Understanding Hearing Impairment: Types, Signs, Causes, and Risks
This comprehensive overview explains the different types of hearing impairment, their symptoms, causes, and risk factors. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and highlights treatment options like hearing aids and surgery. Understanding how hearing functions and the common issues that impair it can aid in prevention and timely intervention, improving quality of life for those affected.
Sponsored

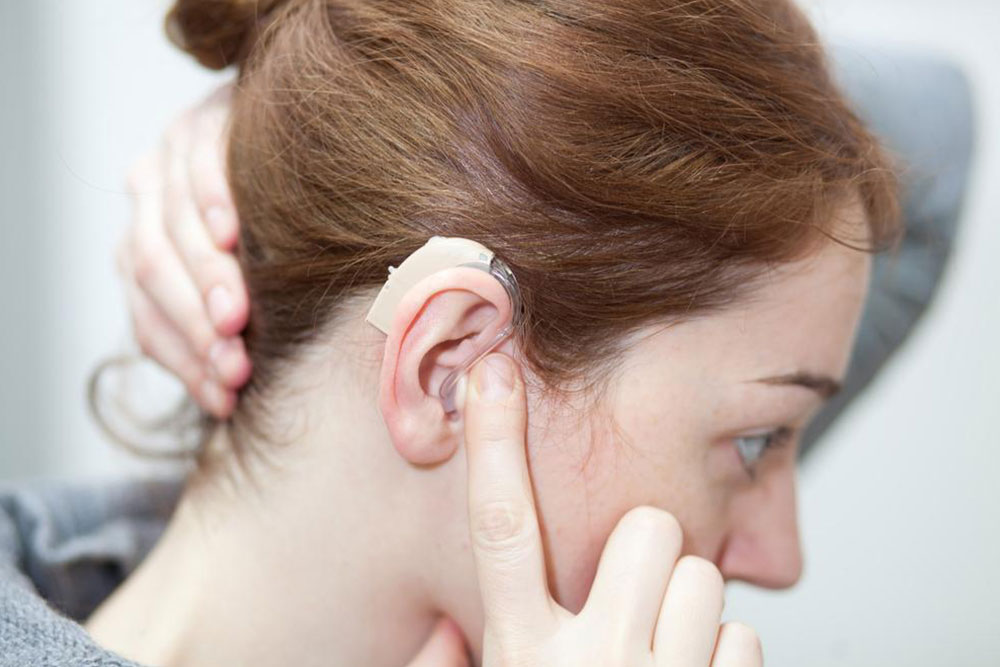
Hearing impairment is often associated with aging, but it can affect individuals of any age due to issues like inner ear or nerve damage. Interestingly, about 66% of those with hearing loss are under 65. Treatment options such as hearing aids or surgery are effective for many cases. This article provides an essential overview of hearing impairment, including its types, symptoms, causes, and factors increasing risk.
Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is classified based on the affected area of the ear into three main types:
Sensorineural Loss
The most prevalent form, comprising 90% of cases, often results from inner ear damage, infections, or head injuries.
Conductive Loss
This occurs when earwax buildup, eardrum perforation, or structural issues block sound transmission. It is largely treatable.
Mixed Hearing Loss
A combination of sensorineural and conductive issues, typically caused by prolonged infections damaging both the eardrum and middle ear bones.
Signs of Hearing Impairment
Recognizing symptoms early is vital. Key indicators include:
Difficulty understanding words, especially in noisy settings
Challenges hearing consonant sounds
Needing others to speak more slowly and clearly
Increasing volume on devices like TV or radio
Causes of Hearing Loss
Understanding how hearing works helps identify causes. Sound waves enter the outer ear, causing vibrations in the eardrum. These vibrations are amplified by small middle ear bones and then transmitted to the inner ear's cochlea, where hair cells convert them into electrical signals sent to the brain. Disruptions at any stage can lead to hearing loss. Common causes include:
Aging and exposure to loud noises
Earwax buildup
Ear infections
Abnormal hair growth in the ear
Tumors
Ruptured eardrum
Risk Factors Influencing Hearing Loss
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing hearing issues:
Aging
Natural degeneration may harm inner ear structures.
Loud noise exposure
Consistent exposure can damage inner ear hair cells, resulting in varying degrees of impairment.
Genetic predisposition
Family history can elevate the risk of hearing problems and loss.