Understanding How Kidney Health Affects Lower Back Discomfort
This article explores the link between lower back pain and kidney health, highlighting common conditions like kidney stones, infections, tumors, and infarction. Recognizing these signs allows for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. Understanding symptoms and treatment options helps in managing kidney-related issues that contribute to lower back discomfort, emphasizing the importance of medical consultation to prevent complications.
Sponsored
Connection Between Kidney Health and Lower Back Pain
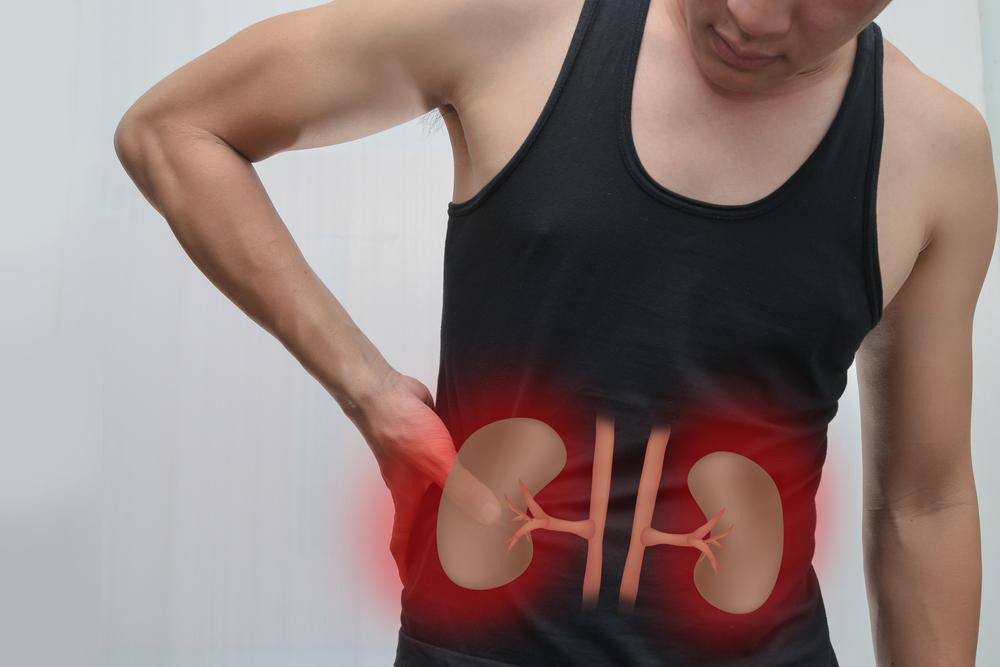
The kidneys are essential bean-shaped organs located on each side of the body in vertebrates. They perform vital functions including filtering blood to produce urine, regulating water and salt balance, hormone production, waste elimination, and controlling blood pressure.
Issues such as kidney stones, infections, tumors, or cysts can impair kidney function, sometimes causing pain in the lower back or abdomen. Recognizing that lower back pain may be linked to kidney conditions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Lower Back Discomfort and Kidney Disorders
The region between the ribs and hips, known as the flank, can be a site of pain associated with kidney issues. Several kidney-related conditions that may cause lower back symptoms are explained below.
1. Kidney Stones: These small, crystal-like formations develop in the kidneys and often cause intense, persistent pain that can radiate towards the groin. The pain might appear as waves or constant sharp sensations.
Kidney stones can result from dietary habits or genetic factors. Small stones may pass unnoticed via urine, but larger stones could require medical intervention such as lithotripsy. Pain relief medications like Ibuprofen or Tylenol may be prescribed.
Self-care tips for kidney stones include:
• Drink plenty of water.
• Limit intake of oxalate-rich foods like spinach and beets.
• Consume a diet of healthy homemade meals.
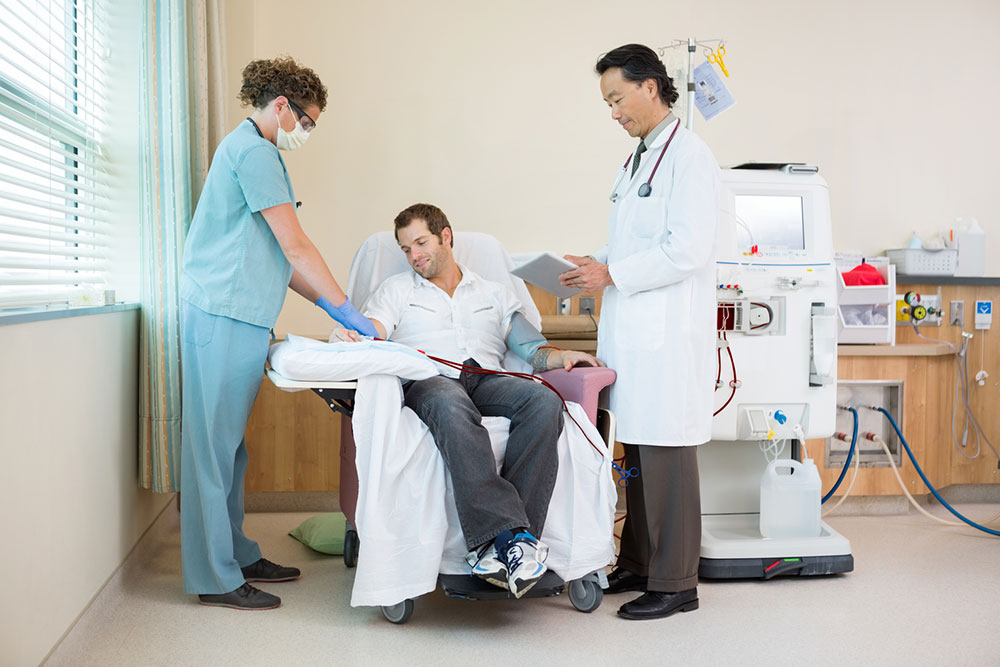
2. Kidney Infections: Pyelonephritis occurs when bacteria, mainly E.coli, infect the kidney through the urinary tract. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is essential. Severe cases may require hospitalization and IV antibiotics.
To alleviate back pain from kidney infections:
• Use heat packets on the affected area.
• Stay well-hydrated.
• Avoid alcohol and caffeine.
3. Kidney Cancer: Also called renal cell carcinoma, is prevalent in adults, with Wilms’ tumor affecting children more often. Causes include aging, obesity, smoking, high blood pressure, and genetic predispositions.
Persistent sharp pain under the ribs may indicate kidney cancer. Treatment options include:
• Nephrectomy: Complete removal of the affected kidney.
• Partial Nephrectomy: Removing just the tumor and part of the kidney to preserve function.
Other therapies involve:
• Cryoablation: Destroying cancer cells with extreme cold.
• Radiofrequency Ablation: Applying heat to eliminate cancer cells.
• Immunotherapy: Boosting the immune system to fight cancer.
• Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells.
• Targeted Therapy: Using drugs to specifically block cancer growth.
4. Renal Infarction: A condition where blood flow to the kidney is obstructed, leading to tissue death. It can cause severe flank pain and should not be mistaken for typical back pain.
Treatment strategies include:
• Pain management with opioids.
• Surgical procedures like angioplasty or embolectomy.
• Use of anti-inflammatory medications.
Seek specialist advice from a nephrologist for appropriate management of these conditions.