Essential Dietary Guidelines for Arthritis Patients
This article offers comprehensive dietary guidance for arthritis sufferers, highlighting foods to avoid and include for inflammation control. Emphasizing a balanced diet, it discusses how reducing processed foods, red meat, and sugars can alleviate symptoms, while recommending omega-3 rich fish, vegetables, and antioxidants to support joint health. Proper medical consultation is advised for personalized treatment plans alongside lifestyle changes like stress reduction techniques to improve mobility and reduce pain.
Sponsored
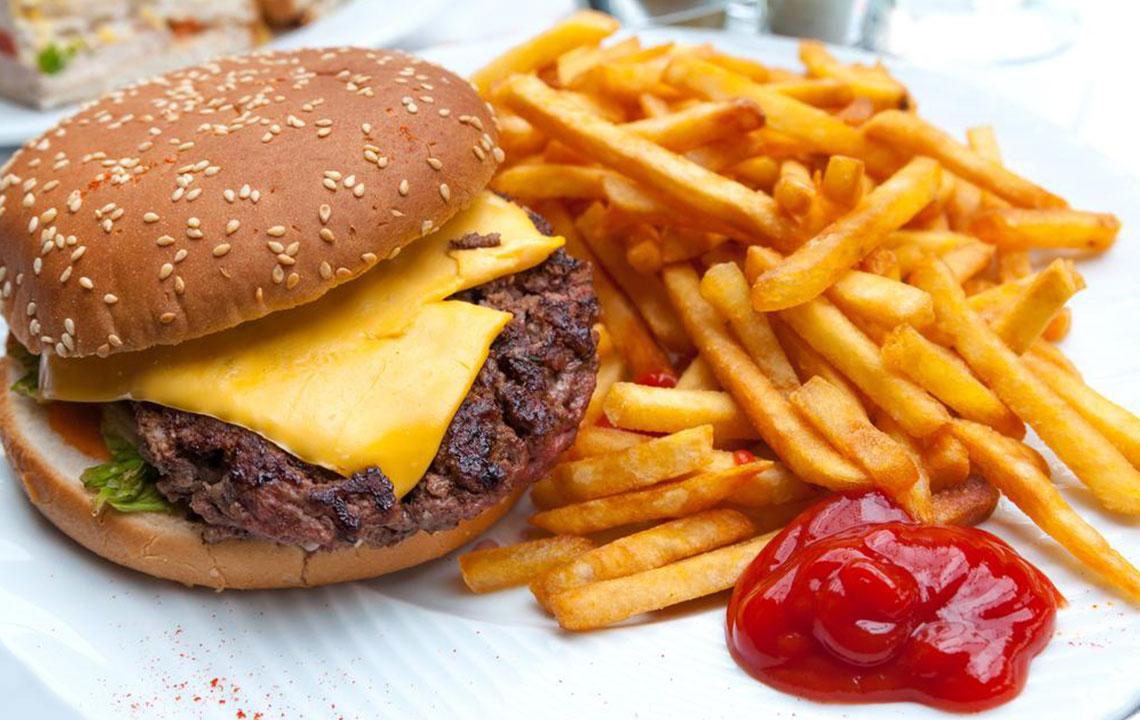

Dietary Tips for Managing Arthritis
Arthritis refers to joint inflammation that causes pain and stiffness. With over 100 identified types, it can affect individuals of any age, gender, or ethnicity. In the United States, arthritis is a leading cause of disability, impacting more than 50 million adults and over 300,000 children. Inflammatory responses in the body can be exacerbated by certain foods, leading to increased pain, swelling, and risk of comorbidities like obesity and heart disease. Modifying your diet by avoiding specific items can help manage symptoms effectively.
While arthritis has no outright cure through diet, certain foods are known to worsen inflammation, damage bones, and weaken immune function. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can significantly alleviate joint discomfort. Being mindful of food triggers is crucial, especially foods that promote inflammation and worsen symptoms.
Fried and processed foods – Numerous studies show that reducing intake of fried, fast, and frozen meals can lower inflammation and restore natural immune functions.
Red meat – Rich in saturated fats and omega-6 fatty acids, red meat often triggers inflammatory responses. Many patients report symptom improvement after limiting red meat consumption.
Sugary and refined carbohydrate foods – High sugar levels contribute to inflammation. It’s advisable to steer clear of candies, pastries, sodas, and processed foods high in refined carbs.
Gluten-containing grains – Wheat, barley, and rye can provoke inflammation in individuals with gluten sensitivities or autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and celiac disease. Avoiding gluten can reduce joint swelling and pain.
Dairy products – Dairy proteins may exacerbate arthritis symptoms, especially in those allergic or sensitive to milk. Transitioning to plant-based alternatives like nuts, lentils, and tofu can help meet protein needs without aggravating pain.
Alcohol and tobacco – Both substances are detrimental to joint health and overall well-being. Smoking, in particular, is linked to higher rheumatoid arthritis risk; quitting is highly recommended.
Conversely, some foods possess anti-inflammatory properties and can help ease arthritis symptoms. Including these in your diet may improve joint comfort over time.
Fatty fish – Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, consuming 3-4 ounces of specific fish varieties can reduce joint inflammation.
Extra virgin olive oil – Packed with healthy fats and oleocanthal, olive oil helps lower cholesterol and fight inflammation when used regularly.
Soy products – High in protein and fiber, soybeans are beneficial for reducing joint pain and supporting overall health.
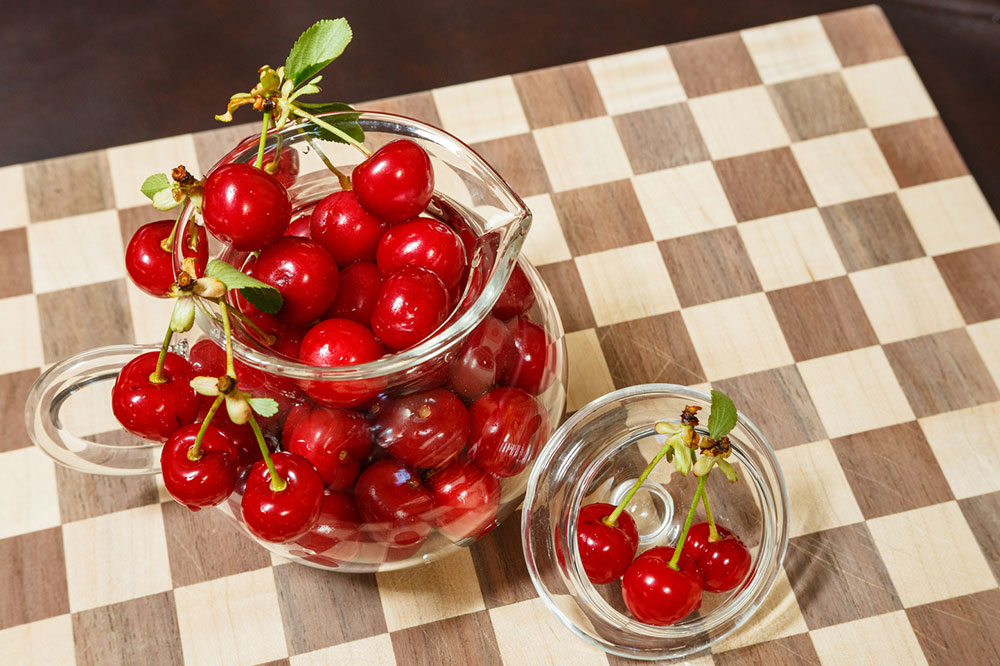
Cherries and berries – Containing anthocyanins, these fruits can lessen gout attacks and joint inflammation.
Broccoli – Loaded with vitamins and sulforaphane, broccoli supports bone health and slows arthritis progression.
Green tea – Its antioxidants combat inflammation and protect joint cartilage.
Citrus fruits – Rich in vitamin C, citrus helps reduce inflammatory responses.
Beans – These nutrient-dense foods help lower inflammation markers like CRP and enhance muscle endurance.
Consult your healthcare provider for personalized medical and dietary advice. Avoid nightshade vegetables as they may increase joint pain in some individuals. Alongside diet modifications, stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can support overall joint health and well-being.