Comprehensive Guide to Bacterial Skin Infections and Management
This article provides a detailed overview of bacterial skin infections, including their causes, risk factors, and symptoms. It covers conditions like cellulitis, erysipelas, folliculitis, and hot tub folliculitis, highlighting prevention and treatment options to manage these common skin issues effectively.
Sponsored

Comprehensive Insights into Bacterial Skin Infections and How to Handle Them
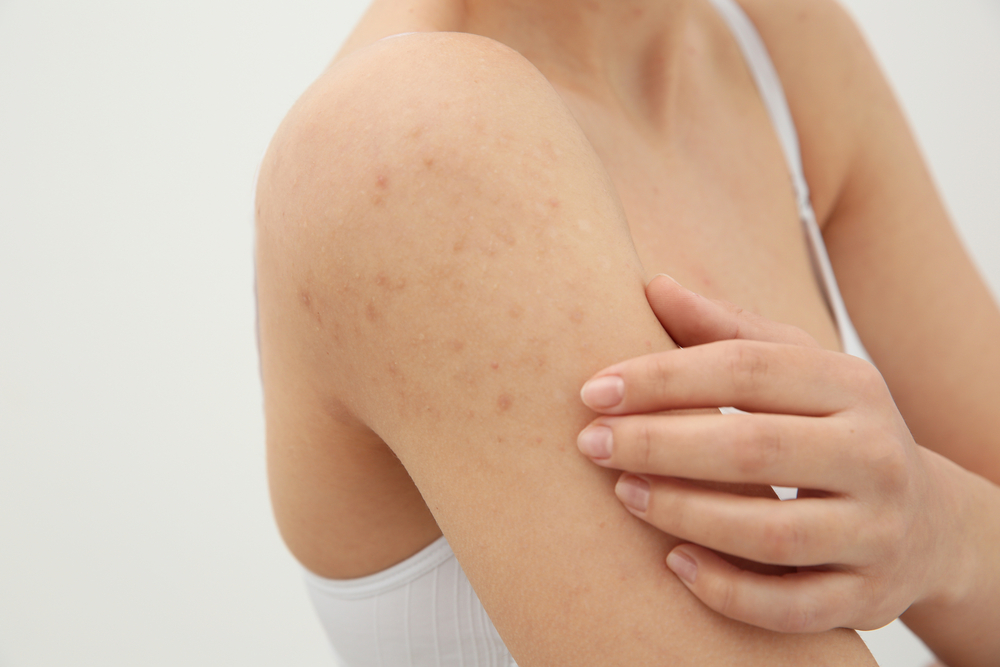
Understanding bacterial skin infections and their symptoms skin conditions can stem from various microorganisms, with symptoms ranging from mild irritation to severe health issues. Mild cases are often manageable with over-the-counter remedies and home care, while more serious infections demand medical attention. Certain skin ailments are caused by bacteria. Here are key facts about bacterial skin infections.
Factors Increasing the Risk of Skin Infections
Several elements can heighten the likelihood of developing bacterial skin infections:
Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible because high blood sugar levels impair white blood cell function, weakening immune response.
Aging can increase vulnerability, particularly in the elderly.
People with immune-compromising conditions like HIV/AIDS or hepatitis face higher risks.
Patients undergoing chemotherapy or immunosuppressive treatments are also more prone.
Skin injuries from sunburn, scratching, or cuts can become contaminated.
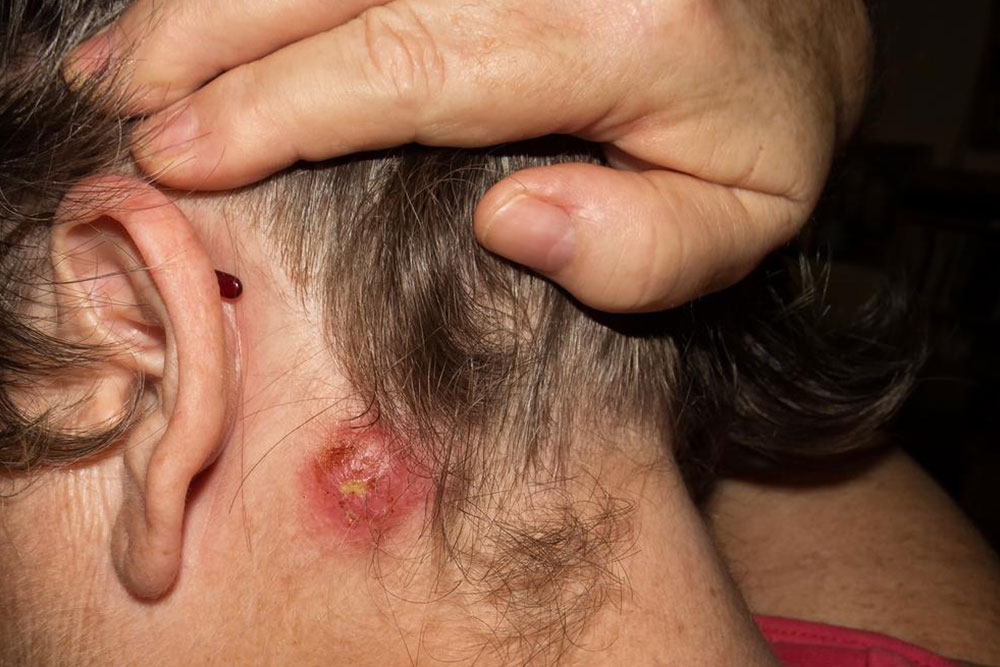
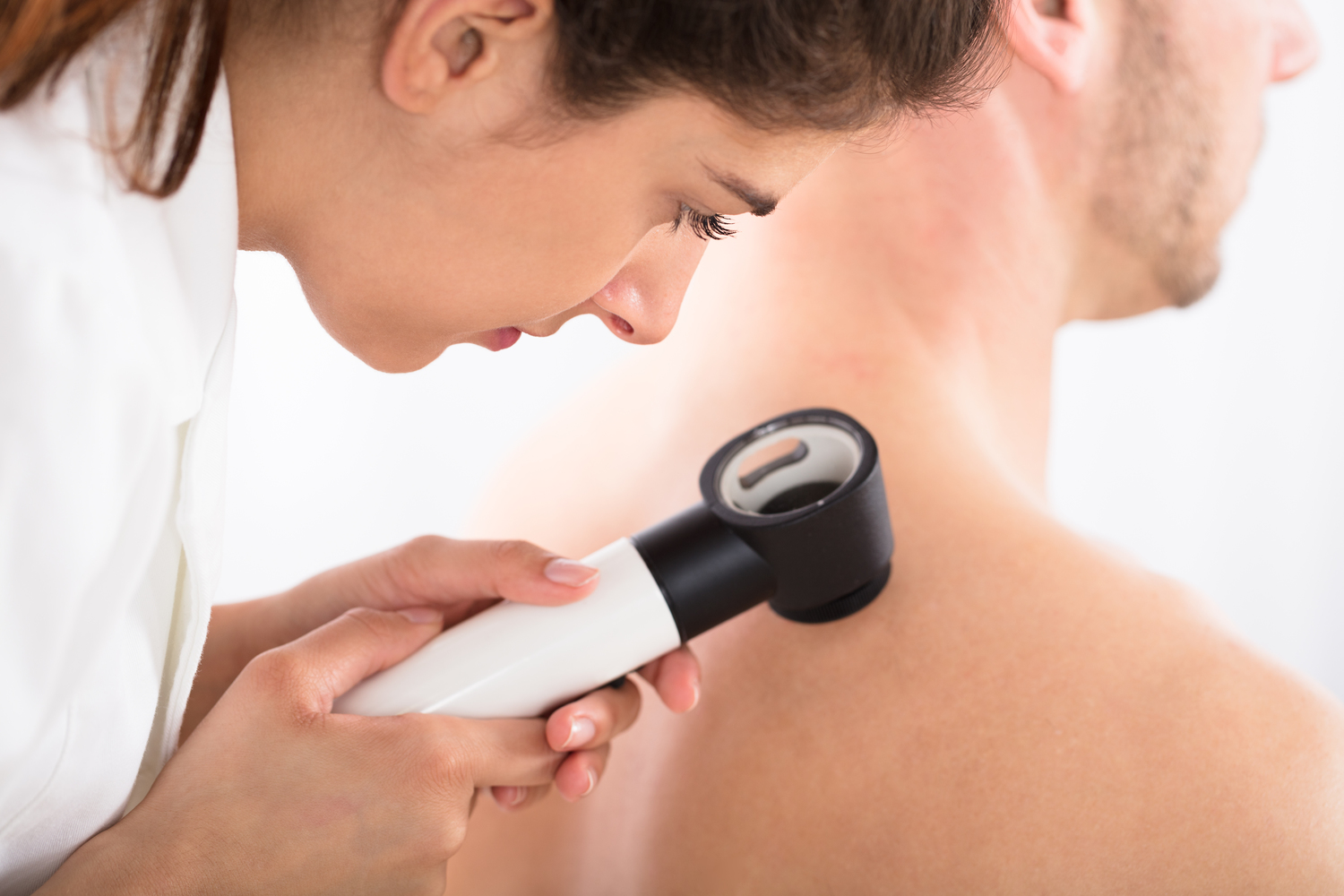
What is cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that begins on the surface and spreads inward.
The infection penetrates the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissues.
It results in redness, swelling, tenderness, warmth, and sometimes fever.
Commonly affecting the legs, it can also involve the face, arms, or hands.
It often starts from a skin injury like a cut or burn.
Conditions such as dermatitis or athlete's foot that compromise skin integrity can lead to cellulitis.
Those with varicose veins, obesity, leg swelling, or diabetes are at increased risk.
What is erysipelas?
Erysipelas, also called St. Anthony's fire, appears as bright redness with clearly defined raised edges.
Often accompanied by lymphatic streaking, it mainly affects the face and legs.
Symptoms may resemble flu and occur without obvious skin wounds.
Common in individuals with weakened immune systems, lymphedema, or chronic illnesses like diabetes.
Caused by beta-hemolytic Streptococcus bacteria, it responds well to penicillin therapy.
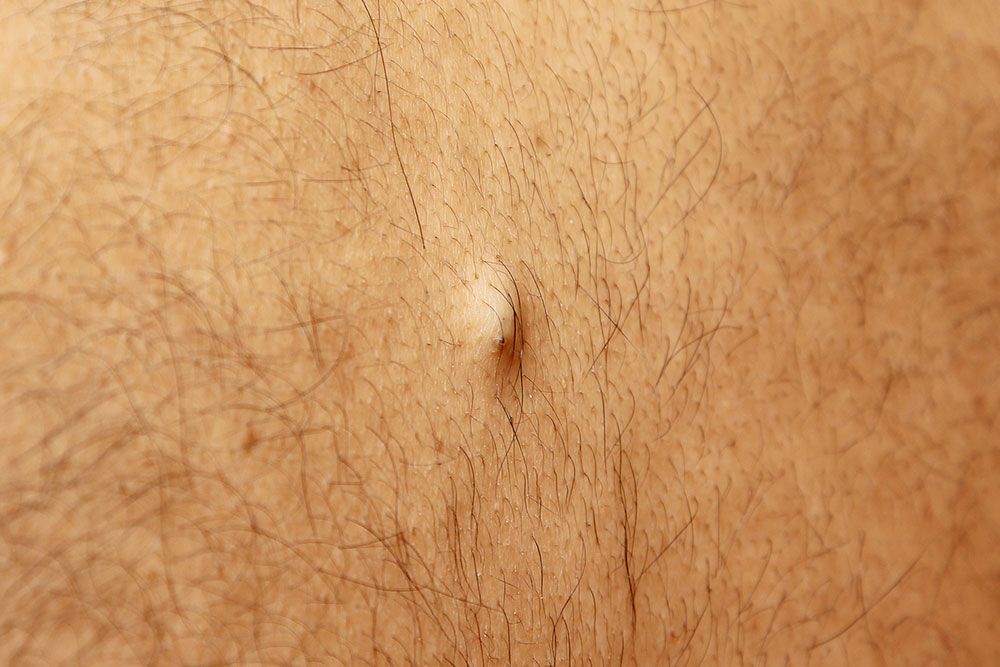
Folliculitis: skin infection of hair follicles
Folliculitis is an infection confined to hair follicles, presenting as small yellow pustules.
Triggers include injury, friction, tight clothing, chemical exposure, excessive sweating, or water contact.
Staphylococcus aureus is a common causative bacteria, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
Lesions often resolve quickly, but deep infections may cause swelling and redness with or without pustules.
Topical antibiotics like erythromycin, clindamycin, or benzoyl peroxide can help expedite healing.
Hot tub folliculitis overview
Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, this infection typically results from contaminated hot tubs.
The bacteria thrive in unsanitary water, but do not survive well on healthy skin.
Symptoms usually resolve within a week or ten days without treatment.
Home treatments include applying warm, moist compresses to the affected area several times daily.
Over-the-counter remedies can alleviate symptoms, but consulting a healthcare provider is advisable before medication use.