Comprehensive Guide to Effective Gout Treatments and Medications
This article provides an in-depth overview of effective gout treatments, including medication options like NSAIDs, colchicine, corticosteroids, and uric acid-lowering drugs. It emphasizes the importance of lifestyle changes such as diet modification and weight management to prevent attacks and manage symptoms. Understanding both pharmacological and lifestyle strategies enables better control of gout, reducing pain and preventing joint damage for those affected by this common condition.
Sponsored

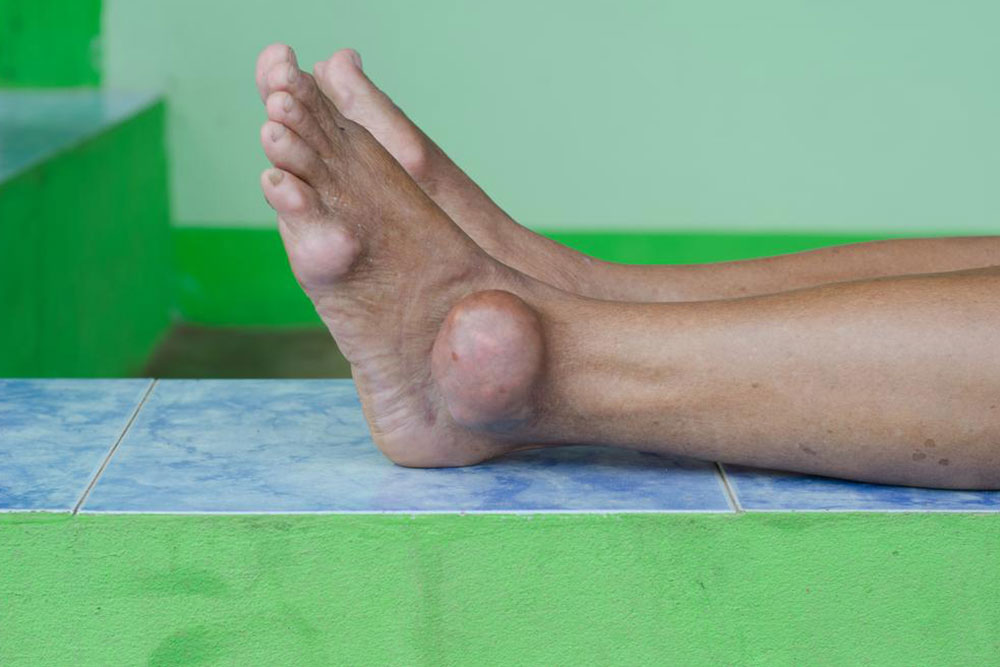
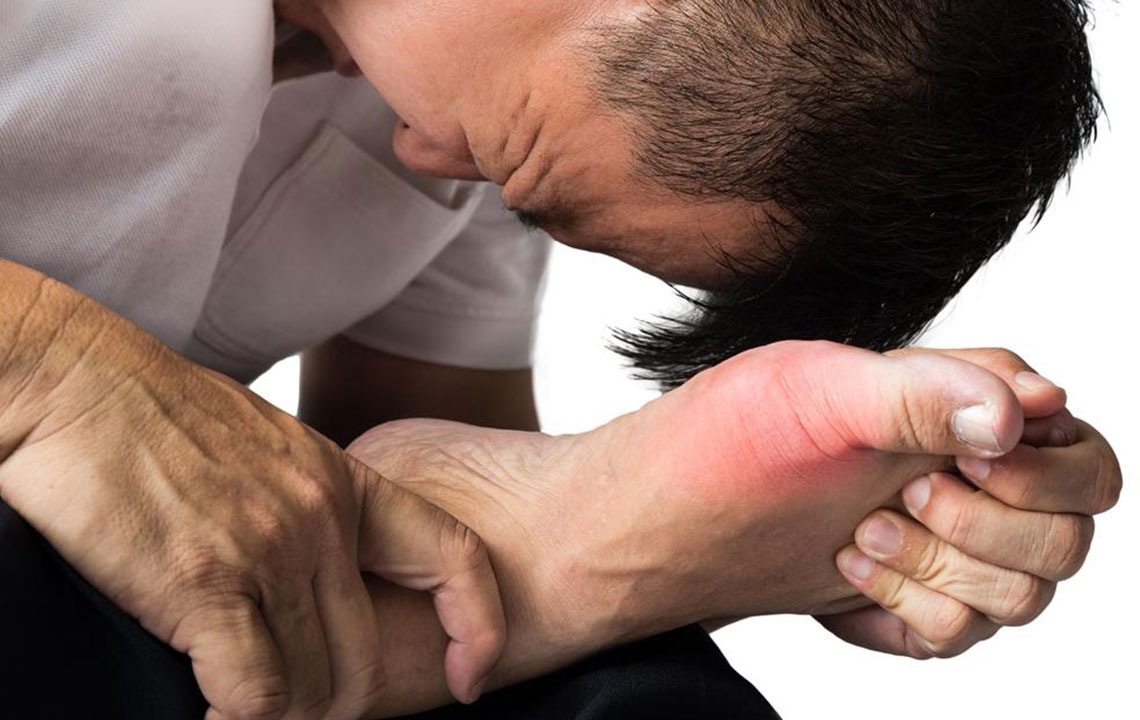
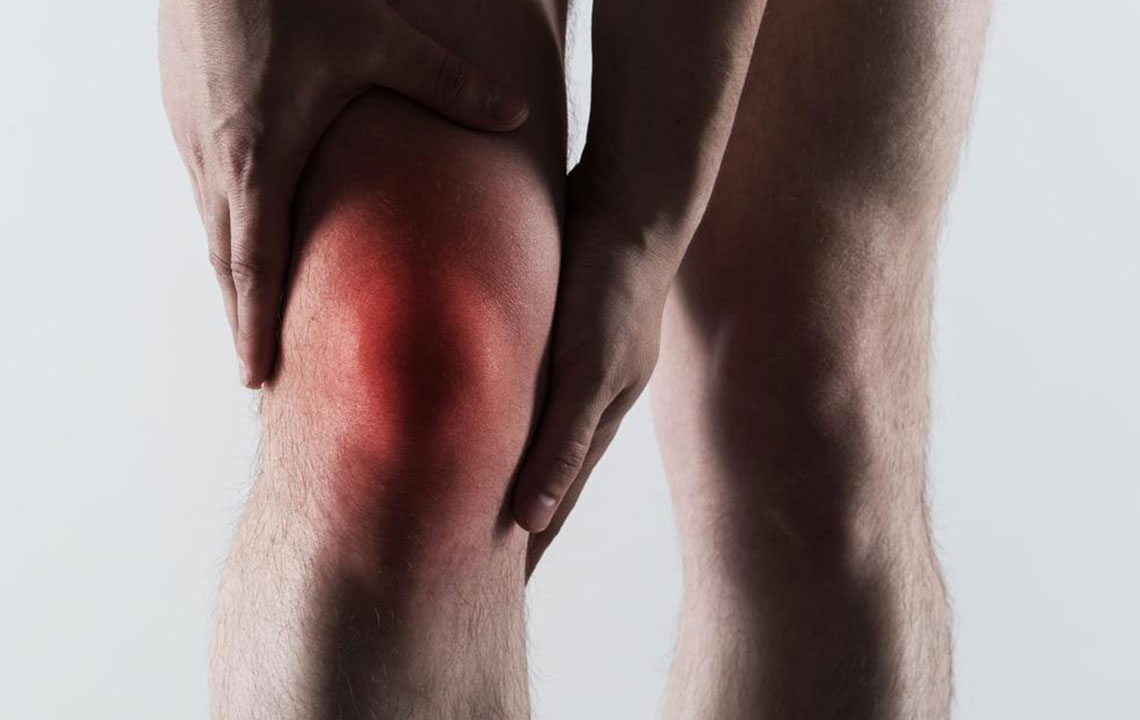
Gout is a sudden, painful form of arthritis characterized by inflammation and redness in the joints. It most often targets the big toe, affecting over half of cases, but can also involve elbows, knees, fingers, and other toes. The condition results from uric acid crystals accumulating in joints, caused by the body's inability to efficiently eliminate uric acid. Risk factors include high intake of red meat, seafood, alcohol, and certain genetic predispositions. Managing gout involves medication and lifestyle changes to reduce attacks, prevent joint damage, and control uric acid levels.
Initial treatments focus on reducing pain and inflammation through medications like NSAIDs, Colchicine, and corticosteroids. For long-term management, drugs such as Allopurinol and Febuxostat help lower uric acid production. Uric acid elimination can be enhanced with Probenecid. Lifestyle modifications—like weight management, dietary changes, and limiting alcohol—play a vital role in prevention. Proper medical therapy combined with healthy habits can significantly improve quality of life for gout sufferers.