Effective Strategies to Increase Your Good Cholesterol (HDL)
Learn effective methods to increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels through diet and exercise. This guide covers the importance of balanced cholesterol, key foods to boost HDL, and lifestyle tips for heart health. Incorporate nuts, fatty fish, olive oil, and fiber-rich foods into your diet, along with regular cardio workouts, to improve your cholesterol profile and protect your heart from disease.
Sponsored

Effective Strategies to Increase Your Good Cholesterol (HDL)
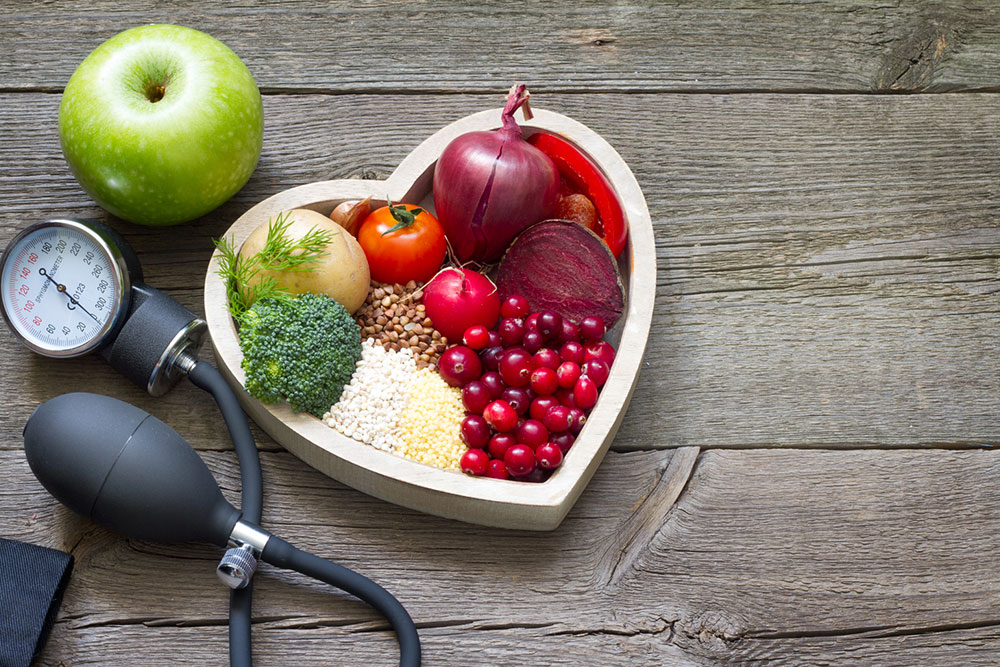
Many people mistakenly believe that all cholesterol is harmful. However, the body requires fats for vital metabolic processes, and not all cholesterol is detrimental. The critical factor is the balance between good (HDL) and bad (LDL) cholesterol. Elevated LDL and low HDL levels can elevate health risks, especially for heart health.
Achieving optimal cholesterol levels involves a nutritious diet combined with regular physical activity. Enhancing HDL levels supports cardiovascular wellness and reduces disease risk.
Understanding Cholesterol Types
HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) is the beneficial cholesterol that aids in protecting your heart. Higher HDL levels can lower harmful LDL cholesterol and reduce the risk of stroke. Doctors emphasize HDL levels during blood tests — a higher proportion of HDL relative to total cholesterol indicates better health. Numerous studies link low HDL with increased heart disease risk.
LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) is the harmful type that promotes plaque formation in arteries, potentially blocking blood flow and causing heart attacks. Lowering LDL through diet and exercise can significantly improve heart health.
Triglycerides are the primary form of stored energy in the body. Excess consumption of food and high-fat diets raise triglycerides, which combined with low HDL and high LDL, increase cardiovascular risk.
High cholesterol levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, narrowing them over time and impeding blood circulation. Managing cholesterol involves decreasing LDL and triglycerides while boosting HDL with dietary choices and lifestyle adjustments.
Diet and Lifestyle Tips
Choosing a low-glycemic diet helps maintain blood sugar levels and supports healthy cholesterol balance. Reducing saturated fats and simple carbs lowers LDL and blood sugar, especially important for diabetics. Increasing fiber and plant sterols benefits cholesterol levels. Incorporating specific foods can raise HDL levels and protect your heart, as HDL also exhibits anti-inflammatory properties.
Top Foods to Elevate HDL
Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, hazelnuts, pecans, and peanuts are packed with healthy fats that improve HDL levels.
Seafood: Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, and halibut supply Omega-3 fats, which support heart health and reduce heart attack risk. Aim for two servings weekly, or consider fish oil supplements. Flaxseed and hemp are alternative Omega-3 sources.
Olive Oil: A staple of the Mediterranean diet, olive oil contains unsaturated fats that boost HDL and protect against cardiovascular disease.
Avocado: Rich in heart-healthy fats, use avocado as a spread or substitute for margarine in your meals.
Oatmeal: High in soluble fiber, oatmeal is excellent for improving HDL levels and overall heart health.
Complement diet improvements with regular physical activity. Exercise, especially cardio, for at least 30 minutes five times a week helps raise HDL levels. Maintaining an active lifestyle is crucial for long-term cardiovascular health.
Monitor your cholesterol regularly and adopt these healthy habits to keep your heart strong and functioning optimally.