Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
This article provides a comprehensive overview of rheumatoid arthritis, detailing its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and ongoing research to better understand this autoimmune disease, which primarily impacts joints and can affect other organs over time.
Sponsored
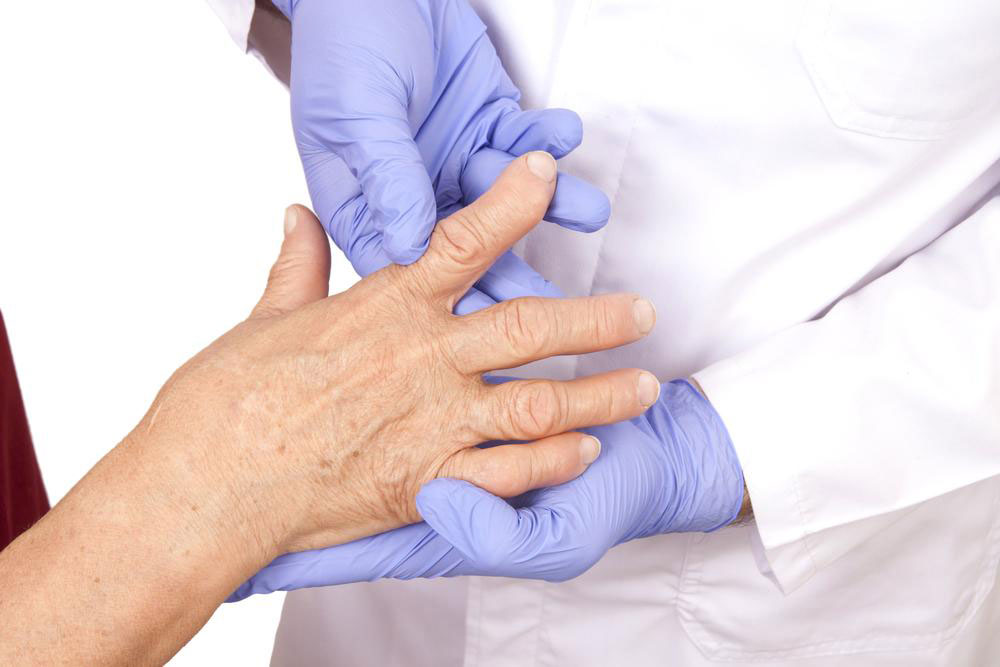
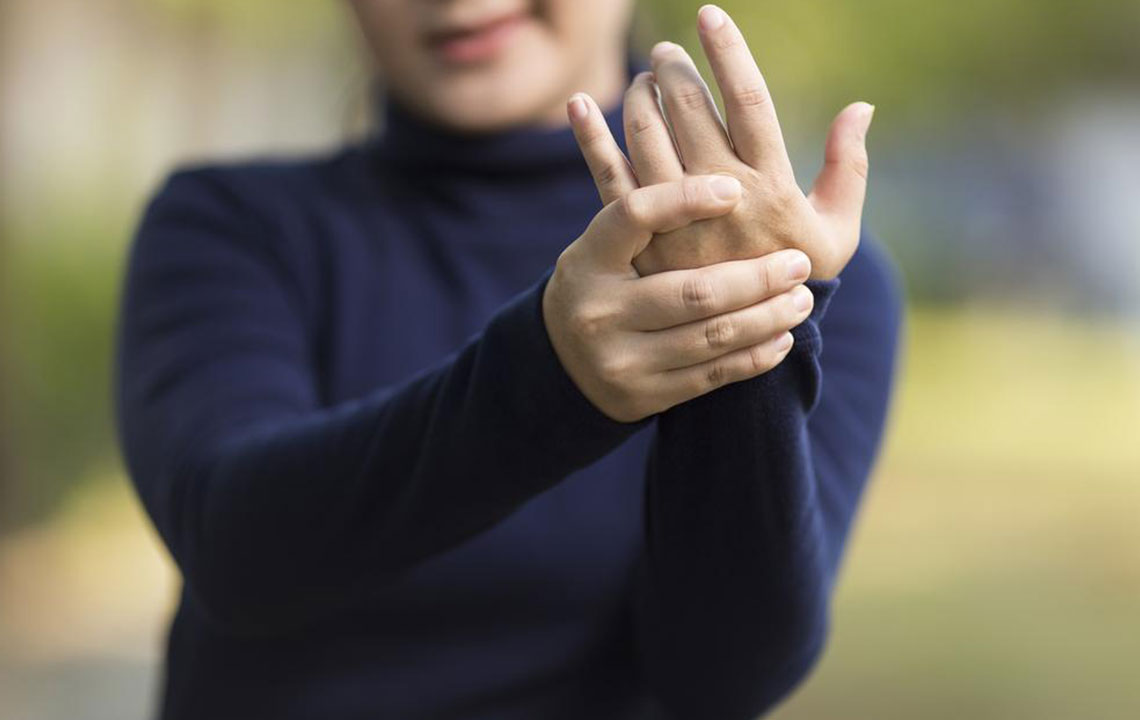
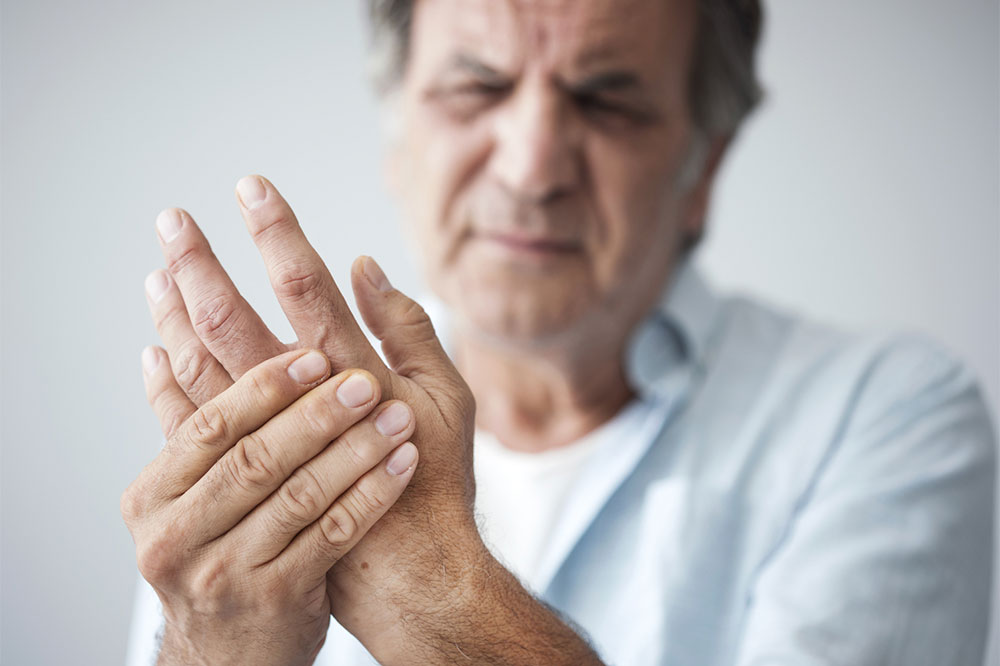
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that targets the joints, including the wrists, elbows, fingers, and feet. Patients often experience pain, stiffness, and swelling in multiple joints. Early signs also include fatigue, poor appetite, illness, fever, and morning stiffness. Flare-ups, marked by heightened inflammation, can last days or weeks. Persistent inflammation may affect other body organs over time. The disease varies in severity, often fluctuating between mild and severe phases, and can persist for years or a lifetime.
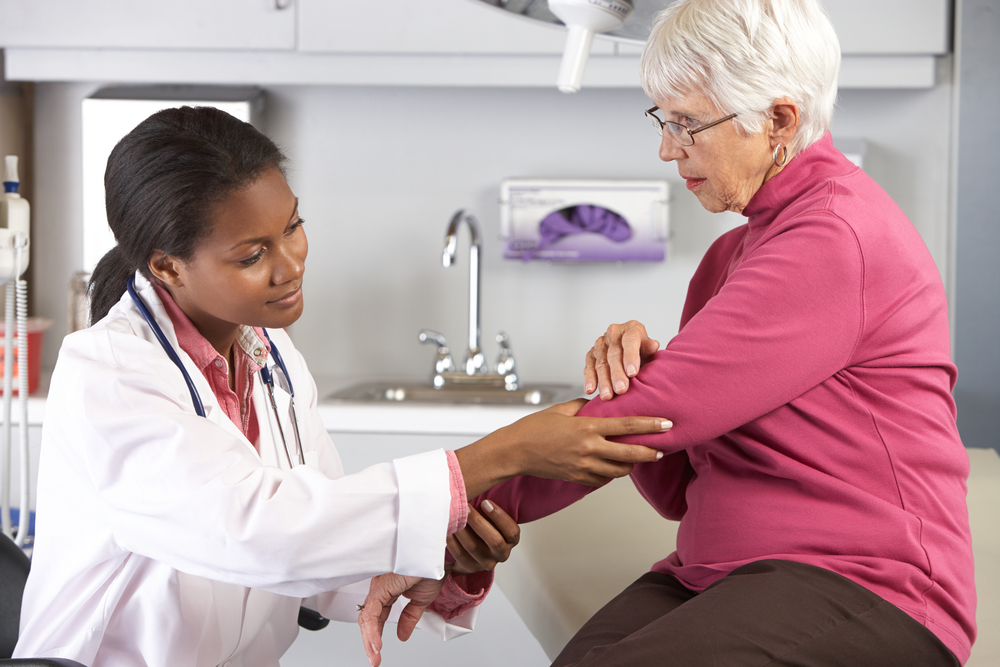
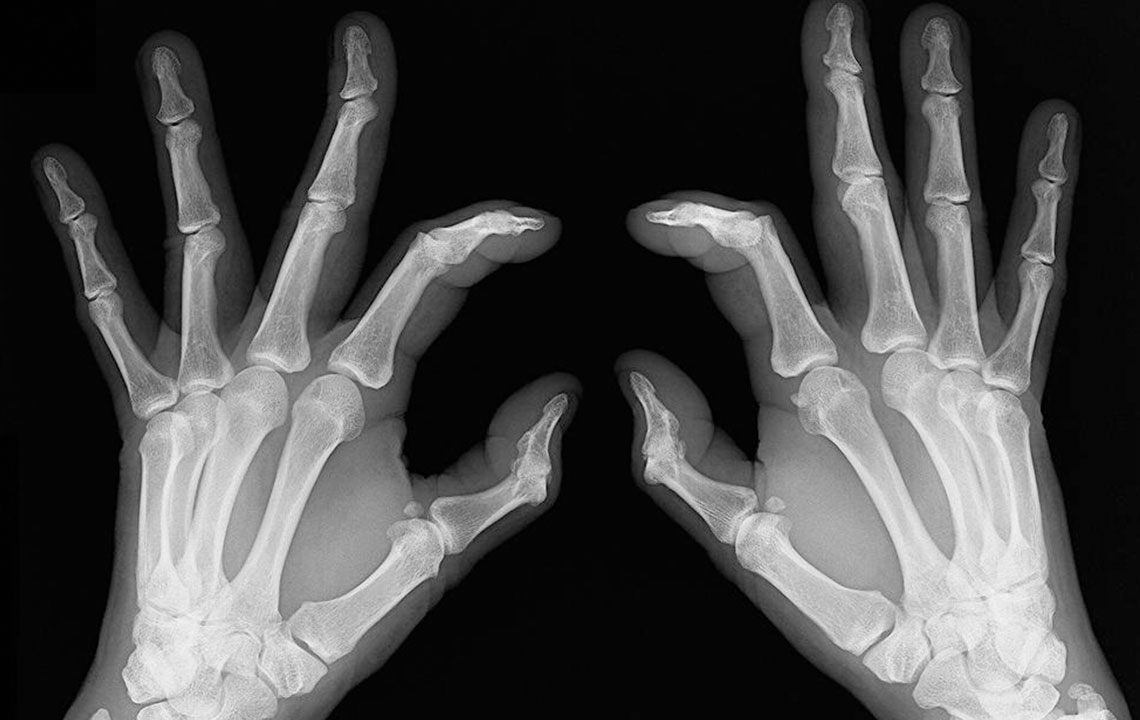
RA is believed to result from an abnormal immune response, though exact causes remain unclear. Genetics, hormones, and lifestyle factors are thought to influence its development. Diagnosing RA involves physical exams, laboratory tests, medical history review, and X-rays, as symptoms can resemble other joint conditions. Treatment primarily aims to alleviate pain, reduce swelling, and prevent joint damage. Although there is no cure, early intervention helps patients maintain activity and improve quality of life. Ongoing research explores infections and genetic factors, with women being disproportionately affected, often linked to hormonal changes, obesity, and stress.