Understanding the Causes and Remedies for Swollen Ankles
Explore the common causes of swollen ankles, including injuries, blood clots, pregnancy, and medical conditions. Learn effective, affordable treatment options such as exercise, compression therapy, and Epsom salt soaks to reduce swelling and discomfort. Seek medical advice for persistent or severe symptoms to ensure proper care and recovery.
Sponsored

Swelling in the ankles can occur due to multiple reasons. Typically, fluid retention causes swollen ankles, often accompanied by mild discomfort or pain, which can sometimes intensify. Underlying factors such as injuries or medical conditions may contribute to this issue. The following information covers common causes and effective treatment options for swollen ankles to help you manage this condition.
Main Causes of Swollen Ankles
Injury – Any trauma to the ankle or foot, including sprains, can result in swelling. Rest and avoiding unnecessary movement are crucial for recovery.
Applying an ice pack wrapped in a cloth for at least 30 minutes, elevating the foot on a pillow, and using compression bandages are recommended. Proper rest is essential to reduce swelling.
Blood Clots – Blood clots in leg veins can hinder blood flow, leading to ankle and foot swelling. Superficial clots occur just below the skin, whereas deep vein thrombosis (DVT) involves larger veins and can be life-threatening. If pain or fever occurs, immediate medical attention is necessary.
Pregnancy-Related Swelling – Mild swelling during pregnancy is normal; however, sudden or severe swelling accompanied by headaches, nausea, or vision problems might indicate pre-eclampsia, requiring urgent care.
Lymphoedema – This condition involves fluid buildup in tissues due to lymphatic system issues, often following cancer treatments that involve lymph node removal. Medical assessment is important if swelling persists post-treatment.
Infection – Ankle swelling may signal an infection, particularly in diabetics or those with nerve issues. Regular foot inspections and prompt treatment of sores or blisters are critical for diabetic patients.
Venous Insufficiency – When leg veins fail to circulate blood properly due to damaged valves, fluid leaks into surrounding tissues, causing swelling, skin changes, ulcers, and infections. Medical intervention is advised.
Heart, Kidney, or Liver Problems – Conditions like heart failure, kidney dysfunction, or liver issues can cause fluid buildup, leading to ankle swelling. Additional symptoms such as fatigue or weight gain should prompt a healthcare consultation.
Medication Side Effects – Certain drugs, including hormonal therapies, calcium channel blockers, and antidepressants, may cause fluid retention and swelling. Discuss any medication-related concerns with your doctor for possible adjustments.
Effective Treatments for Swollen Ankles
Physical Activity – Avoid prolonged sitting; instead, perform leg movements, ankle rotations, or engage in swimming and yoga. Elevating your legs and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce swelling.
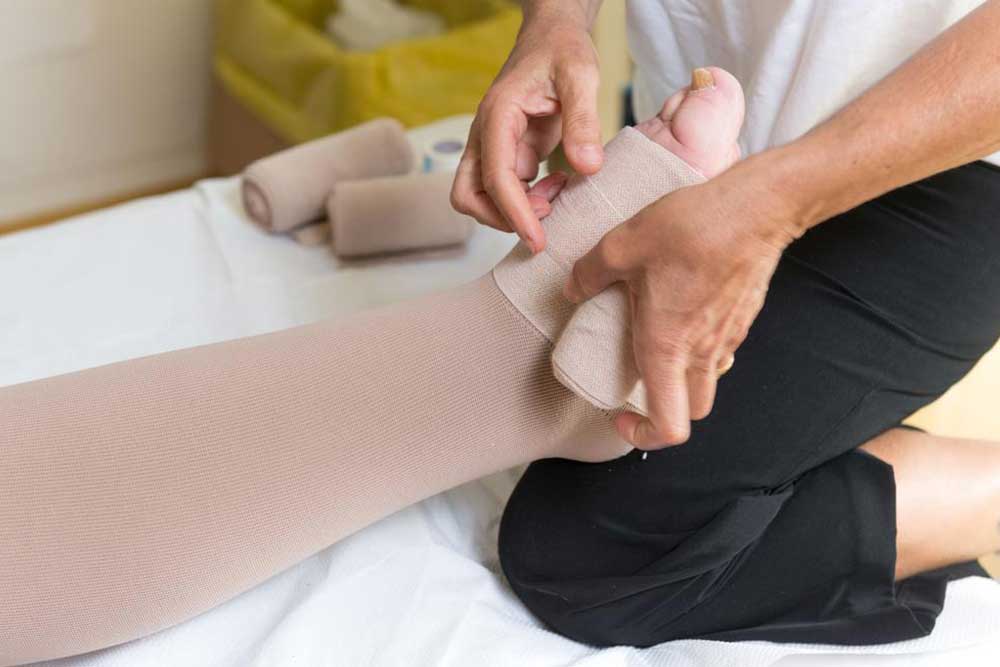
Compression Wear – Wearing compression socks helps improve circulation and prevents fluid accumulation, providing relief and preventing future swelling.
Magnesium Supplements – Consult your physician about taking magnesium supplements, which can help decrease water retention and improve symptoms.
Epsom Salt Baths – Soaking the feet and ankles in warm water with Epsom salt for about 30 minutes can alleviate pain and reduce swelling, thanks to its healing properties.
These cost-effective remedies can effectively manage swollen ankles and promote recovery. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment plans.