Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Diagnosing, Treating, and Preventing Asthma
This comprehensive guide explores asthma's causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies. It covers symptoms, triggers, diagnostic procedures, medication options, and lifestyle changes to manage and prevent asthma attacks effectively. Suitable for patients and caregivers, the article emphasizes understanding the condition to improve quality of life.
Sponsored
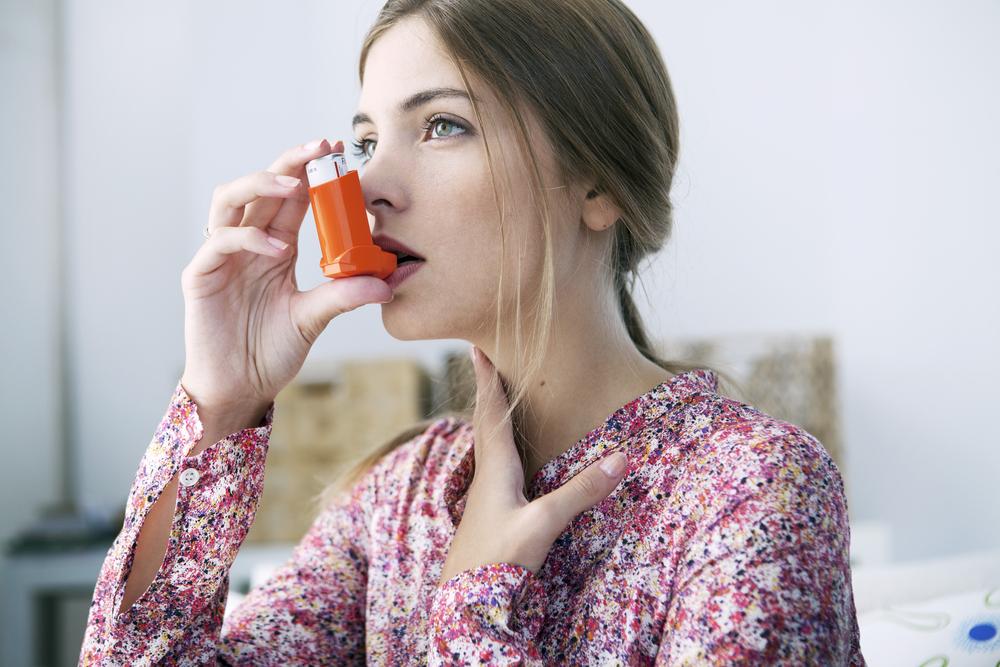
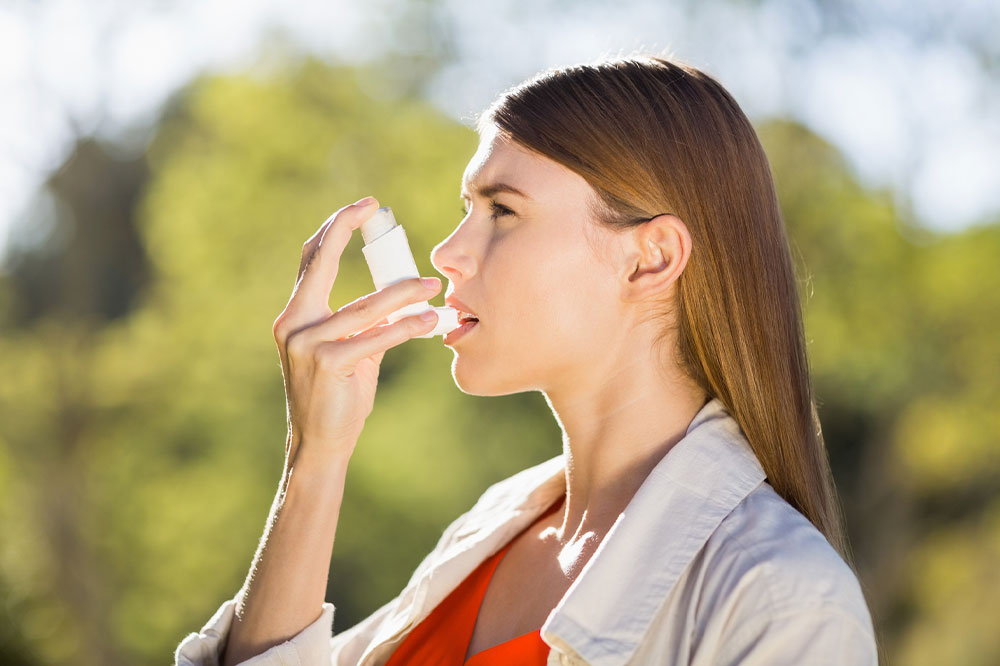
Asthma is a persistent respiratory condition where the airways become inflamed and constricted due to exposure to allergens or irritants. This reaction leads to excess mucus production, causing symptoms such as coughing, chest discomfort, breathing difficulty, and wheezing. Symptoms vary from person to person, ranging from mild to severe, significantly impacting daily life. Medical professionals categorize asthma into four levels: mild intermittent, mild persistent, moderate persistent, and severe persistent.
Causes
While the exact cause of asthma remains unknown, it is believed to result from a mix of genetic and environmental influences. Triggers vary among individuals but commonly include:
Allergens like dust, pollen, mold spores, or pet dander
Physical activities or exertion
Cold weather
Respiratory infections such as colds
Pollutants like smoke, chemicals, and fumes
Certain medications including aspirin, ibuprofen, and beta-blockers
Chronic stress
Additives like sulfites in food
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Diagnosis
A pulmonologist will perform physical examinations and review symptoms to distinguish asthma from other respiratory issues. Diagnostic tests like spirometry and peak flow measurements assess lung function. Additional evaluations such as methacholine challenge, allergy tests, imaging, sputum analysis, nitric oxide measurements, and provocative testing may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment and Prevention
Depending on severity, doctors may prescribe a combination of medications. Long-term control drugs include inhaled corticosteroids, combination inhalers, beta-agonists, and leukotriene modifiers. For immediate relief, quick-action medications like short-acting beta-agonists and corticosteroids can be used. Severe cases might benefit from bronchial thermoplasty. Preventative strategies involve healthy lifestyle changes: regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing GERD. Reducing triggers by cleaning the home, using air conditioning and humidifiers, grooming pets, and covering the mouth and nose in cold weather can help prevent attacks.