Comprehensive Guide to Managing Severe Asthma
This comprehensive guide details severe asthma diagnosis, treatment options, including medications, bronchial thermoplasty, and lifestyle modifications. It highlights the importance of proper management to improve quality of life and prevent complications.
Sponsored

Managing Severe Asthma: Essential Information
Understanding Severe Asthma
Severe asthma is a complex respiratory condition characterized by persistent airway inflammation leading to narrowed airways. Symptoms include chest tightness, breathlessness, wheezing, difficulty sleeping due to coughing or wheezing, and frequent colds or flu. When these signs occur regularly, most days of the week, it may indicate a more serious form of asthma. Proper diagnosis and treatment are vital to ensure a good quality of life without complications.
Diagnosing Severe Asthma
Because symptoms of severe asthma can mimic other respiratory illnesses, accurate diagnosis is essential. A pulmonologist will evaluate your condition through various assessments. Essential methods include:
Physical examination: To exclude other issues such as COPD or infections, the doctor will review symptoms and perform a physical check.
To assess lung function, tests like spirometry and peak flow measurements are used before and after administering bronchodilators. Improvement with medication confirms asthma. Additional tests may include:
Spirometry to measure airway narrowing
Peak flow monitoring to assess exhalation effort
Nitric oxide tests, methacholine challenge, imaging scans (X-ray, CT), sputum eosinophils, exercise or cold air challenge, and allergy testing
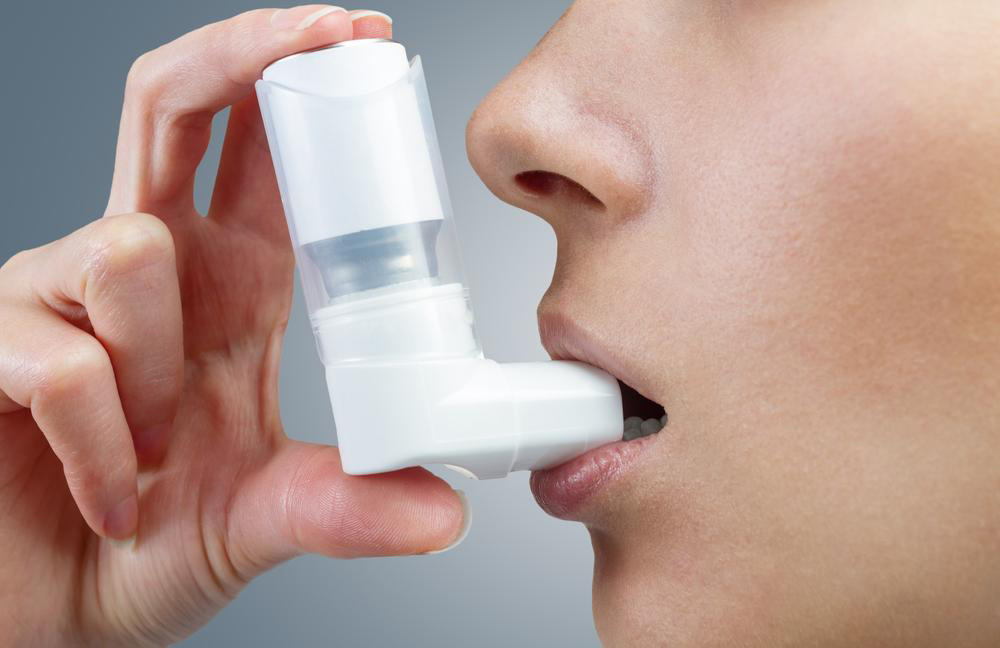
Medications for Severe Asthma Control
Managing severe asthma involves a combination of long-term control drugs and rescue medications. Daily medications help prevent attacks, while rescue drugs offer quick relief during flare-ups.
Long-term medicines:
Leukotriene receptor antagonists
Long-acting beta-agonists
Inhaled corticosteroids
Combination inhaler therapies
Rescue medications:
Short-acting beta-agonists
Oral or IV corticosteroids during crisis
Allergy sufferers may also benefit from immunotherapy or allergy shots to enhance their immune response.
Advanced Treatment: Bronchial Thermoplasty
If medication doesn’t adequately control symptoms, bronchial thermoplasty might be recommended. This procedure involves heating the airway walls to reduce smooth muscle, preventing airway tightening and decreasing attack frequency.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Severity Reduction
Avoid exposure to allergens and irritants
Maintain a healthy weight
Refrain from smoking and secondhand smoke
Ensure vaccination against flu and pneumonia
Monitor breathing changes for early signs of exacerbation
Tags – severe asthma management, asthma medications, respiratory health, asthma treatment options, chronic respiratory care