Monitoring Blood Glucose Trends for Better Health
This article emphasizes the importance of tracking and managing blood glucose levels through charts for optimal health. It highlights how fluctuating blood sugar impacts overall wellbeing, especially for diabetics. Regular monitoring with proper lifestyle adjustments can prevent complications, ensuring better long-term health outcomes.
Sponsored
Blood glucose levels reflect the amount of sugar present in a person's bloodstream at any given moment. The glucose is delivered to body cells to supply energy for various bodily functions. Our diet provides the primary source of this sugar, which is then regulated by our body's systems to prevent excessive highs or lows. The key form of sugar in blood is glucose, distinct from dietary sucrose.
Blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day, typically lowest before breakfast and rising after meals before stabilizing. In healthy individuals, fasting blood sugar remains below 99 mg/dL, whereas diabetics often experience greater variability. The goal is to keep pre-meal levels under 130 mg/dL and post-meal levels below 180 mg/dL.
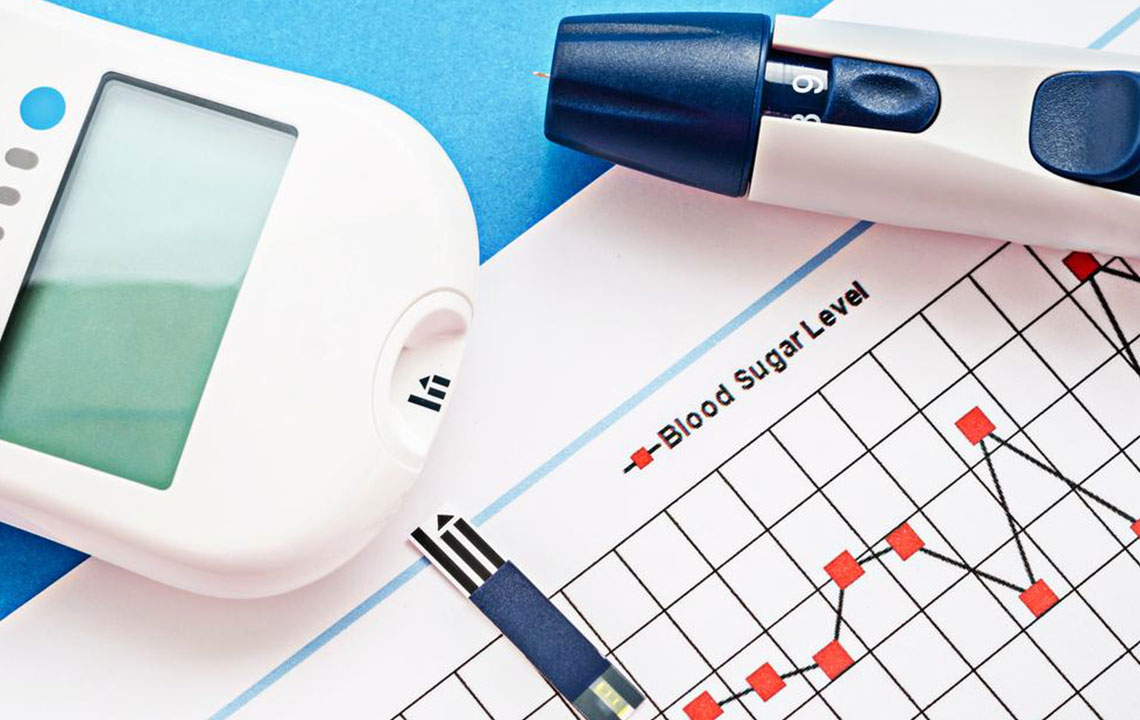
A blood glucose chart tracks the changing levels of blood sugar over a day. These graphs are crucial for managing diabetes and maintaining health. Blood sugar isn't static but varies naturally throughout the day, influenced by meals, activity, and other factors.
Maintaining consistent glucose levels is essential, much like monitoring blood pressure or cholesterol. Regularly recording your blood sugar helps detect sudden changes that could impact kidney function, vision, or heart health. Diabetics should monitor their levels frequently to stay within safe limits and prevent complications.
Why Tracking Blood Glucose Levels Is Vital
Monitoring blood sugar provides insights into overall health and helps identify abnormalities. Both healthy individuals and those with diabetes should keep records to avoid health issues. Uncontrolled blood sugar can lead to organ damage, affecting kidney health, eyesight, and heart function.
For diabetics, consistent tracking helps prevent dangerous spikes or drops, facilitating better management and reducing risk of future health problems. Devices for measuring blood sugar are available, but consulting a healthcare professional for proper use is essential.
Components and Usage of Blood Glucose Charts
Blood glucose charts typically include fasting measurements and post-meal levels. Comparing these with recommended ranges offers insight into current health status. Normal fasting blood sugar is less than 100 mg/dL, and post-meal levels should be under 140 mg/dL.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels depends on a balanced lifestyle, including nutritious eating, regular physical activity like walking or jogging, adequate sleep, and stress management. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol also contributes to better glucose control.