Comprehensive Guide to White Blood Cells and Their Role in Immunity
This article provides an in-depth overview of white blood cells, their importance in immune defense, causes of low WBC counts, symptoms, and natural ways to enhance immunity. Learn how dietary choices, like omega-3 rich foods and green tea, can support healthy WBC levels and overall well-being.
Sponsored

Understanding White Blood Cells (WBCs) and Their Significance
White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are essential components of blood responsible for defending the body against infections and diseases. These cells lack hemoglobin but possess nuclei, enabling them to move freely within the bloodstream. A healthy WBC count is vital for immune strength, and any decrease requires medical attention. Consulting a healthcare professional can help determine the best strategies to boost WBC levels.
Apart from medical treatments, dietary adjustments can support WBC production. Increasing intake of vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits, can aid in raising WBC levels. Below, you'll find key information about the importance of WBCs, causes of low counts, symptoms, and ways to naturally enhance immunity.
Factors Leading to Low WBC Count
WBCs are produced in the bone marrow, a spongy tissue inside large bones. Their count can decline due to various factors, including:
Viruses and severe infections
Genetic conditions
Cancers like leukemia
Autoimmune disorders
Medications such as antibiotics
Poor nutrition
Alcohol consumption
Specific Causes of Reduced WBC Levels
Aplastic anemia
Chemotherapy treatments
HIV/AIDS infections
Enlarged spleen (hypersplenism)
Congenital neutropenia (Kostmann’s syndrome)
Blood cancers
Lupus and other autoimmune diseases
Malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies
Myelodysplastic syndromes
Congenital disorders like myelokathexis
Radiation therapy
Infections such as tuberculosis
Symptoms of Low WBC Count
Depending on the underlying cause, symptoms may vary. Common signs include:High fever
Chills and sweating
Swelling and redness
Bruising in the mouth
Sore throat
Persistent cough
Difficulty breathing
Assessing WBC Levels
To check if your WBC count is within a healthy range, refer to a blood test report. The typical values are:Normal: 3,500 to 10,500 WBCs per microliter
Low: Less than 4,500 WBCs per microliter
High: Over 11,000 WBCs per microliter
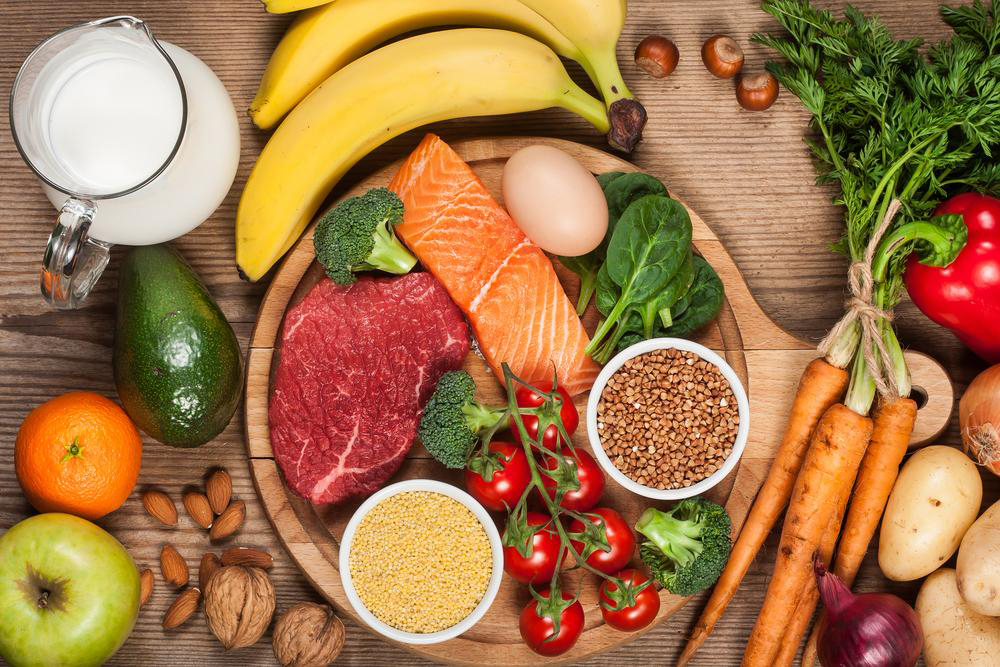
Foods Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s are beneficial for boosting WBC production and strengthening immunity. Key sources include:Salmon
Sardines
Mackerel
Dark leafy greens
Flax seeds
Chia seeds
Walnuts
Canola oil
Broccoli
Cauliflower
Green Tea's Role in Increasing WBC Counts
Green tea is renowned for its health benefits, thanks to its rich antioxidant content. It contains flavonoids and EGCG, which enhance immune function and promote WBC production. The amino acid L-theanine in green tea stimulates immune cells to produce germ-fighting chemicals, further strengthening defenses against infections.Monitoring WBC levels through regular blood tests and maintaining a balanced diet can help keep your immune system functioning optimally. Incorporate immunity-boosting foods and beverages, and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.