Understanding Urine Color Indicators and Their Health Implications
Learn how to interpret urine color changes and what they reveal about your health. Recognizing signs of dehydration, infections, or organ issues can enable early intervention. The article explains normal and abnormal urine colors, their causes, and when to seek medical advice, emphasizing the importance of urine monitoring for overall well-being.
Sponsored

Decoding Your Urine Color and What It Reveals About Your Health
Deciphering Urine Colors and Their Significance
Urine, as the body's waste excretory fluid, contains byproducts like urea, creatinine, and uric acid. Its typical hue ranges from light yellow to darker shades, influenced by hydration levels and health status. Monitoring urine color can serve as a helpful health indicator, offering early signs of potential issues before symptoms become severe. Abnormal colors may signal dehydration, liver issues, infections, or other conditions. If persistent unusual coloration occurs, consulting a healthcare professional is advised. Using a urine color chart can assist in initial self-assessment.
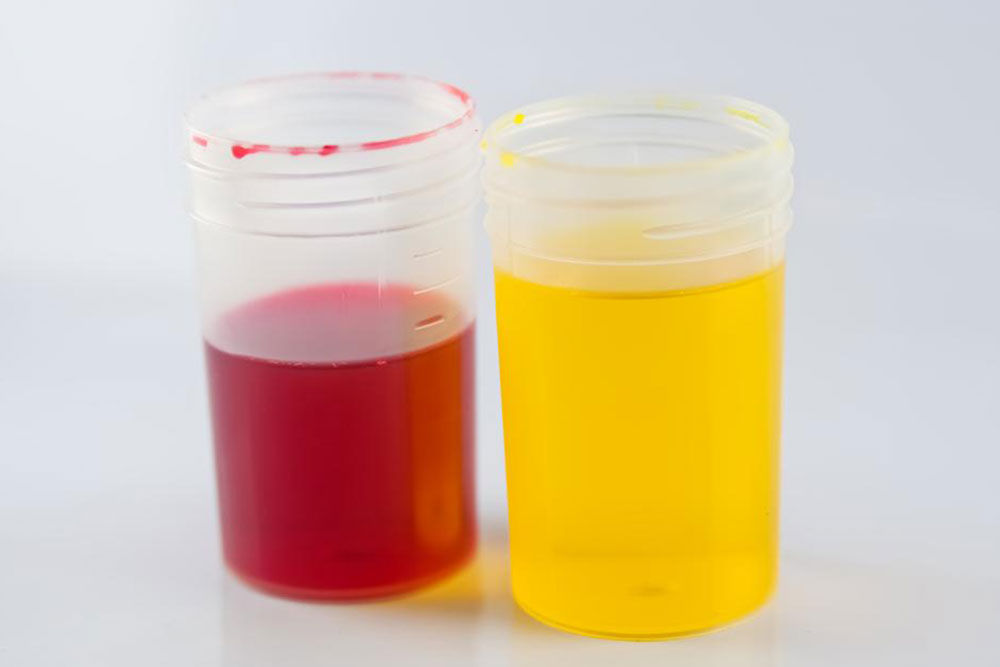
Color changes in urine often reflect underlying health states, especially when imbalances or organ dysfunctions start showing signs through excretory products. Many overlook these early signals, delaying diagnosis. Monitoring urine color can help identify issues early, prompting timely medical intervention. For example, pale yellow indicates hydration, while dark yellow suggests dehydration. Orange may point to liver concerns or medication effects, and green could imply infections or dietary factors. Sudden red or pink hues warrant medical review for blood presence, potentially linked to infections or menstruation. Aside from color, factors like odor, consistency, and foaminess provide additional health clues.
Clear or pale yellow urine indicates high water intake; restrict fluids accordingly.
Normal light yellow suggests optimal hydration and health.
Dark yellow signals dehydration; increase fluid consumption.
Orange hue may suggest liver problems or medication effects.
Green can imply food dye influence or bacterial infections.
Red or pink urine requires medical assessment for blood indications.
Monitoring urine color helps detect health issues early. If unusual colors persist, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation. Remember, factors like odor, consistency, and frequency also reveal important health information. Staying hydrated, maintaining good hygiene, and observing your body's signals are key to urinary health.