Comprehensive Guide to Hepatitis C: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
This comprehensive guide explores Hepatitis C, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and prevention methods. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and safe practices to prevent severe liver damage and associated health risks. While no vaccine exists, effective antiviral treatments and preventive measures can significantly reduce the disease's impact on individuals and communities.
Sponsored

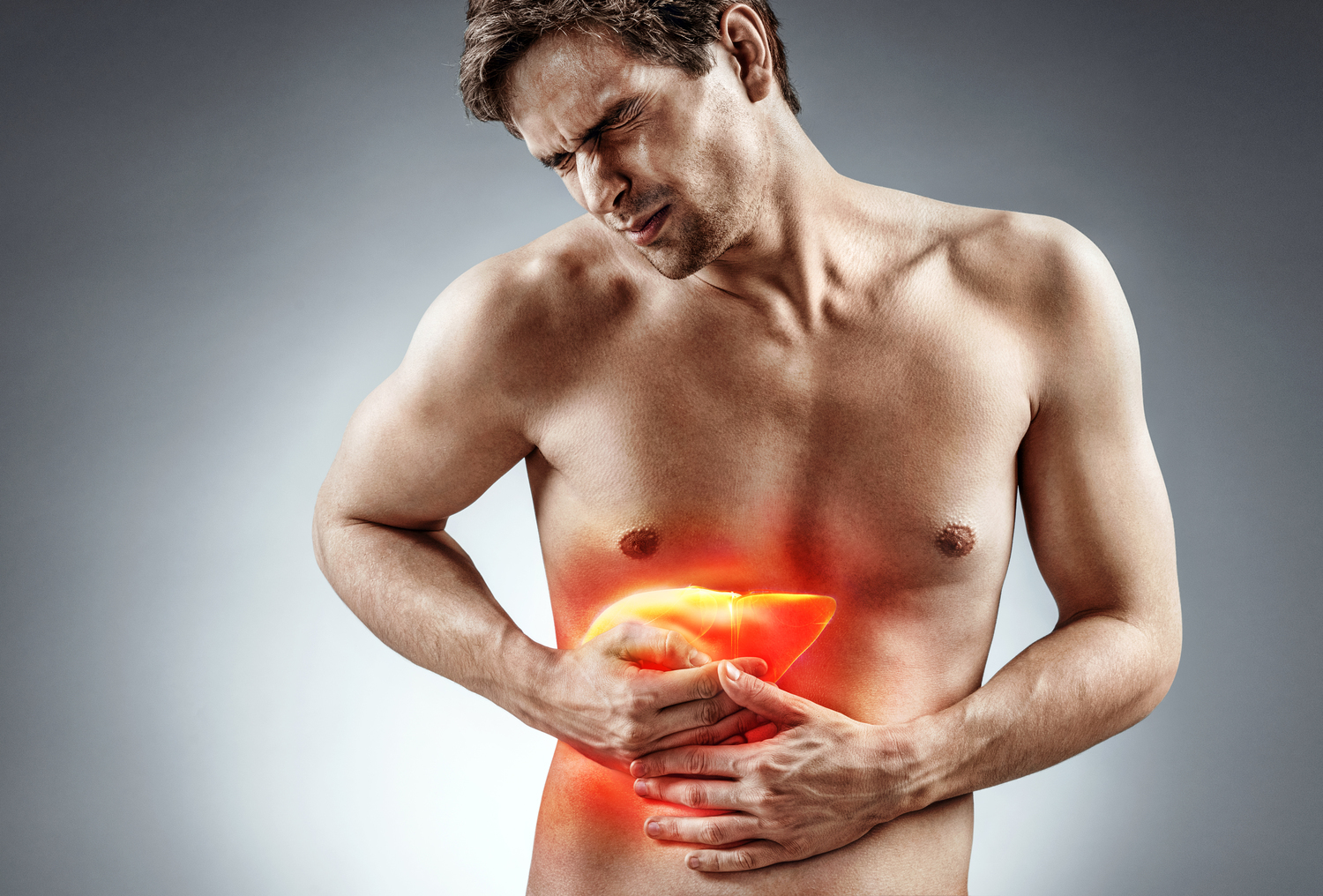
The liver plays a crucial role in detoxification and metabolism, making it highly vulnerable to toxins. Despite its regenerative ability, liver damage can go unnoticed initially. Among liver infections, Hepatitis C caused by the HCV virus can lead to severe conditions like cirrhosis and liver cancer. It can be acute or chronic, with some cases resolving on their own, while others progress. Globally, Hepatitis C accounts for thousands of deaths annually and is a leading reason for liver transplants.
Transmission of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads primarily through blood-to-blood contact. Common transmission routes include sharing needles during drug use, exposure to unsterilized medical equipment, and rarely, from mother to child during birth.Signs and Symptoms
The incubation period varies from 2 weeks to 6 months. Most individuals remain asymptomatic in early stages. Symptoms, if they appear, include fatigue, muscle aches, nausea, fever, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, joint pain, dark urine, pale stools, and jaundice. Often, without obvious symptoms, diagnosis occurs only after significant liver damage.Potential Complications
Untreated Hepatitis C can cause serious health problems such as artery blockages, heart disease, diabetes, blood platelet reduction, skin conditions, and even blood cancers like B-cell lymphoma.Diagnosis Process
Diagnosis involves blood tests detecting anti-HCV antibodies, followed by RNA testing to confirm active infection. Liver biopsies assess damage extent. Imaging tests like ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans help evaluate possible liver cancer. Viral genotyping is necessary for tailored treatment.Treatment Options
Early-stage infections often go unnoticed; when diagnosed, antiviral medications can cure over 95% of cases. For chronic cases, treatment varies based on liver health and viral genotype. Lifestyle changes and medical management are vital to prevent progression.Prevention Strategies
Currently, there is no vaccine for Hepatitis C. Prevention focuses on reducing exposure—safe injection practices, sterilizing medical tools, blood screening, and harm reduction strategies for drug users are essential. High-risk groups, including those with blood transfusions, tattoos, piercings, or drug use, should undergo regular screening to identify infections early and prevent complications like cirrhosis and cancer.