Understanding and Managing Elevated Cholesterol Levels
Manage high cholesterol by understanding its causes and adopting lifestyle changes. Eating a heart-friendly diet, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce risks of cardiovascular diseases. Regular screening is crucial as high cholesterol often lacks symptoms. Take charge of your heart health today.
Sponsored

Cholesterol plays a vital role in body functions but can be harmful if excessive. While necessary for cell structure, hormone production, and vitamin D synthesis, too much cholesterol can lead to serious health issues like heart disease. Cholesterol resides in every cell and aids digestion through bile acids.
Key functions include:
Building cell membranes
Generating digestive bile acids
Assisting in vitamin D synthesis
Supporting hormone production
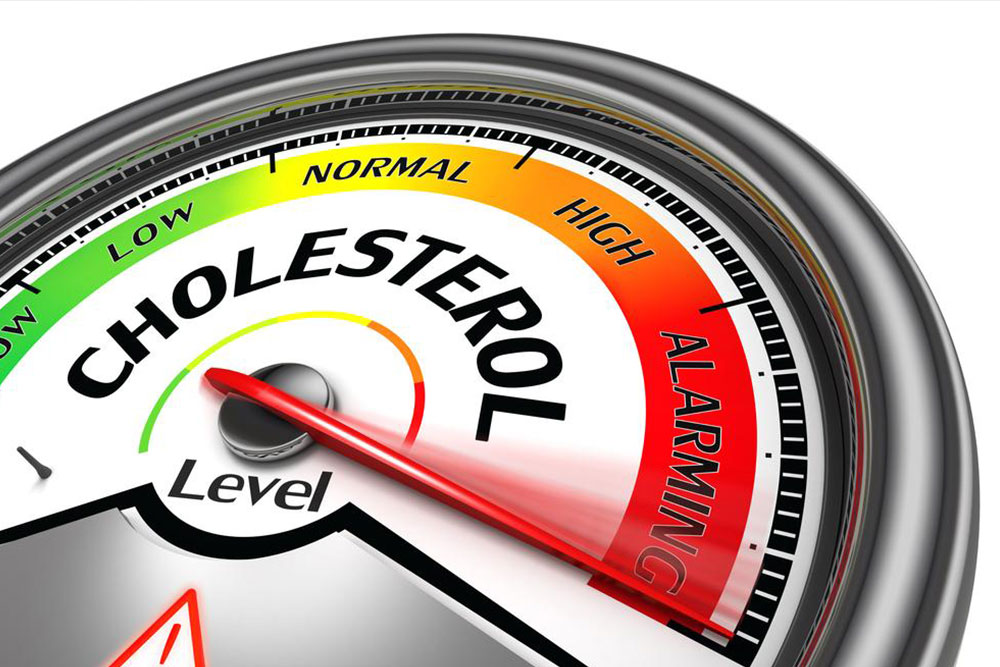
Cholesterol is transported via lipoproteins, mainly LDL (bad cholesterol) and HDL (good cholesterol). Elevated LDL levels can clog arteries, increasing heart attack risk, while HDL helps remove excess cholesterol from the blood.
Factors contributing to high cholesterol include:
Saturated and trans fats consumption
Smoking, which damages blood vessels and promotes plaque formation
Physical inactivity
Obesity and excess body weight
High cholesterol often shows no symptoms, making regular blood tests essential for detection.
To lower cholesterol levels and promote cardiovascular health:
Eat a heart-healthy diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while avoiding saturated fats
Engage in regular physical activity
Avoid smoking entirely
Maintain a healthy weight
Adopt a balanced lifestyle for overall well-being