Signs and Early Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Learn to identify the early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, including joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and fatigue. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing the condition effectively and preventing joint deformity. This guide helps you recognize warning signs and seek timely medical advice to maintain a better quality of life.
Sponsored
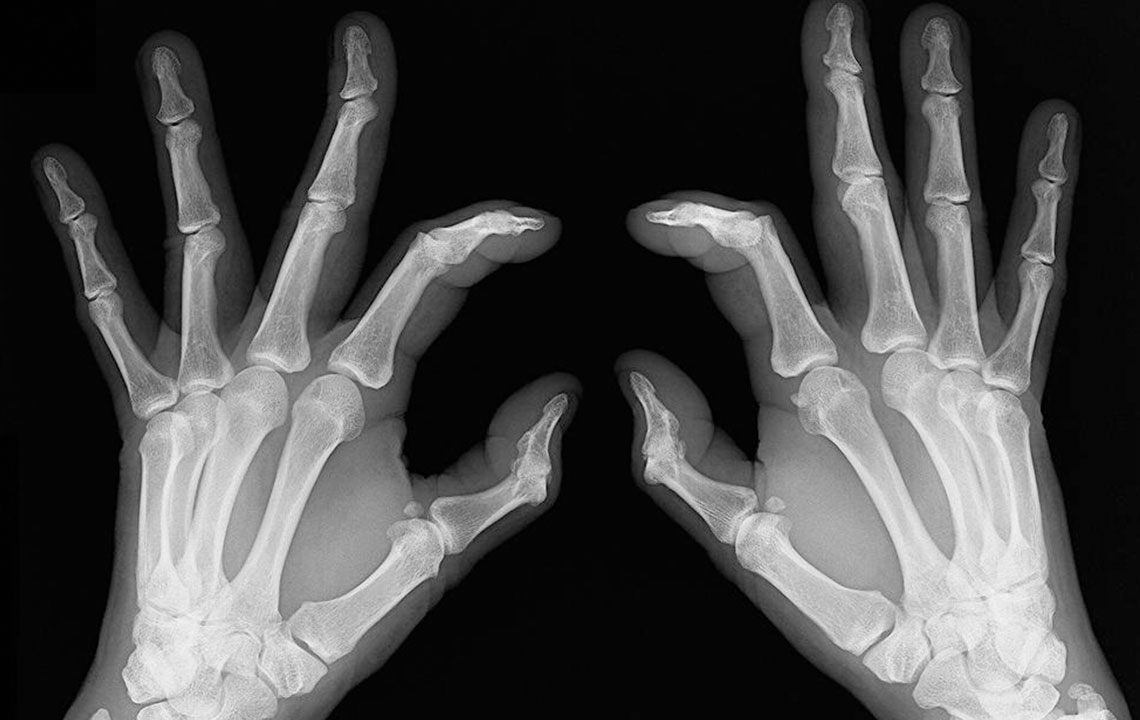
Recognizing Early Indicators of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune condition causing persistent joint inflammation, leading to pain, swelling, and potential deformity. It often begins gradually, with intermittent discomfort that can spread over weeks or months. Staying vigilant about health and promptly addressing minor joint pains is crucial. Symptoms vary among individuals. Below are key signs to monitor:
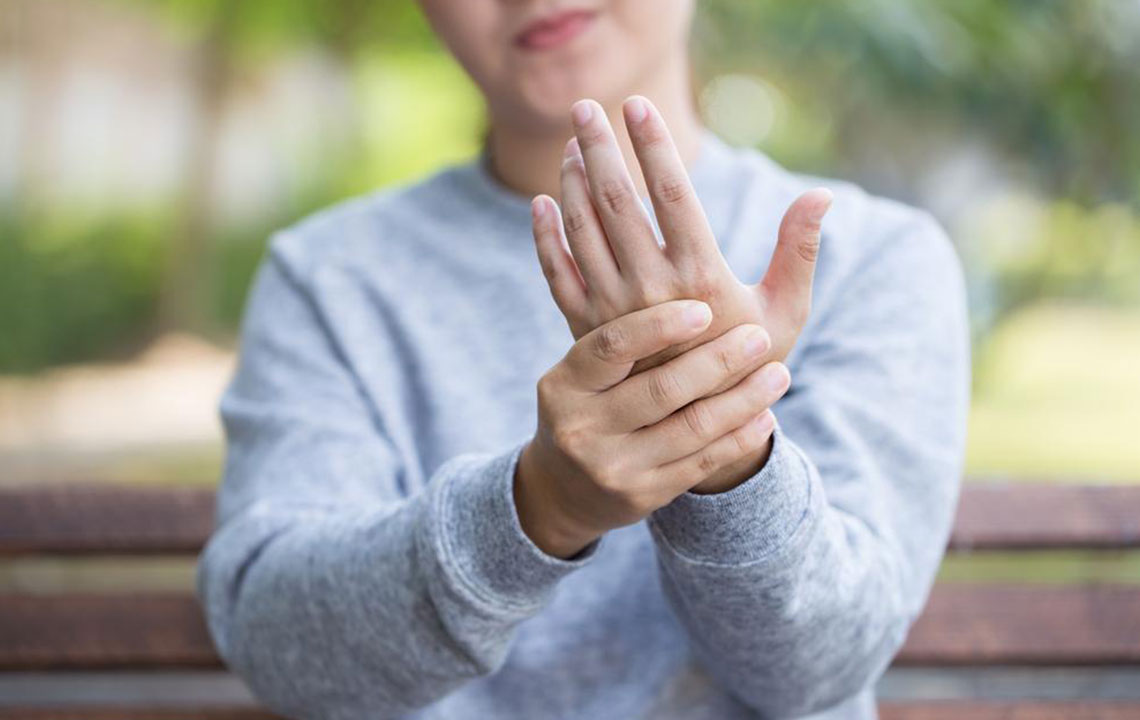
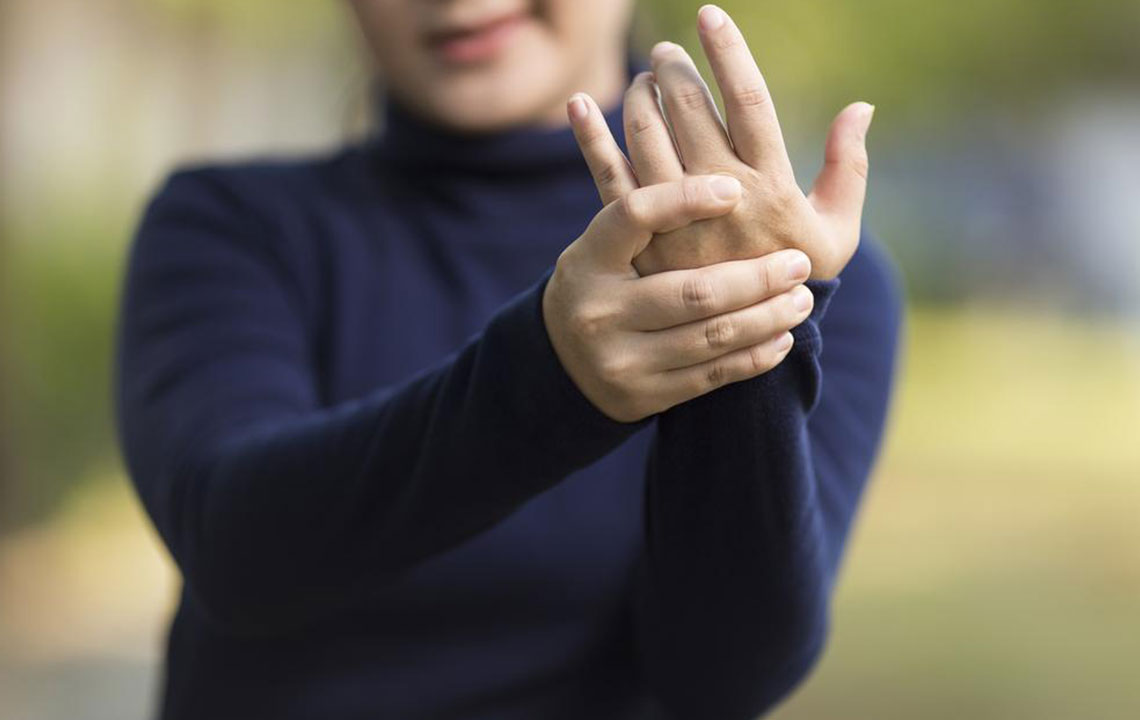
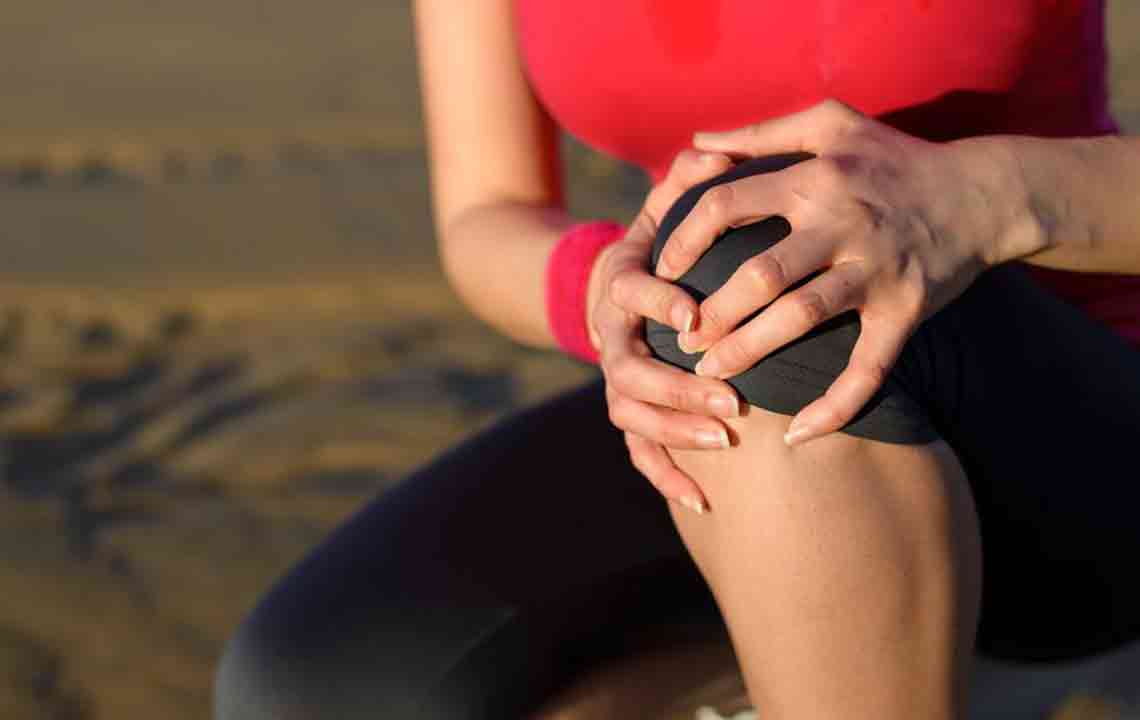
Joint discomfort: Initial symptoms usually involve pain in knees, hips, wrists, neck, or ankles. These pains may come and go initially.
Fatigue: Rheumatoid arthritis can cause overall tiredness, often accompanied by fever or a general sense of feeling unwell.
Swelling and inflammation: Chronic flare-ups may result in swollen, inflamed joints; these symptoms should be differentiated from other conditions like lupus.
Morning joint stiffness: People often wake with stiff joints, experiencing limited movement that improves gradually.
Redness and warmth: Occasionally, affected joints exhibit redness and warmth, but this should be distinguished from skin injuries or bruises.
Bone changes: Arthritis can lead to joint deformities, so monitor for subtle alterations in joint shape or discomfort.
Early detection allows for effective management, alleviating pain and maintaining joint function. If you notice these signs, consult a healthcare professional promptly.