Managing Epilepsy with Ketogenic Nutrition Plans
This article explores how ketogenic diets can effectively help manage epilepsy, especially in patients unresponsive to medication. It details the diet's focus on high fats, moderate proteins, and low carbohydrates, along with practical food sources like dairy, nuts, and oils, essential for maintaining ketosis and controlling seizures. The content emphasizes optimal food choices and their nutritional benefits, providing valuable guidance for those considering a keto-based approach for epilepsy treatment.
Sponsored

Ketogenic approaches for epilepsy management
The ketogenic diet aims to induce a state called ketosis, a natural metabolic condition. This high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet encourages the body to utilize stored fats for energy instead of relying on glucose derived from carbs. Besides aiding weight loss, managing type 2 diabetes, and supporting cancer therapy, the ketogenic diet has demonstrated effectiveness in controlling epilepsy. It is mainly recommended for patients unresponsive to traditional anti-epileptic drugs. A typical ketogenic diet emphasizes increased fat intake, moderate protein, and minimal carbohydrates.
Consume foods rich in healthy fats, moderate proteins, and minimal carbs. Below are key macronutrients in the keto diet and their roles:
Fats (lipids)
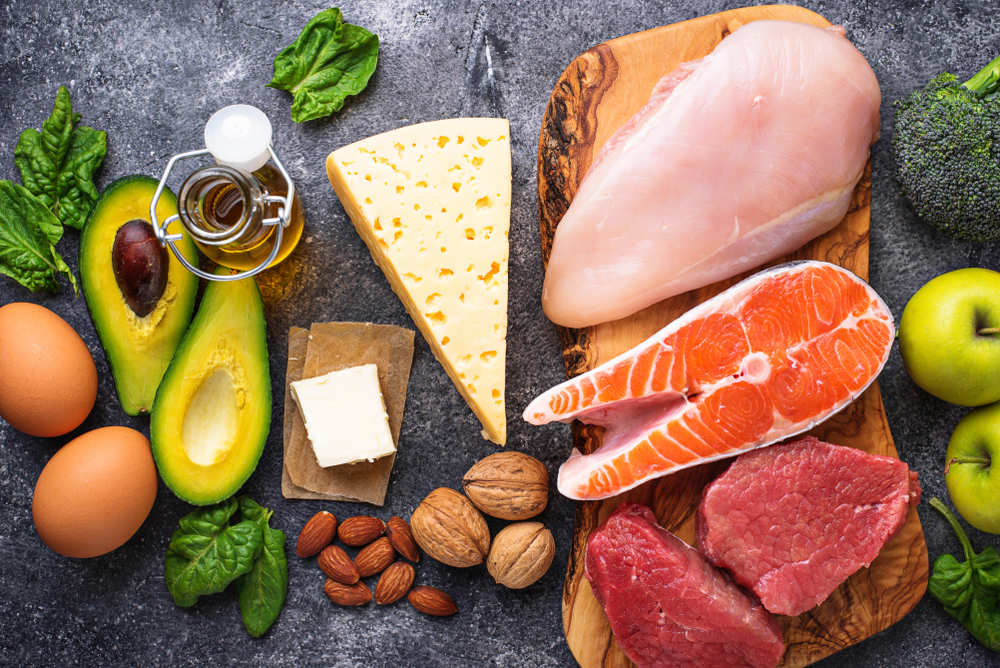
Fats are abundant in oils, oily fish, nuts, and seeds. High-fat dairy products like butter, cheeses, and coconut oil are also included. Fats are essential for cell health, especially those forming the myelin sheath that protects nerve fibers in the brain.
Proteins
Proteins supply vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, and amino acids. They help build muscles, support red blood cell production, hormones, enzymes, and boost immunity. Sources include dairy products, eggs, meats, fish, lentils, and beans.
Carbohydrates are the main energy source for the body. While fiber-rich, whole-food carbs are healthy, refined carbs and sugars are avoided. Starchy vegetables, fruits, grains, and legumes are primary carbohydrate sources.
The following foods provide guidance on suitable intake for an epilepsy-focused ketogenic diet:
Plain Greek yogurt and cottage cheese: High in protein with low carbs; 150 grams of Greek yogurt contain 11 grams of protein and 5 grams of carbs, while 100 grams of cottage cheese offer 18 grams of protein and 5 grams of carbs. They promote fullness and curtail appetite.
Butter and cream: Rich in healthy fats, these are nearly carb-free and ideal for keto diets centered on epilepsy management.
Olives and olive oil: Olive oil is high in beneficial fats and contains no carbs. Olives, depending on size, provide about 2 grams of carbs per 28 grams and are suitable for salads or dressings.
Nuts and seeds: Provide healthy fats with minimal carbs; for example, 28 grams of walnuts contain approximately 2 grams of carbs, whereas cashews have about 9 grams.
Unsweetened coffee and tea: Free of carbs, these beverages can enhance mental focus and physical energy while adhering to the diet. It's recommended to avoid added sugars.