Understanding Common Yeast Infection Sites and Treatments
This article explores various types of yeast infections, their common causes, affected body parts, and effective treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of hygiene, proper medication, and preventive measures, especially for vulnerable groups like diabetics and immunocompromised individuals. Understanding where and how yeast infections occur helps in early detection and management, ensuring better health outcomes.
Sponsored

Persistent moisture on the skin makes it susceptible to yeast infections. When the immune system weakens or cannot combat the fungi effectively, infections can develop. Individuals with diabetes or compromised immunity are at higher risk. Treatment often involves prescribed medications and topical creams.
Types and Prevention
Yeast infections can affect various body parts and areas:
Skin folds are common sites; applying miconazole cream helps treat extensive infections that may require medical prescription.
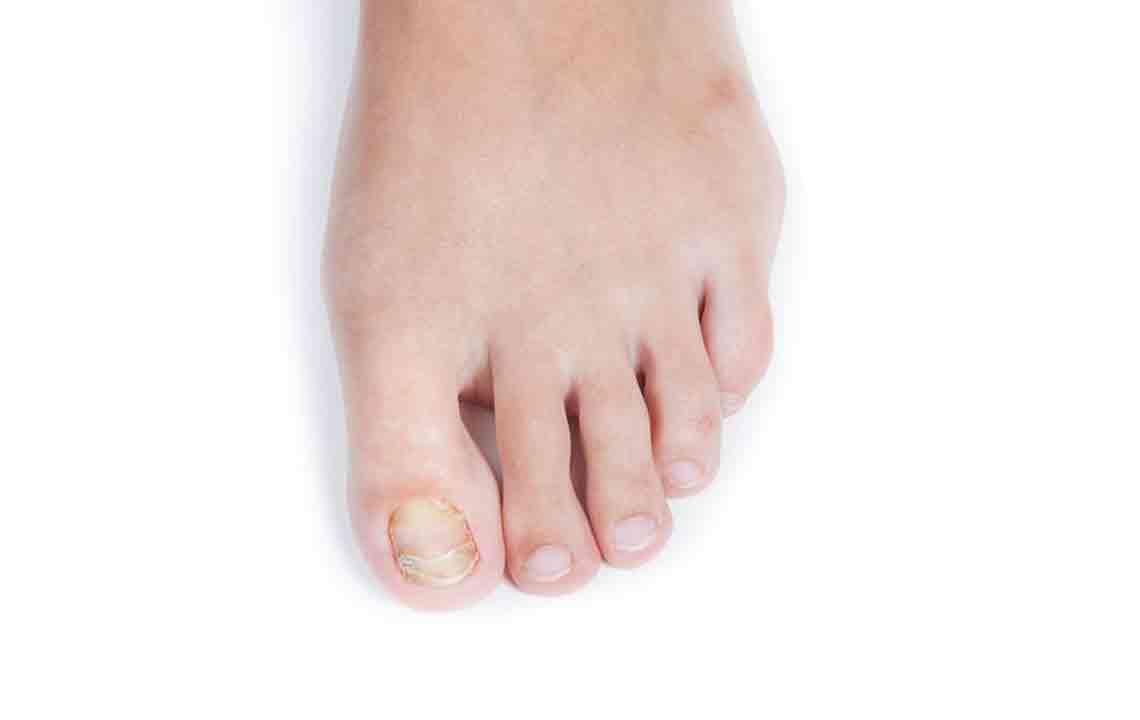
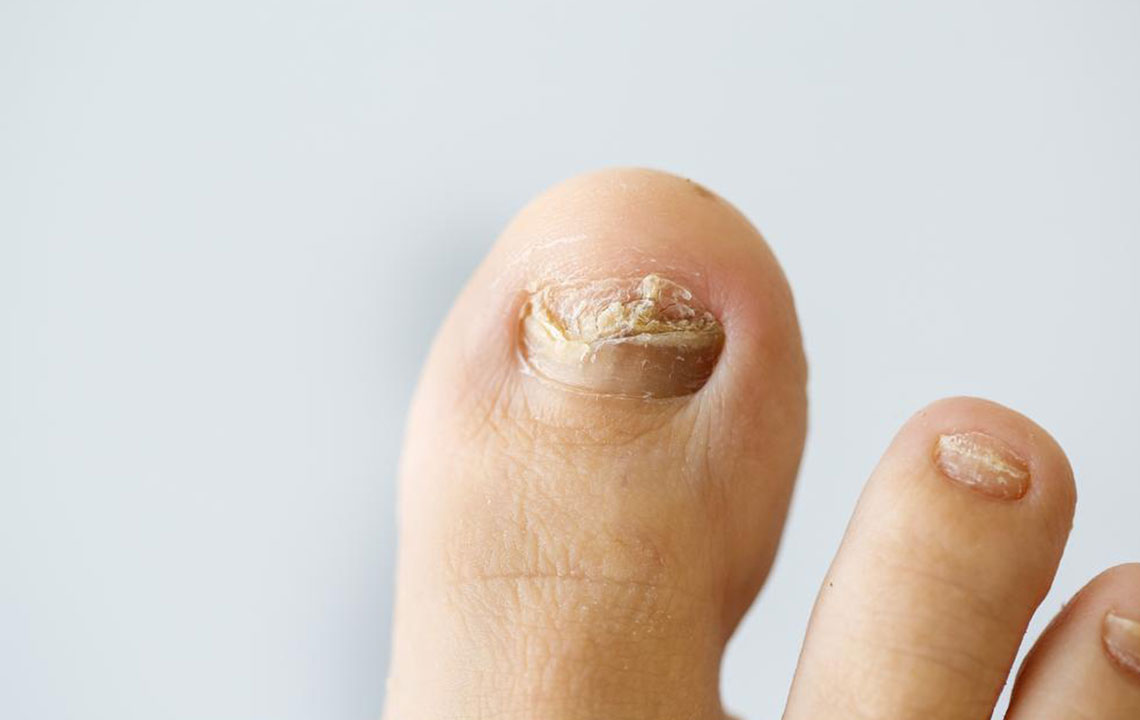
Fungal infections frequently occur on sweaty feet, which can be managed by keeping feet dry and clean. Over-the-counter antifungal creams are effective.
Babies can develop oral thrush from milk remaining in their mouths if they are bottle-fed improperly. Doctors usually prescribe oral medication until clear.
During breastfeeding, women might experience yeast infections due to moisture and pH changes, especially under the breasts. Maintaining hygiene and wearing breathable clothing helps prevent infections. Antifungal creams are typically used for treatment.
Immunocompromised individuals, such as chemotherapy patients or those with autoimmune conditions, are more prone to yeast infections in the throat.
Vaginal yeast infections are often linked to poor hygiene or contamination from fecal matter. Using antifungal creams like Monistat and completing a course of 3-7 days effectively clears the infection.
Antibiotic usage can disrupt normal bacterial flora, leading to increased risk. Taking fluconazole at the beginning and end of therapy helps prevent yeast overgrowth.
Yeast infections are not sexually transmitted and can occur regardless of sexual activity.