Effective Strategies for Managing Osteoarthritis
Discover effective strategies for managing osteoarthritis, including early symptom recognition, lifestyle changes, dietary recommendations, and treatment options. Learn how to minimize joint pain, improve mobility, and maintain better quality of life with proactive care and medical support.
Sponsored

How to Handle Osteoarthritis Effectively
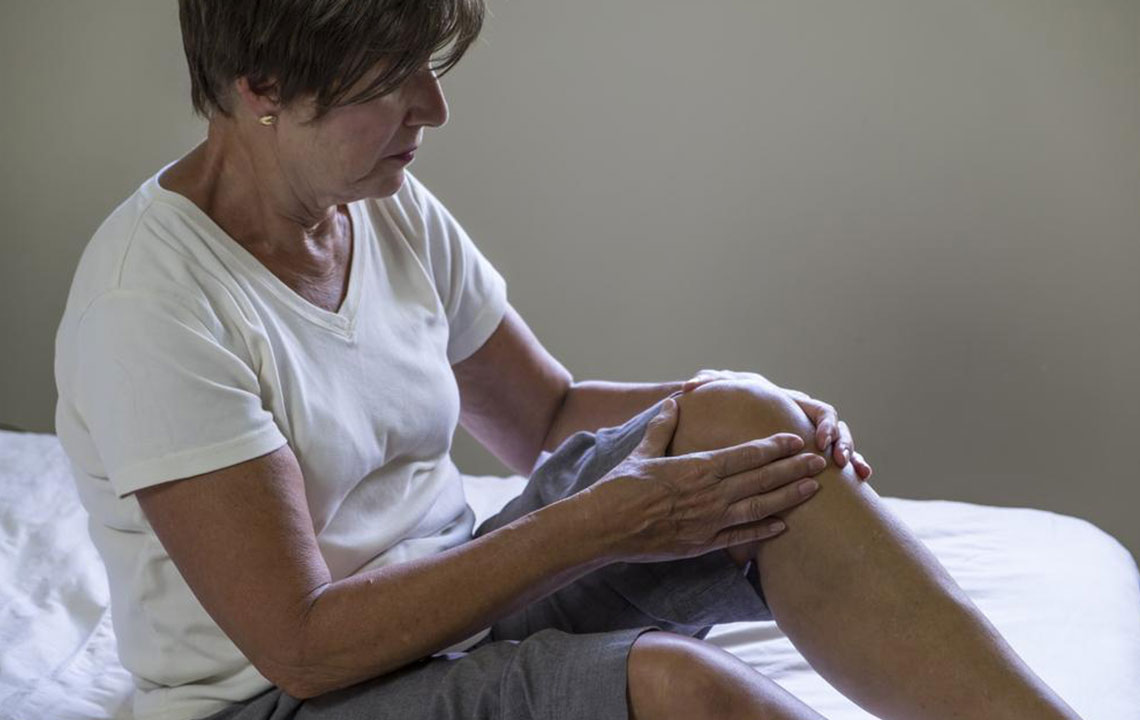
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a persistent joint condition impacting over 27 million individuals nationwide. It primarily affects joints like hips, knees, fingers, neck, lower back, and toes. Unlike autoimmune arthritis, OA results from cartilage degeneration—the cushioning tissue between bones. When cartilage wears down, it causes pain, stiffness, and potential joint damage. Early detection and proactive care are essential for better management. With medical support and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can reduce symptoms and improve joint function.
Learn about osteoarthritis symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive tips to maintain joint health.
How Is Osteoarthritis Recognized?
Signs vary depending on affected joints but commonly include:
Persistent pain and stiffness after inactivity or sleep
Swelling around the joints (mild to moderate)
Crepitus or snapping sounds when moving joints
These symptoms can hinder daily activities, making early identification crucial for effective management.
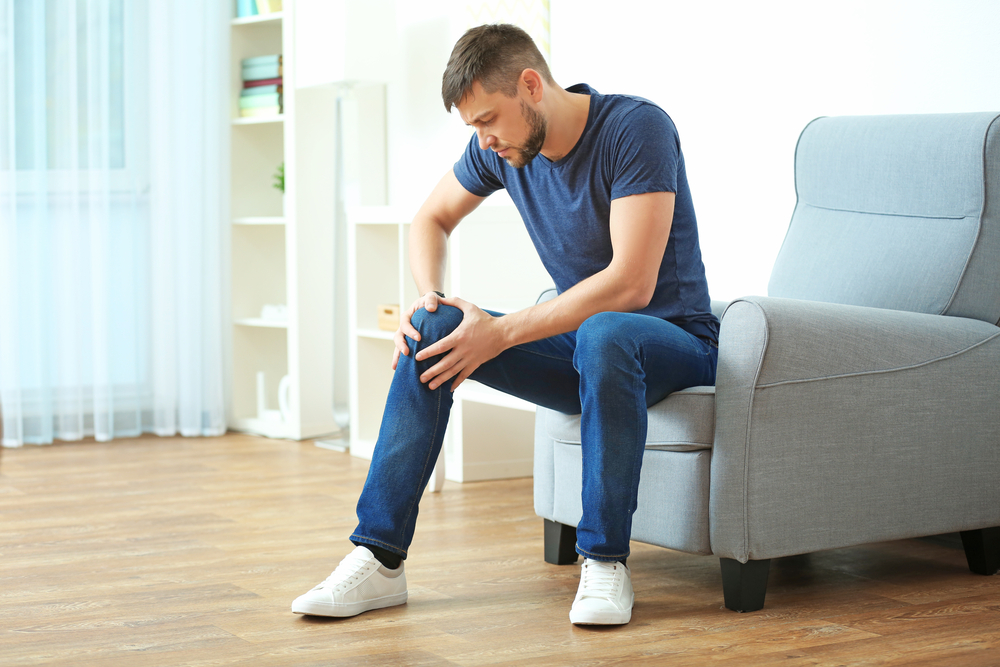
What Are the Main Causes of Osteoarthritis?
While aging-related cartilage wear is typical, other factors contribute, such as:
Overweight or obesity, increasing joint stress and inflammation
Genetic predispositions affecting cartilage development
Joint injuries from accidents, surgeries, or ligament tears
Repetitive activities like heavy lifting or prolonged standing
Recognizing these risks can help in early intervention and prevention strategies.
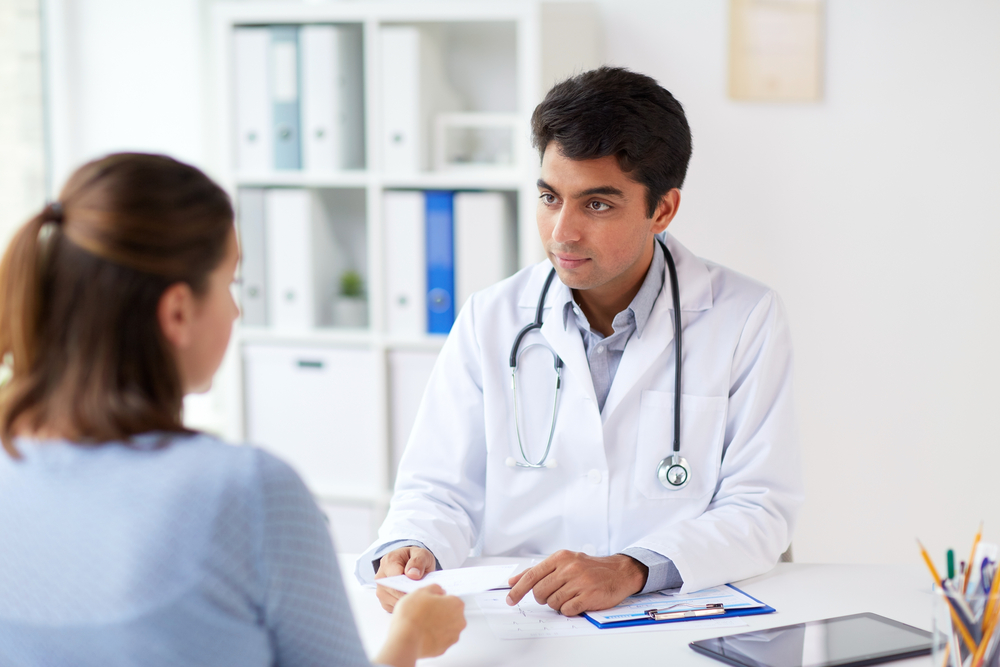
How Is Osteoarthritis Diagnosed?
Healthcare professionals use a combination of methods, including:
Detailed symptom review—onset, frequency, associated health issues
Medical and family history assessment
Physical examinations to identify pain points and swelling
Imaging tests such as X-rays and MRIs to detect joint changes
Joint fluid analysis for inflammation markers
These steps help confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment planning.
Available Medical Treatments for Osteoarthritis
Although OA cannot be cured, various therapies can alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
NSAIDs—Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen to reduce pain and swelling
Corticosteroid injections to control inflammation
Analgesics—Pain relief medications
Hyaluronic acid injections to restore joint lubrication
In severe cases, procedures like joint surgery or supportive devices such as braces and canes may be recommended.
Diet and Lifestyle Tips to Combat Osteoarthritis
Incorporating specific foods can support joint health, including fatty fish, nuts, ginger, turmeric, green tea, and vitamin C-rich fruits. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in gentle exercises, and applying hot or cold packs can also ease symptoms. Natural therapies such as massage, hydrotherapy, and relaxation techniques can further aid in joint comfort and mobility.