Managing Severe Asthma: Effective Treatment Options
Severe asthma management involves quick-relief inhalers, long-term medications, desensitization shots, and advanced procedures like bronchial thermoplasty. Improved inhaler technology and nebulizers enhance treatment effectiveness. Regular monitoring and physician consultation are key to controlling symptoms and reducing attacks.
Sponsored
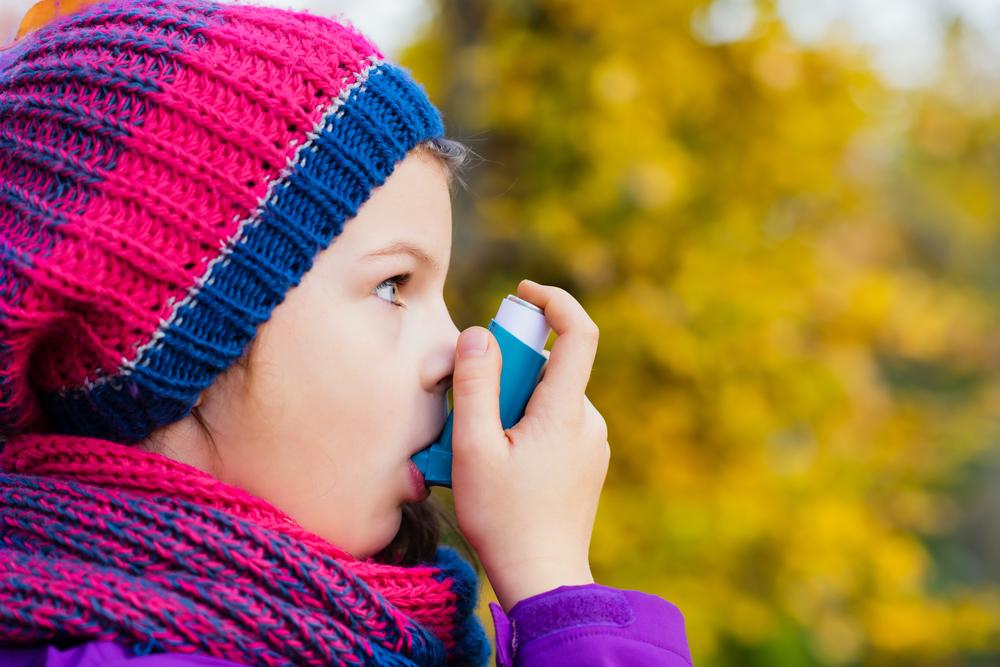
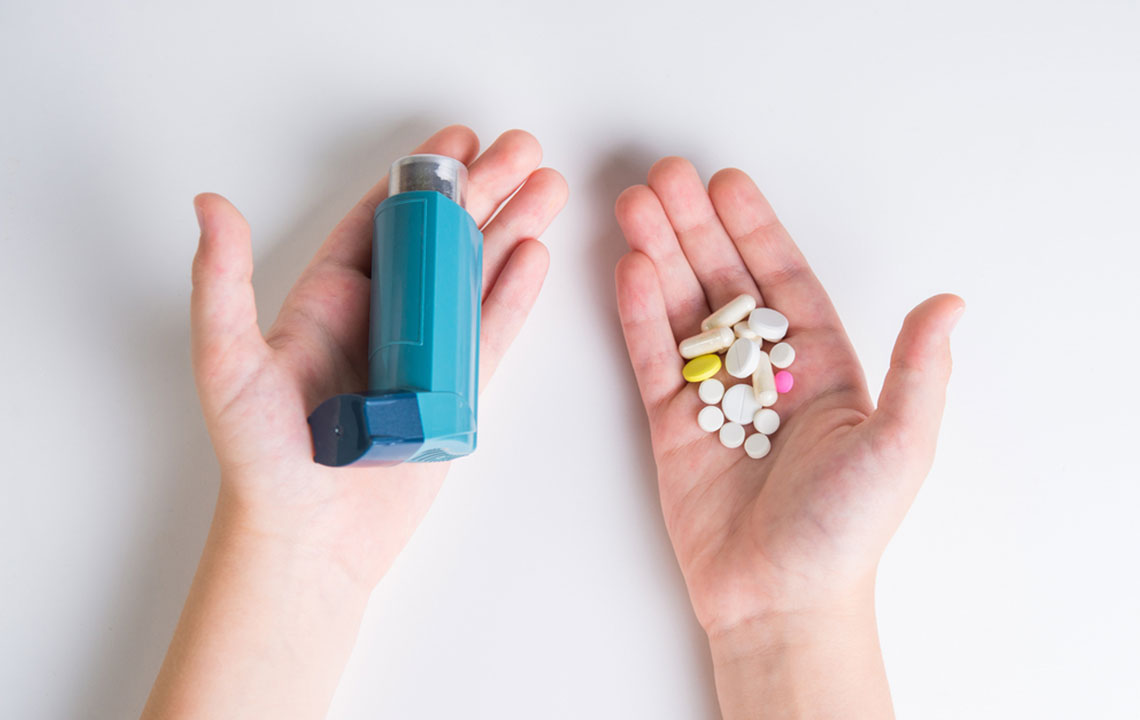
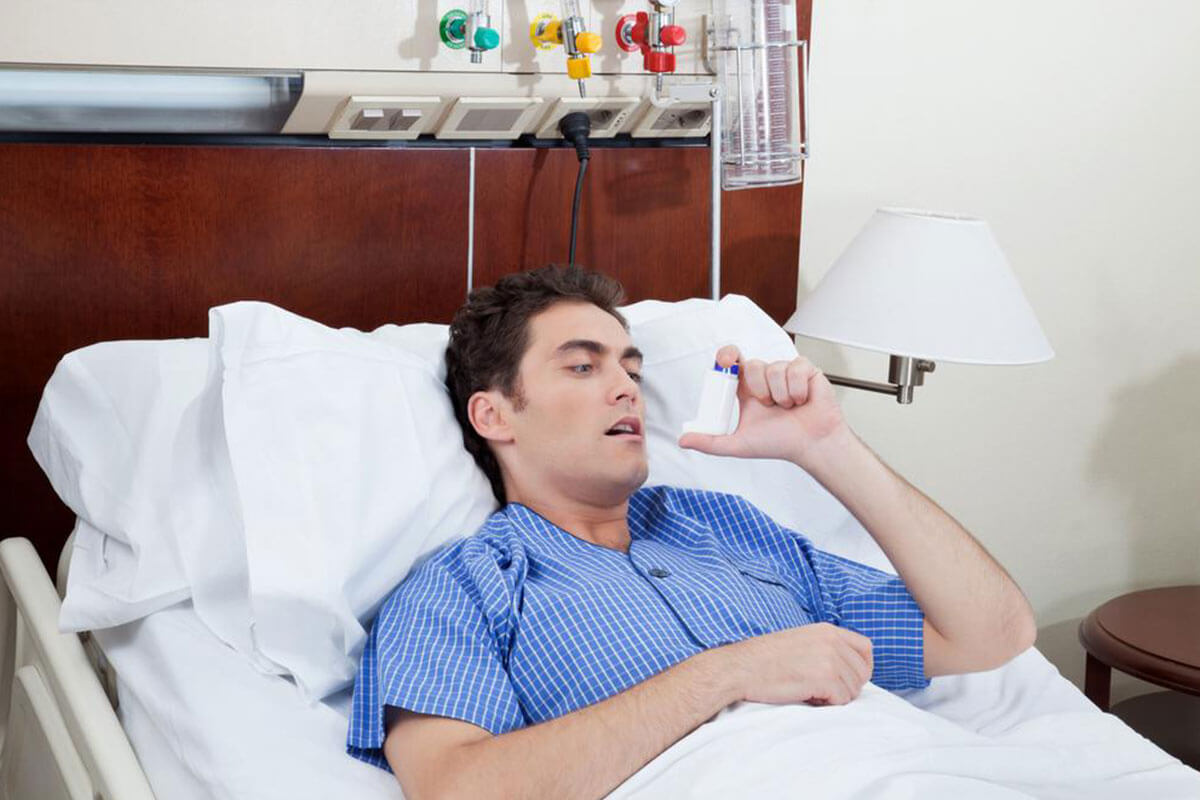
Severe asthma is a chronic lung condition characterized by recurrent episodes of airway narrowing. Rapid-acting medications, known as rescue inhalers, are essential for immediate relief during attacks. These include short-acting beta-agonists that quickly relax airway muscles. Additional treatments for severe symptoms involve fast-acting drugs that can be administered orally or intravenously, though long-term use may cause side effects.
Effective long-term control reduces the need for emergency remedies. Patients should monitor their inhaler usage and consult their physician regularly. Desensitization shots can help in allergic asthma, decreasing immune sensitivity over time. Bronchial thermoplasty, a less common procedure, uses heat to shrink airway smooth muscles across sessions, helping keep airways open. Advances in inhaler design, including spacer devices, ensure better medication delivery, while nebulizers are used for larger doses or weaker breathing patients.






