Understanding and Recognizing Ingrown Hairs
Learn about ingrown hairs, their causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options like laser removal. This comprehensive guide helps identify signs and prevent recurrence, ensuring smoother skin and reduced irritation for all skin types.
Sponsored
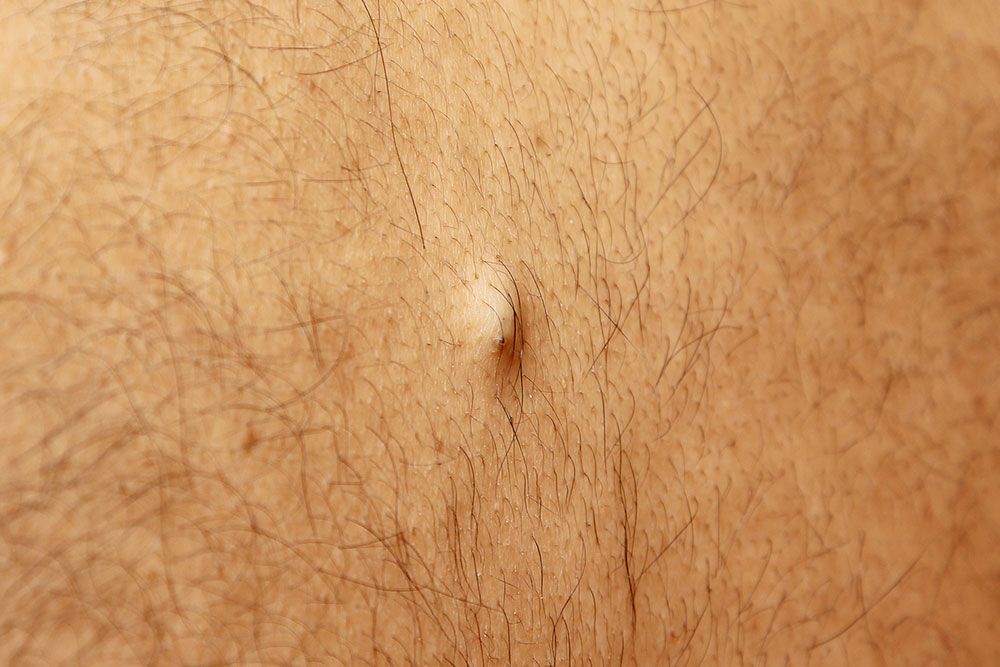
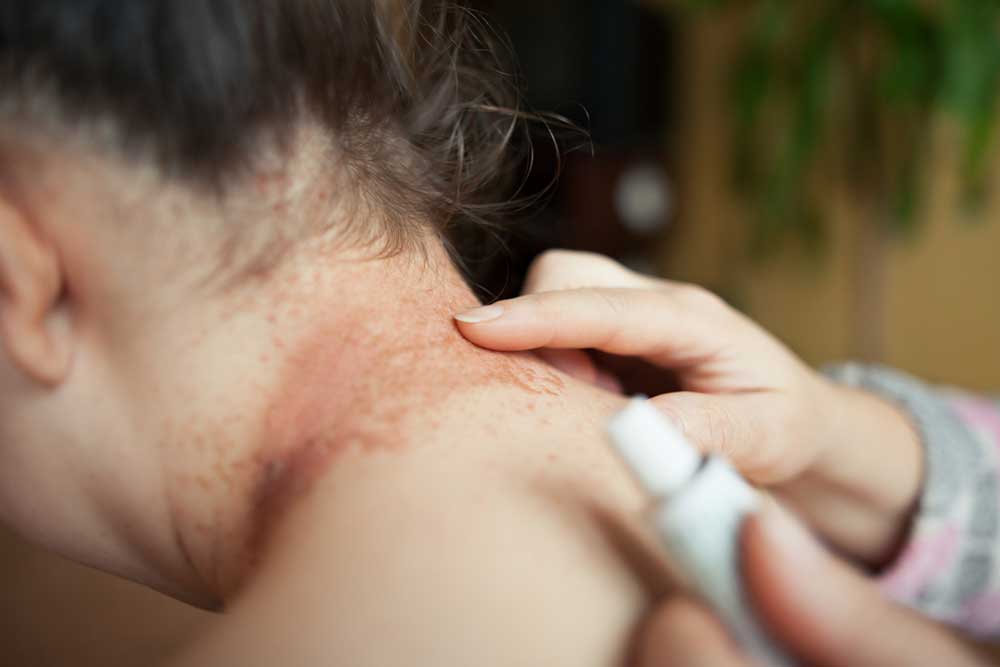
Ingrown hairs are a common skin issue affecting individuals of all genders and ages. Typically, hair grows outward from the skin’s surface, originating from the dermal layer, which contains blood vessels, sweat glands, and connective tissue. An ingrown hair occurs when a hair curls back or grows sideways beneath the skin instead of emerging outward, causing discomfort and skin irritation.
Interesting facts about ingrown hairs
People of any age can develop ingrown hairs.
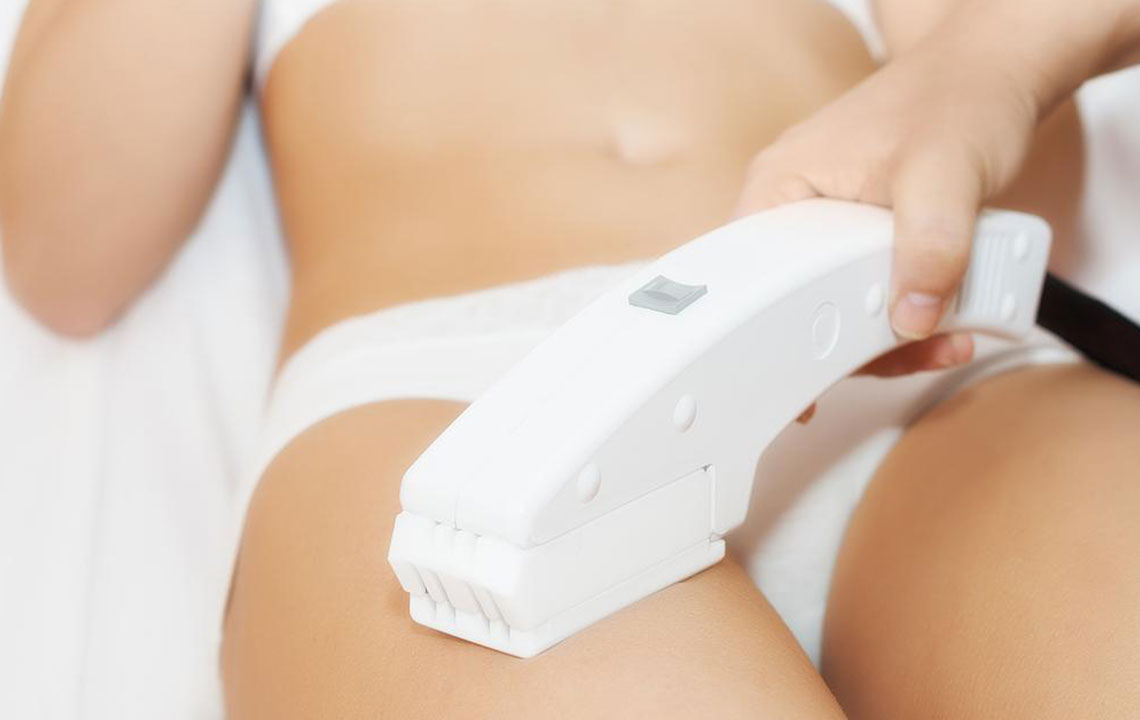
Ingrown hairs are harmless but common skin conditions that can affect anyone. Those with curly or thick hair are particularly susceptible, especially after shaving. To prevent worsening, it's advisable not to shave too closely. Laser hair removal offers an effective solution, removing existing ingrown hairs and preventing future occurrences.
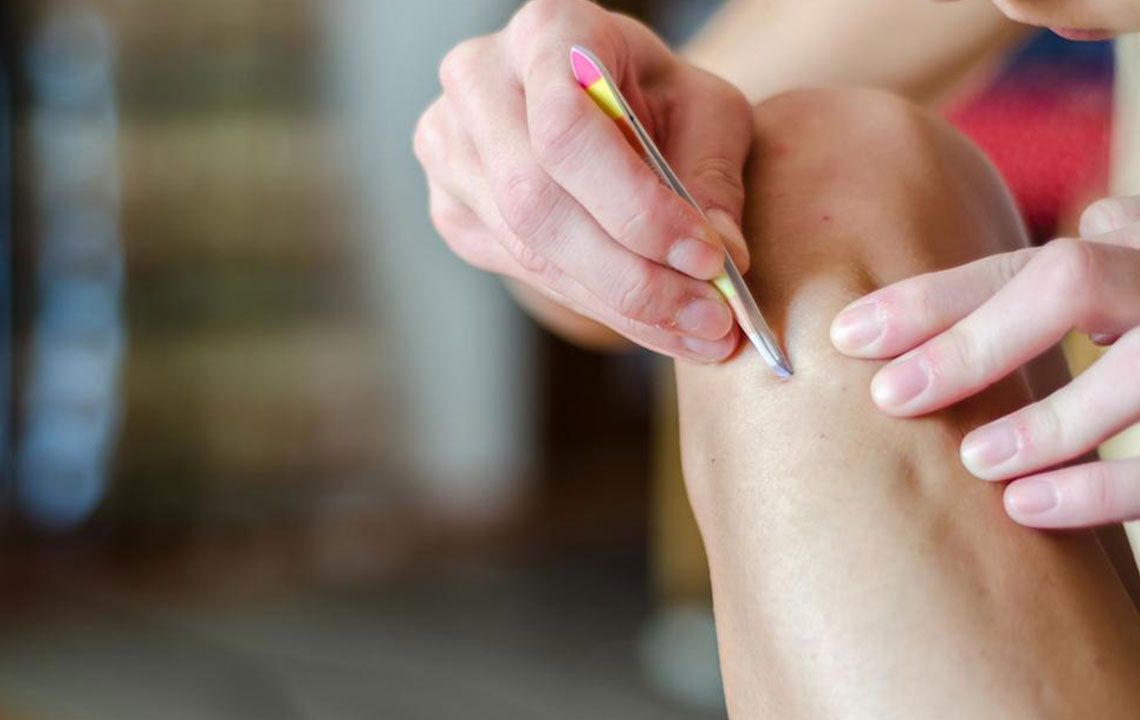
Usually, ingrown hairs don't disappear on their own and may require medical treatment. Persistent or stubborn ingrown hairs might need multiple therapies. Dark spots resembling tans or red bumps often mark the affected area, especially when the hair is thick. Despite misconceptions, laser treatments are painless and effective, with topical creams available for maintenance. Success often depends on consistent care to minimize recurrence.
Origins and causes of ingrown hair
Both teenagers and adults are prone to ingrown hairs at various points in life. They can be congenital or result from skin trauma or improper hair removal methods.
Common causes include:
Genetic predisposition, with some individuals naturally prone to ingrown hairs.
Hair that curls back or grows sideways due to sharp tips or improper grooming.
Unhygienic shaving practices, such as shaving too close or irritating the skin.
Waxing, especially with hot wax and incorrect technique, can aggravate the problem.
Tight clothing causing friction and pressure on the skin, encouraging inward hair growth.
Repeated or aggressive hair removal, leading to hair growing sideways or inward, often blocked by dead skin cells and debris.
Signs and symptoms
Itching and skin irritation are common.
Red or pink bumps may appear, sometimes with a reddish halo, indicating inflammation.
Post-shaving inflammation, especially in sensitive skin areas, can result in pustules or reddish bumps.
Infection may occur if bacteria like Staphylococcus interact with ingrown hairs, leading to folliculitis.
Persistent redness, tenderness, and bumps over the affected follicles are frequent.
While ingrown hairs are usually not serious, they can be embarrassing and uncomfortable, especially when visible. Proper care and treatment help reduce irritation and improve skin appearance.