Understanding Hemolytic Disease in Newborns: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Hemolytic disease in newborns is a critical condition caused by blood type incompatibility, especially involving the Rh factor. It leads to premature destruction of red blood cells, resulting in jaundice, swelling, and anemia. Treatments like phototherapy and blood transfusions are effective when administered early. Proper prenatal testing and medical care can prevent severe outcomes, ensuring healthier beginnings for affected infants.
Sponsored
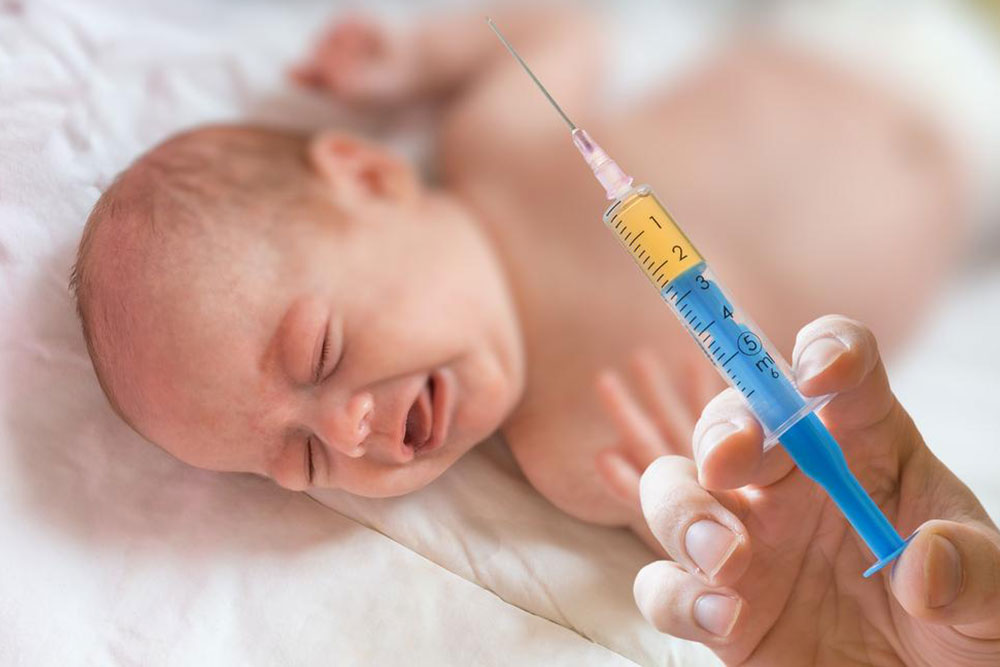
Hemolytic disease of the newborn is a serious blood condition that can affect infants, potentially posing life-threatening risks. It occurs when the mother's immune system attacks the baby's red blood cells, which are prematurely destroyed. This condition often arises from incompatibilities between the mother and fetus's blood types, especially involving the Rh factor. Symptoms include jaundice, swelling, anemia, and enlarged organs. Treatments involve phototherapy, blood transfusions, and immune therapies. Early identification and proper medical management are crucial to prevent severe complications in newborns.