Everything You Should Know About Excessive Tear Production
Discover comprehensive insights into excessive tearing, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Learn how to manage this common eye condition effectively to maintain healthy vision and comfort. Whether caused by allergies, infections, or structural issues, understanding these aspects helps in seeking timely care and relief.
Sponsored
Key Insights on Excessive Tear Production
Our eyes are highly sensitive organs that require careful care. Even minor irritations can cause significant discomfort and interfere with daily activities. One common eye issue is excessive tearing, which can stem from various causes. Although allergies are the primary reason, other factors can contribute. Understanding these causes and symptoms is essential for proper treatment and eye health maintenance.
What Leads to Excessive Tearing?
Allergic conjunctivitis and infectious conjunctivitis are among the most frequent culprits behind watery eyes.
Symptoms of the common cold often include watery eyes.
Corneal issues, such as abrasions, can also trigger excessive tearing.
Scleritis, a serious eye inflammation, may cause tearing as well.
Conditions like allergic rhinitis and internal eyelid sty infections are other common causes.
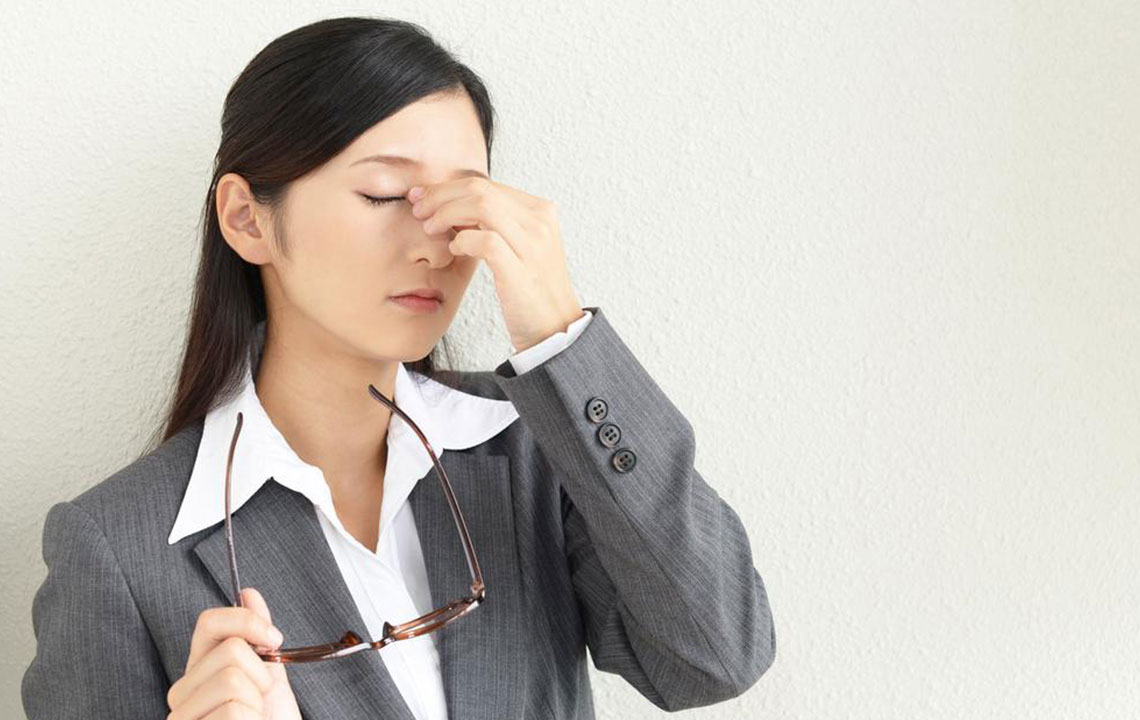
Overuse of electronic devices can strain the eyes, leading to increased tearing.
Additional causes include chalazion formation, cluster headaches, and reactive arthritis.
When Is Tearing Concerning?
Excessive tearing becomes problematic when it’s accompanied by abnormal tear rates or other symptoms.
While tears are vital for keeping the eyes moist and healthy, imbalance indicates an underlying issue.
The tear-producing glands located above the eyes are responsible for this natural process.
These tears drain via small ducts into the nasal cavity, maintaining eye health.
Blockages in these tear ducts can cause a buildup of tears, leading to inflammation and infections.
Such blockages might occur in the eyelid tear duct, the duct at the eyelid margin, or within the nasal duct, warranting medical attention.
Signs of a Tearing Problem
While some tearing is normal, persistent or excessive tearing alongside other symptoms indicates a potential health issue.
If vision sharpness declines or pain accompanies tearing, consult an eye specialist.
Swollen or red eyes, twitching, or the sensation of having a foreign object also signal concern.
Persistent redness and discomfort need professional evaluation.
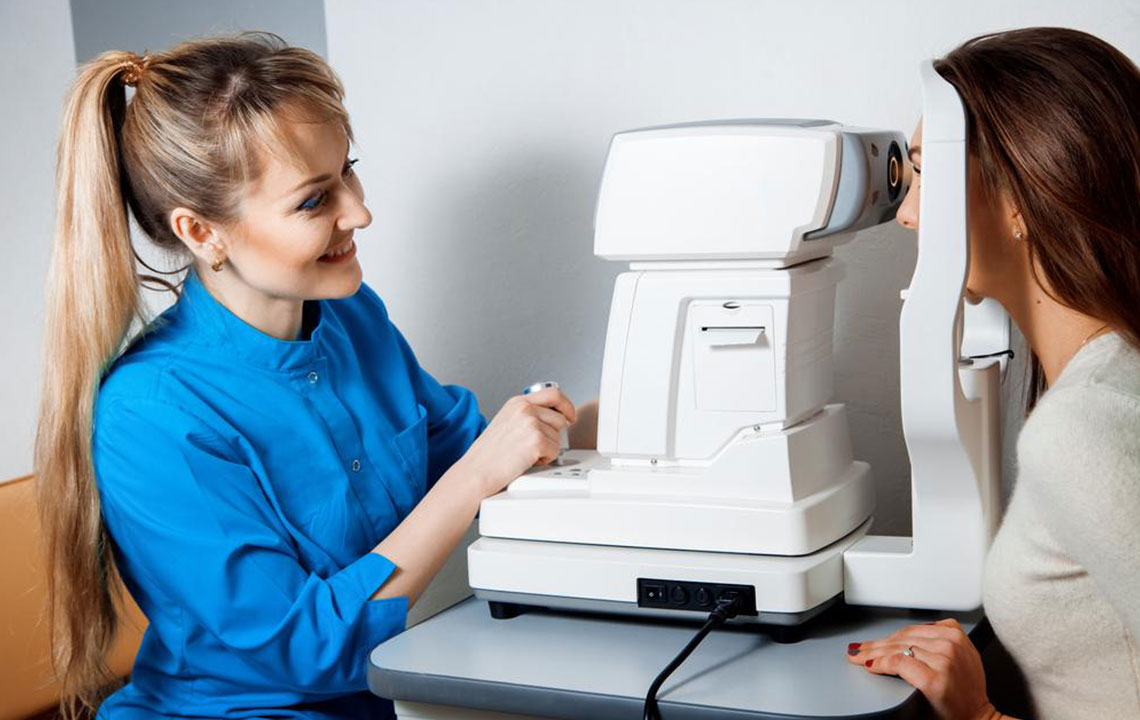
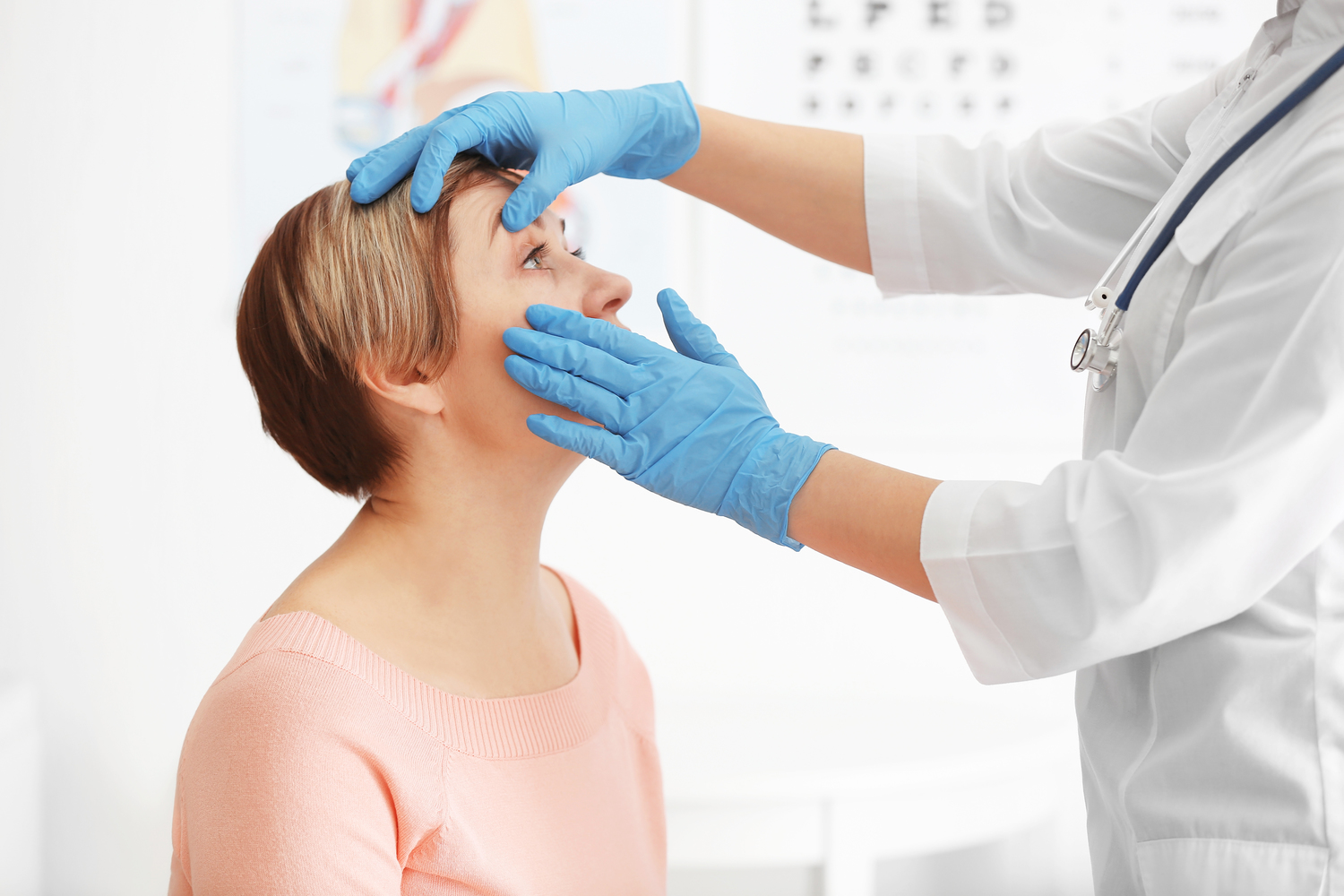
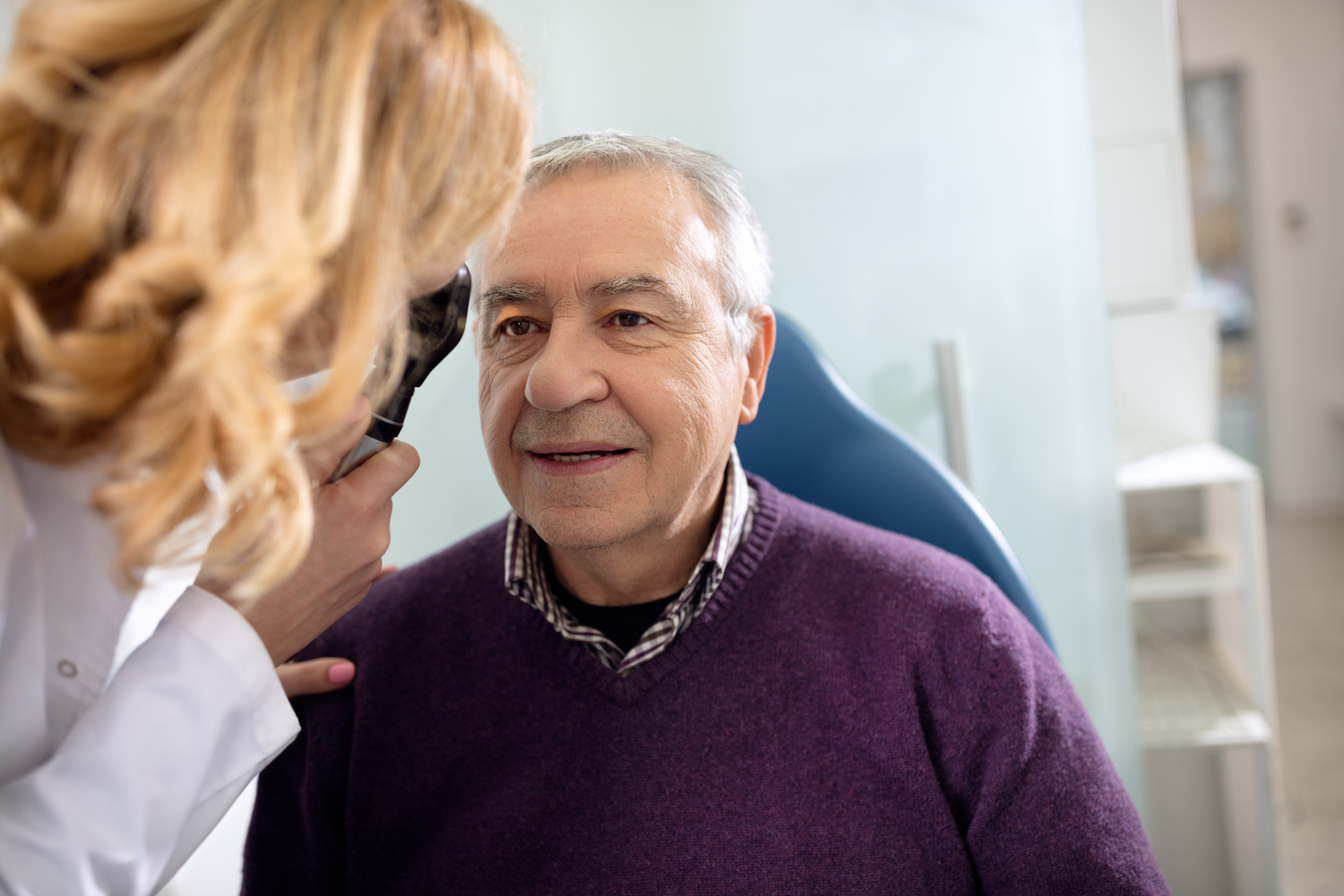
Diagnosing Excessive Tear Production
This condition, also called epiphora, is diagnosable through simple examination.
The ophthalmologist assesses symptoms and may perform diagnostic tests to identify causes.
In some cases, numbing drops are used during examination to evaluate the eye’s response.
Probe insertion into tear channels helps detect blockages, guiding treatment options.
Treatment Strategies
Treatment varies depending on the root cause.
For irritation, doctors may recommend observation and antibiotics if needed.
In cases like inward-growing eyelashes (trichiasis), removal can resolve tearing.
Procedures such as eyelid correction (ectropion) may be necessary in some cases.
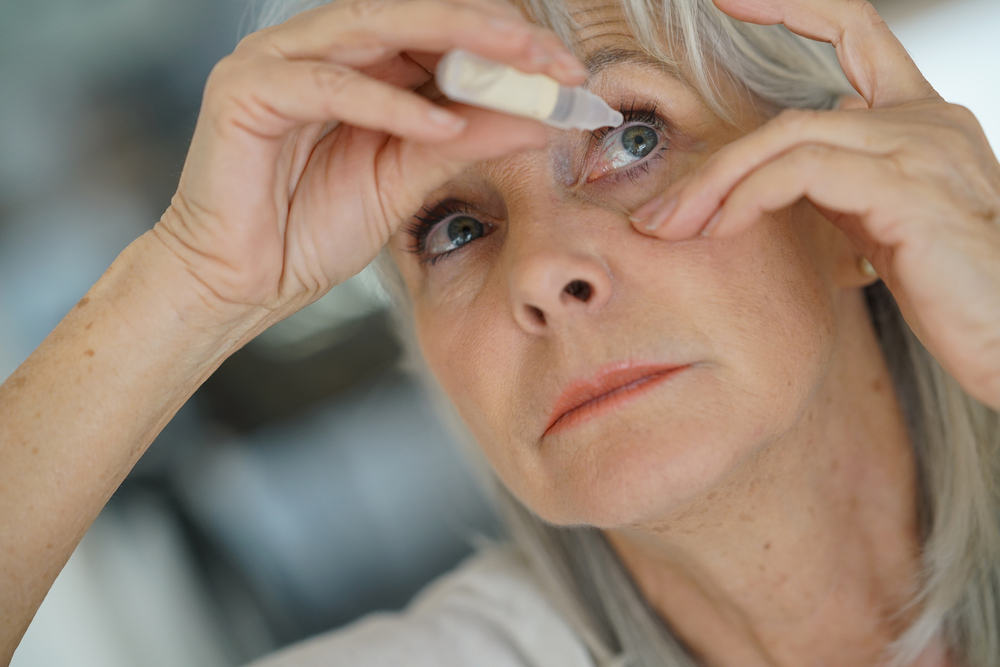
Blocked tear ducts can be addressed with surgery or medicated drops to unblock channels.
Simple home remedies include applying a warm, damp cloth over closed eyes for relief.
Managing allergy-related tearing requires accurate diagnosis to effective treatment promptly, ensuring optimal eye health.