Understanding Melanoma: Detection and Treatment Strategies
This article offers essential insights into melanoma, focusing on detection, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and prevention tips. It highlights reliable sources for melanoma images, explains biopsy methods, and discusses stages-specific treatments. Practical advice on sun safety and skin monitoring is emphasized for early detection, aiming to empower readers to identify and address melanoma promptly for better health outcomes.
Sponsored
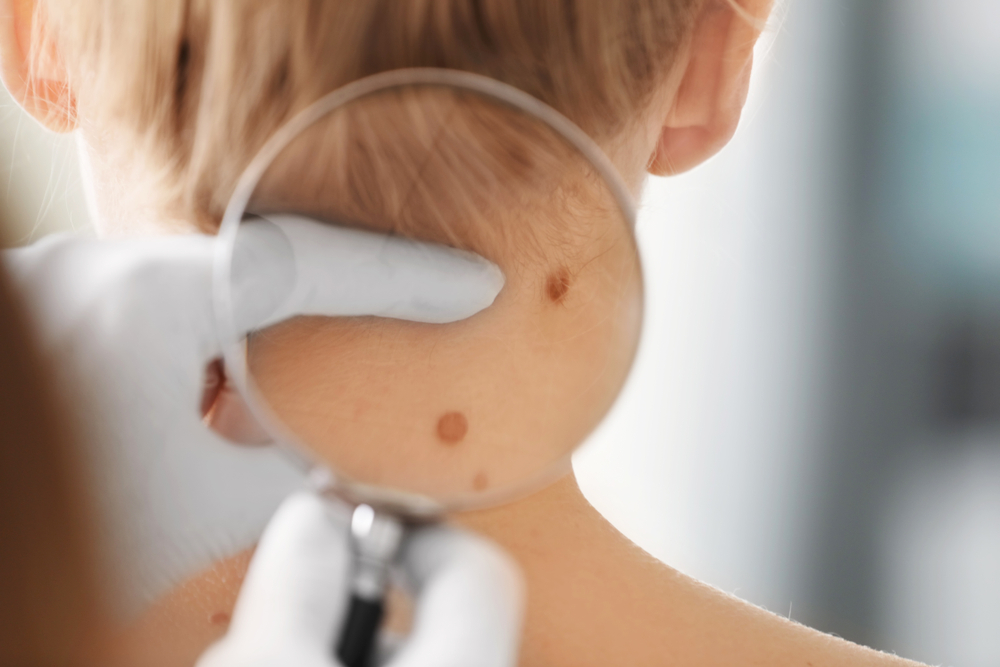
Detection and management options for melanoma skin cancer
Melanoma is an aggressive form of skin cancer originating in melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin pigmentation. Early detection is challenging since initial symptoms resemble benign moles. This article covers crucial information about melanoma visuals, diagnostic methods, and treatment options.
Where can you find melanoma images?
Several reliable websites offer visuals of early-stage melanoma, featuring shapes, sizes, and growth patterns. Note that detailed images of advanced stages or symptom-specific visuals are less common.
mayoclinic.org: This leading health portal provides comprehensive information on various diseases, including melanoma. They include detailed images illustrating the morphology and development of moles affected by melanoma.
melanoma.org: Dedicated exclusively to melanoma, this site offers visual guides to help identify abnormal skin growths and track their progression over time.
melanoma.gov: A government-backed resource sharing images to help distinguish normal moles from malignant ones, facilitating early detection.
How is melanoma diagnosed?
Common biopsy procedures for diagnosing melanoma include:
Excisional biopsy: Complete removal of the suspicious lesion along with a small margin of surrounding skin for analysis.
Punch biopsy: A circular blade extracts a round tissue sample around the lesion for examination.
Incisional biopsy: The most irregular or suspicious part of the mole is sampled for lab testing.
Treatment options for melanoma: The approach depends on melanoma's size, stage, and patient health. Common treatments include:
Early-stage melanoma: Surgical removal of the mole along with a margin of healthy skin often suffices, potentially eliminating the need for additional therapy.
Treatment for later stages, such as stage I-III, involves more comprehensive procedures:
Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to destroy cancer cells, administered intravenously or orally.
Radiation therapy: More effective in some cases, employing high-energy X-rays to target malignant cells.
Lymph node removal: Surgical removal of affected lymph nodes to prevent spread.
Biological therapies: Immunotherapy boosts the body's immune response to fight melanoma, often involving substances naturally produced by the body.
Preventive measures against melanoma
Sun protection: Use broad-spectrum sunscreens with high SPF, especially in sun-exposed areas.
Avoid tanning beds: UV-emitting devices increase melanoma risk, so limit exposure.
Monitor skin changes: Regular self-examinations to notice abnormal moles or skin patches. Use trusted online images for reference and consult specialists promptly.
Healthy immune system: Maintain a nutritious diet to bolster your body's defenses against disease.