
• Lemon Juice: Lemon's citric acid renews skin cells and brightens skin tone. Applying lemon juice mixed with rose water twice daily can lead to noticeable improvements.
• Tomatoes: Enzymes and lycopene in tomatoes serve as antioxidants and natural bleaching agents, reducing pigmentation and enhancing skin vibrancy.
• Castor Oil: Regular application of castor oil over pigmented areas can assist in lightening dark spots with consistent massage until absorbed.
Medical Treatments for Pigmentation
• Chemical Peels: This involves applying a chemical solution to peel away the outer skin layer, revealing fresh, even-toned skin beneath. Post-treatment sun protection is crucial.
• Cryotherapy: Liquid nitrogen is used to freeze pigment deposits in the skin, causing them to break down and fade over time.
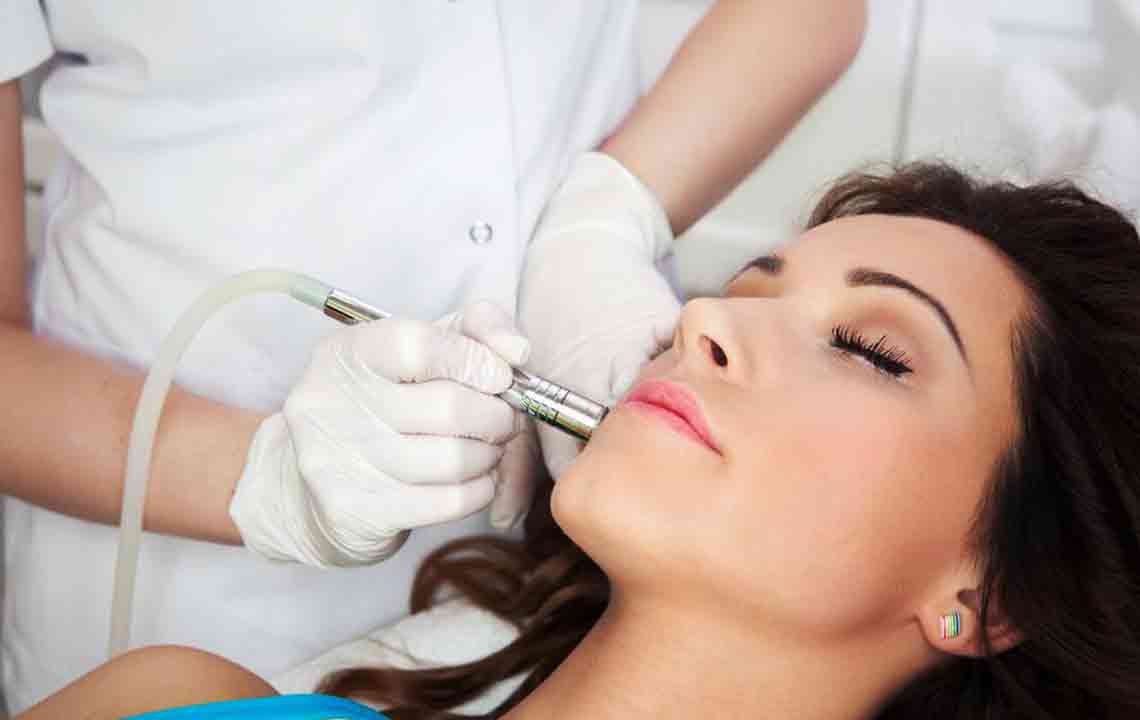
• Laser and Light Therapy: These treatments target melanin-producing cells, diminishing pigment spots with minimal damage to surrounding tissue. Multiple sessions are typically needed, with minor side effects like temporary discoloration.
• Dermabrasion: This exfoliation method uses a rotating brush to remove the pigmented outer layer, promoting new, clear skin. It may cause brief redness and requires multiple sessions.