Effective Strategies to Address Age Spots
Learn effective methods to treat age spots, including topical treatments and advanced procedures like laser therapy, cryotherapy, and chemical peels. Consulting with a dermatologist ensures safe and personalized care to improve skin appearance.
Sponsored
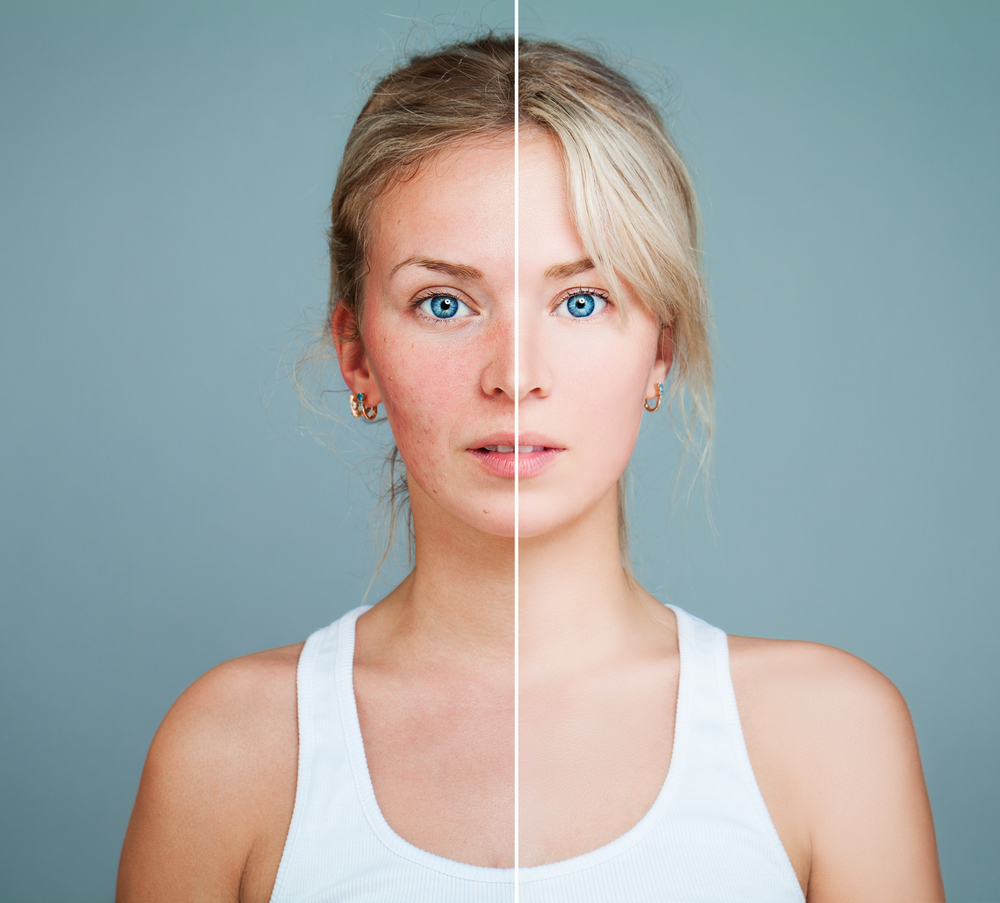
Age spots result from increased melanin production in the skin. While the exact cause remains uncertain, prolonged sun exposure and skin aging are primary factors contributing to their development. These spots commonly appear on sun-exposed areas like the hands, forearms, shoulders, and face. Anyone can develop age spots, but risk increases with age over 40, frequent tanning, and extensive sun exposure. They typically range from light brown to darker shades, are painless, and resemble surrounding skin texture.
How are age spots diagnosed?
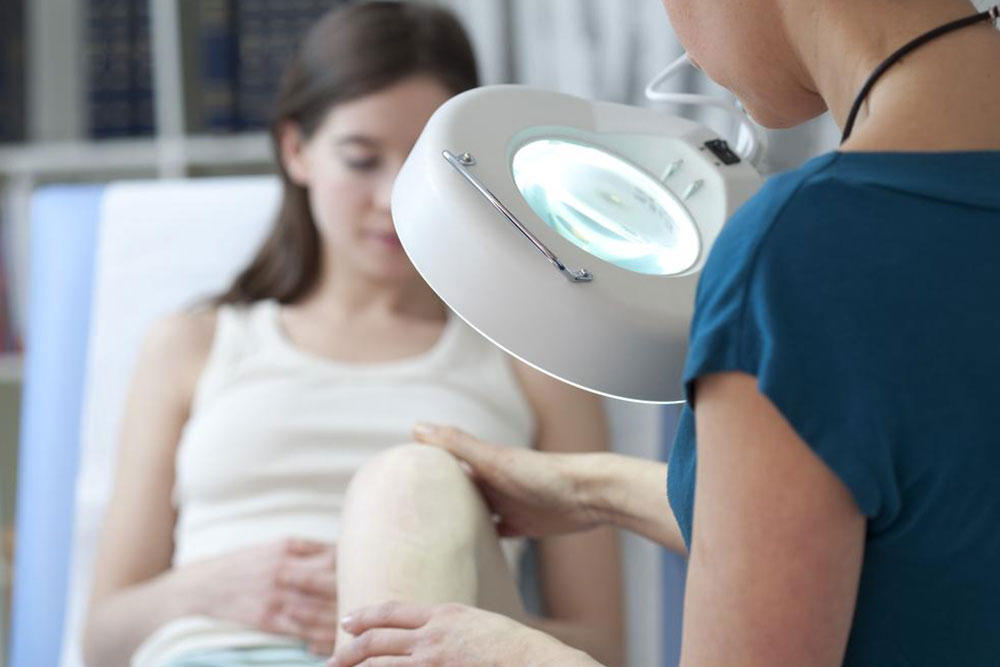
Dermatologists identify age spots by visual examination. If the spots appear suspicious, a biopsy might be performed to rule out skin cancer or abnormalities.
Treatment options for age spots
Although generally harmless and not causing health issues, many seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Common approaches include:
Topical medications
Doctors may recommend creams with hydroquinone or retinoids to gradually fade spots. Sunscreen use is essential during treatment to prevent further pigmentation. These creams may cause skin dryness, redness, or irritation.
Medical procedures
Several advanced treatments can remove or reduce age spots, but each carries potential side effects. Consult a dermatologist to choose the safest option. Available treatments include:
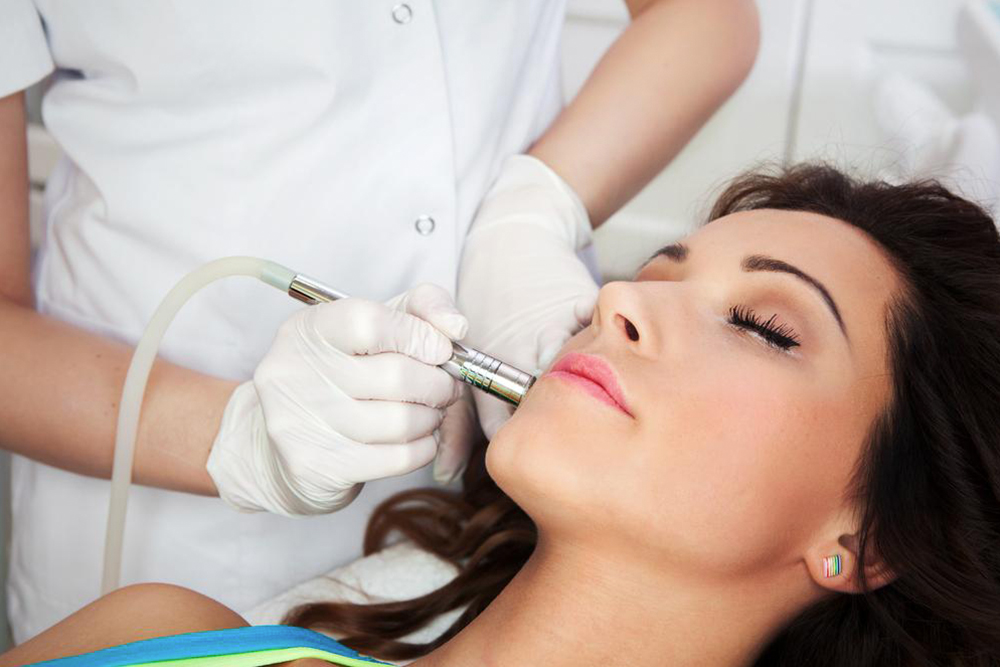
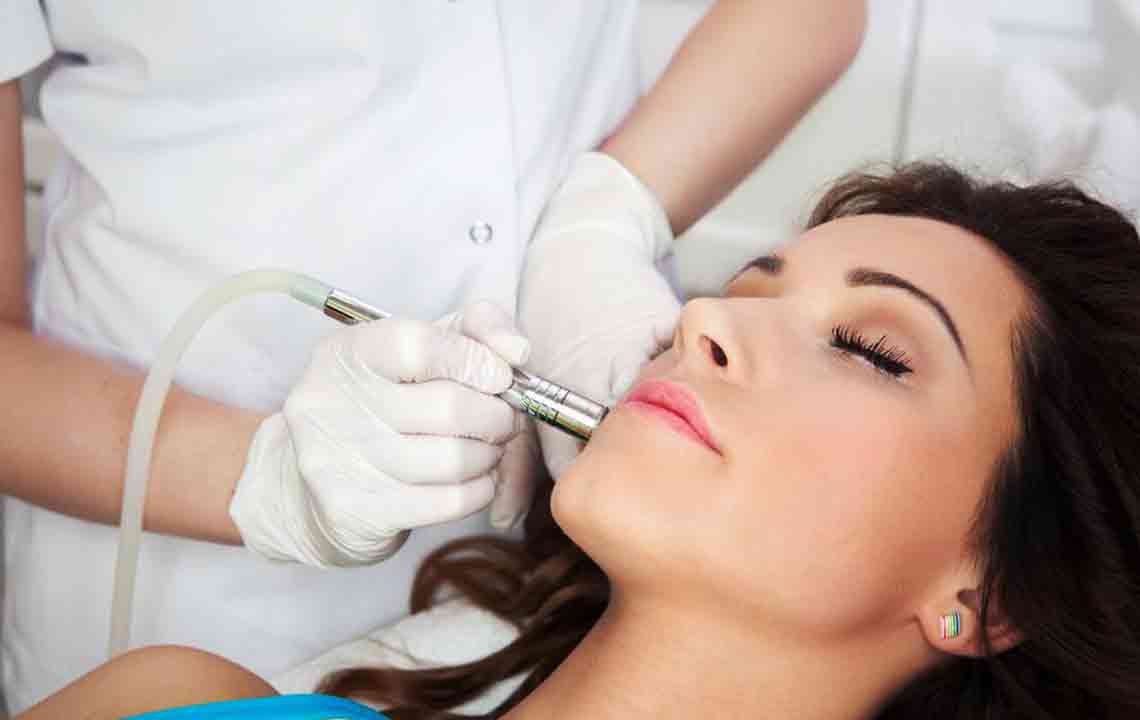
• Laser and IPL therapy: These techniques target melanin-producing cells without harming the skin surface, typically requiring two to three sessions. Post-treatment, spots fade over months. Sun protection afterward is vital to prevent recurrence.
• Cryotherapy: Liquid nitrogen application destroys pigment cells, causing the spots to lighten as the skin heals. This method is suitable for individual or multiple spots but may cause temporary irritation, discoloration, or scarring.
• Chemical peel: An acid solution removes damaged skin layers to promote new skin growth. Several sessions may be needed, and sun protection is crucial. Redness and the risk of permanent discoloration are considerations.
Microdermabrasion and dermabrasion are other options, but as cosmetic procedures, insurance usually does not cover costs. Prioritize consulting a qualified dermatologist to safely select the best treatment suited for your skin type and condition.