Effective Strategies for Managing Kidney Pain Causes
Learn about various causes of kidney pain and the appropriate treatment options. Early diagnosis is vital for effective management. Treatments include medications, surgical procedures, and non-invasive techniques tailored to the underlying condition, such as infections, stones, or blockages. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures correct diagnosis and optimal care to prevent complications and restore kidney health.
Sponsored
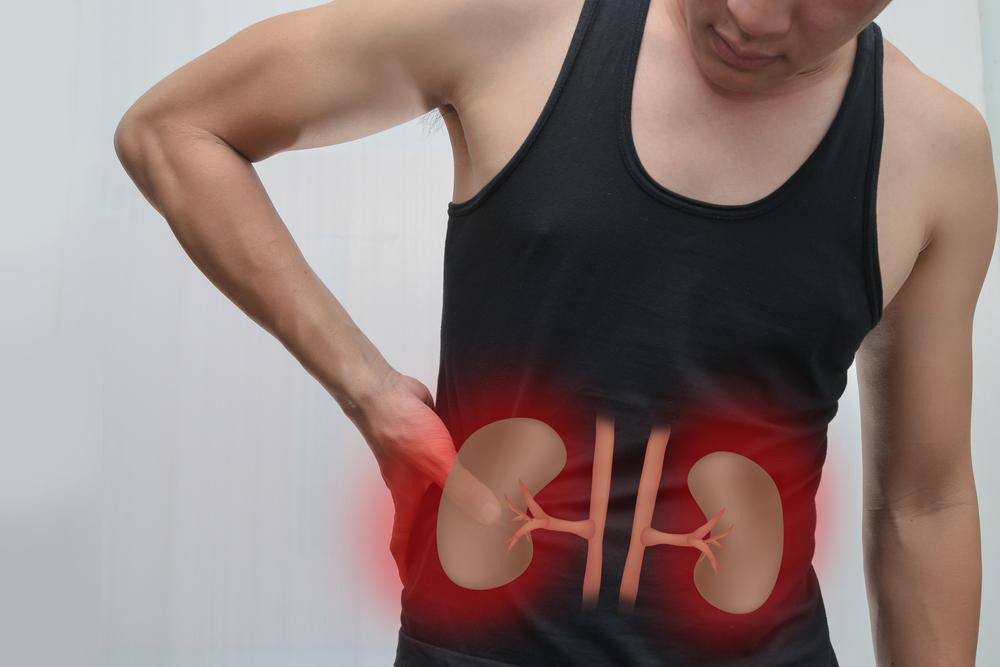
Kidney discomfort is typically felt as an ache around the upper abdomen, near the kidneys, which are situated in the upper part of the abdomen. Unlike lower back pain, this pain can sometimes radiate to the groin or flanks. Several factors can lead to kidney pain, and accurate diagnosis is essential for proper treatment.
Main causes of kidney pain:
Kidney infections
Hydronephrosis, which is swelling caused by urine buildup due to blockages
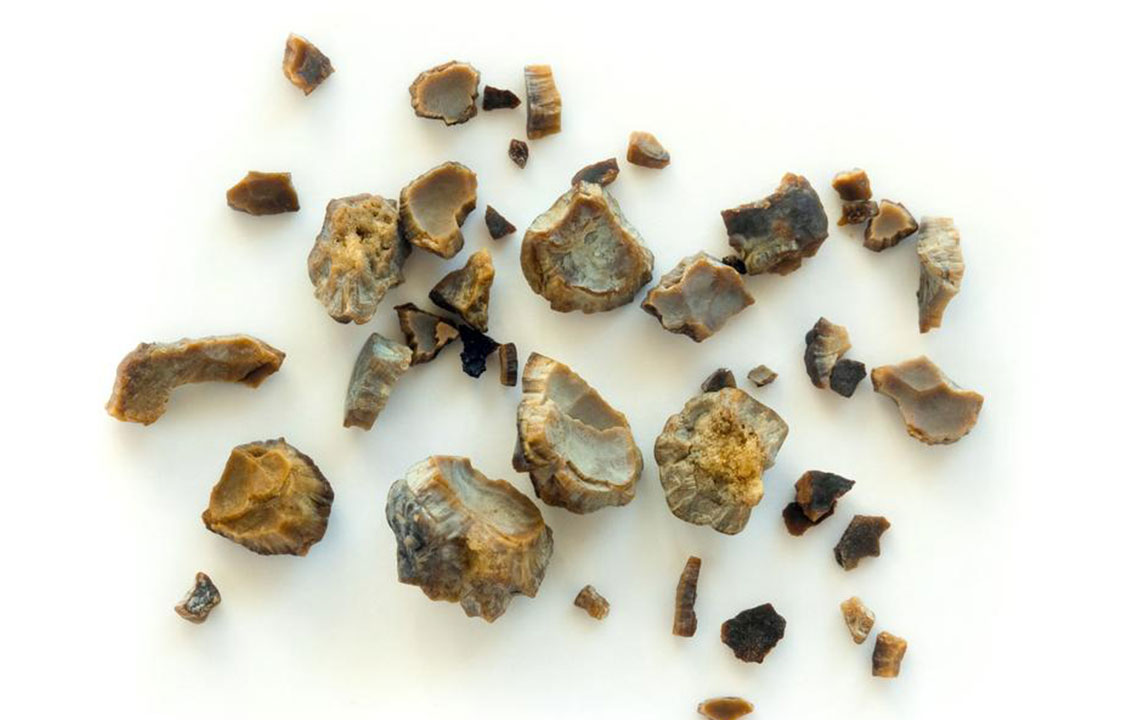
Kidney stones
Polycystic kidney disease
Bleeding within the kidney
Hemorrhage in kidney veins
Kidney cyst formation
Kidney tumors or malignancies
Identifying the cause involves a thorough review of your medical history, physical examination, and possibly laboratory tests like blood and urine analysis. Advanced imaging such as CT scans or MRIs may be used for precise diagnosis. Early detection is key to preventing complications, and treatment strategies vary based on the specific condition.
For instance, kidney infections are primarily treated with antibiotics. Mild cases might see symptom relief within days, while severe infections could require hospital-administered antibiotics. Persistent infections may necessitate specialist intervention or surgical procedures.
Hydronephrosis treatment aims to eliminate the obstruction causing urine backflow and kidney swelling. Approaches include inserting stents to unblock ureters or surgery to remove blood clots or scar tissue.
Kidney stones' management depends on their size and type. Small stones often pass naturally with hydration and pain relief, whereas larger stones may need procedures like shockwave lithotripsy, surgical removal, or endoscopic extraction to prevent kidney damage and recurrent infections.