Understanding Jock Itch: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Strategies
Jock itch is a contagious fungal infection affecting the groin area, characterized by itchy, ring-shaped rashes and irritation. It spreads through contact with infected surfaces or persons and thrives in warm, moist environments. Preventative measures like good hygiene, wearing loose clothing, and prompt treatment with antifungal remedies can effectively control and prevent this condition. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and risk factors helps in early detection and management, reducing discomfort and transmission.
Sponsored
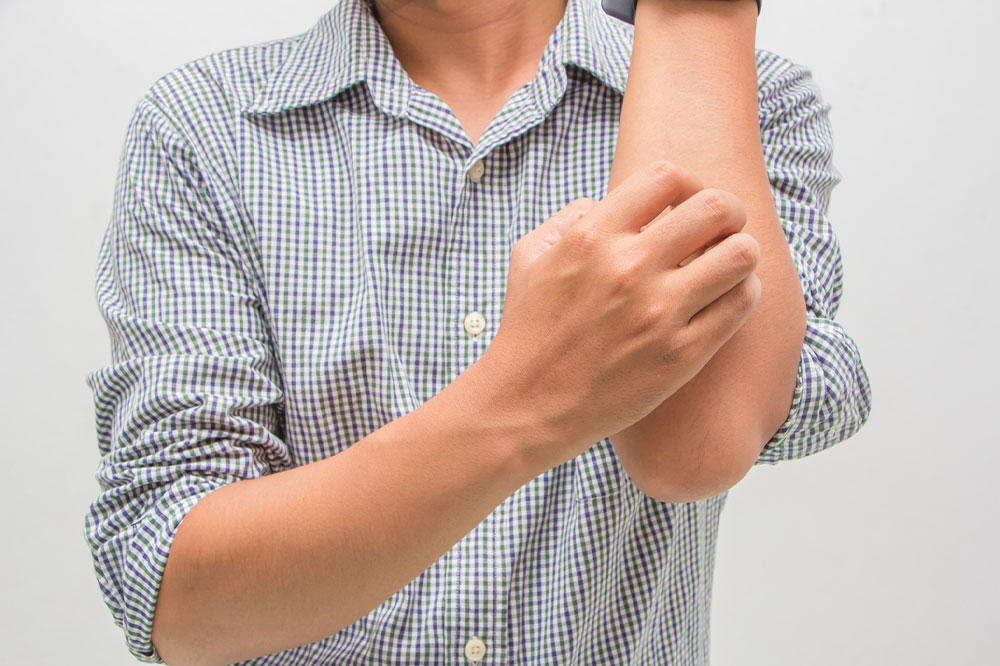

Jock itch, also known as tinea cruris, is a fungal infection that affects warm and moist areas like the groin. It causes a distinctive circular rash that often appears between the thigh and groin, sometimes extending upward. The infected skin may become irritated, flaky, and itchy. The same fungus responsible for athlete's foot can lead to this condition, making it highly contagious. Recognizing its symptoms early and understanding how it spreads are key to effective management and prevention.
Symptoms
Signs of jock itch usually appear within 4 to 14 days after contact with the fungus. The rash often takes a half-moon shape and may feature a ring of tiny blisters along its border. The affected skin can feel irritated, flaky, or scaly, with some patches being red, bumpy, or prone to blistering and oozing. Sometimes, the skin around these patches becomes darker or lighter, and scarring may occur in persistent cases.
Jock itch commonly manifests as a ring-shaped rash that may extend to the upper thighs. The borders are usually well-defined, and the skin around the affected area may display abnormal pigmentation. It is characterized by intense itching and discomfort, especially in humid conditions.
Causes
This fungal condition thrives in environments that are warm, moist, and crowded. The fungus behind jock itch is contagious, spreading through direct skin contact or contaminated items like towels and clothing. It often originates from athlete's foot and can transfer from the feet to the groin, especially if tight clothing traps sweat and moisture against the skin.
Transmission occurs through skin-to-skin contact, sharing of infected clothing or towels, or sexual activity. Wearing tight clothes or clothing that doesn't allow the skin to breathe can facilitate fungal growth and spread. To prevent transmission, wearing socks before underwear and maintaining good hygiene are recommended. Using antifungal creams can also help limit the spread.
Risk Factors
Men are more susceptible to jock itch than women. Overweight individuals, those who sweat excessively, and teenagers are at higher risk due to increased skin folds and moisture retention. Wearing tight clothing, having a weakened immune system, or having diabetes can also increase vulnerability to this fungal infection.
Diagnosis usually involves a physical exam by a healthcare provider, who may take skin scrapings for laboratory testing to confirm a fungal infection. Additional tests like skin cultures or specialized stains such as PAS can help differentiate it from other skin conditions.
Prevention Tips
Keep the groin area dry by thoroughly drying after bathing or exercising.
Change underwear daily and more frequently if sweating heavily.
Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing to reduce moisture build-up.
Never share towels, clothing, or personal items to prevent spreading.
Address athlete's foot promptly to avoid spreading the fungus to the groin area.
Treatment Options
Topical antifungal creams, gels, powders, or sprays are most effective in treating jock itch. Applying these medications directly to the affected area usually yields rapid relief. Severe cases or recurring infections might require oral antifungal medications, but these should be used cautiously under medical supervision due to potential side effects like nausea or liver issues.