Nutritional Strategies to Reduce Osteoporosis Risk
Discover effective dietary and medical strategies to help lower osteoporosis risk. This article highlights key nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, K, protein, and magnesium, along with medical treatments such as Evenity®, Prolia®, and Fosamax® to strengthen bones and prevent fractures as you age.
Sponsored

Dietary Approaches to Lower Osteoporosis Risk
As we age, our bones undergo continual cycles of tissue breakdown and renewal. Over time, the body's ability to repair diminishes, increasing vulnerability to osteoporosis—a condition characterized by decreased bone density and fragility. To help prevent or mitigate this risk, adopting a balanced diet paired with physical activity is essential. Below are key foods that can support bone health and reduce osteoporosis chances.
Foods Rich in Calcium
Calcium is vital for maintaining strong bones. It also supports cardiovascular health, nerve function, and blood clotting. The USDA database highlights dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese as calcium sources. Other options include dark leafy greens such as kale and collards, broccoli, canned fish like salmon and sardines, nuts, and tofu.
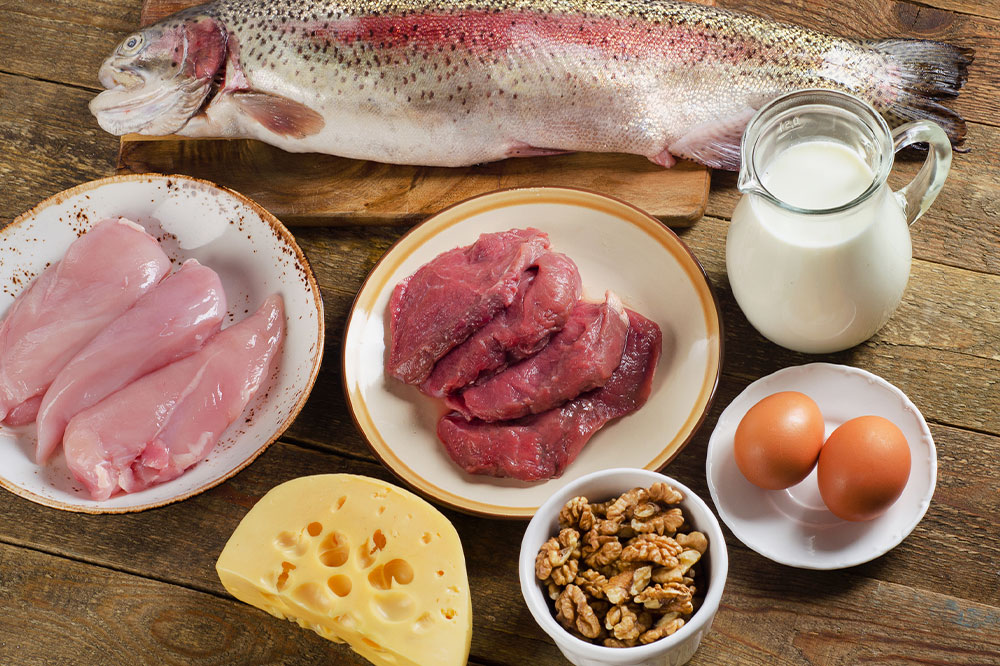
Sources of Protein and Magnesium
Protein contributes to bone strength, requiring at least 15 grams per meal. Foods like poultry, fish, eggs, beans, nuts, and nut butters are excellent protein sources. Magnesium, found in nuts and seeds, is essential for bone mineralization. Including them in your diet supports overall bone health.
Vitamins C and K for Bone Support
Vitamin D, produced upon sunlight exposure, enhances calcium absorption and bone cell activity. Dietary sources include oranges, lemons, tomatoes, kiwis, and red peppers. Vitamin K is crucial for bone maintenance; deficiencies are linked to osteoporosis. Rich sources include Brussels sprouts, broccoli, cauliflower, turnip greens, collards, and cabbage.
Managing Osteoporosis
In certain cases, healthcare providers may recommend lifestyle modifications alongside medication. Prescribed treatments include:
Evenity® (romosozumab): For postmenopausal women at high risk of fractures; administered via injection twice a month for a year.
Prolia® (denosumab): Used in men and women to decrease fracture risk and increase bone mass, available as a prefilled syringe.
Fosamax® (alendronate): A bisphosphonate to prevent bone loss, primarily prescribed to postmenopausal women and for Paget's disease.