Understanding Arthritis: Stages, Diagnosis, and Preventive Measures
This article explores the various stages of arthritis, how it is diagnosed, and effective prevention methods. Understanding these aspects can help individuals manage or avoid joint issues through lifestyle choices and timely medical care. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and proactive strategies to maintain joint health.
Sponsored
Understanding Arthritis: Stages, Diagnosis, and Preventive Strategies
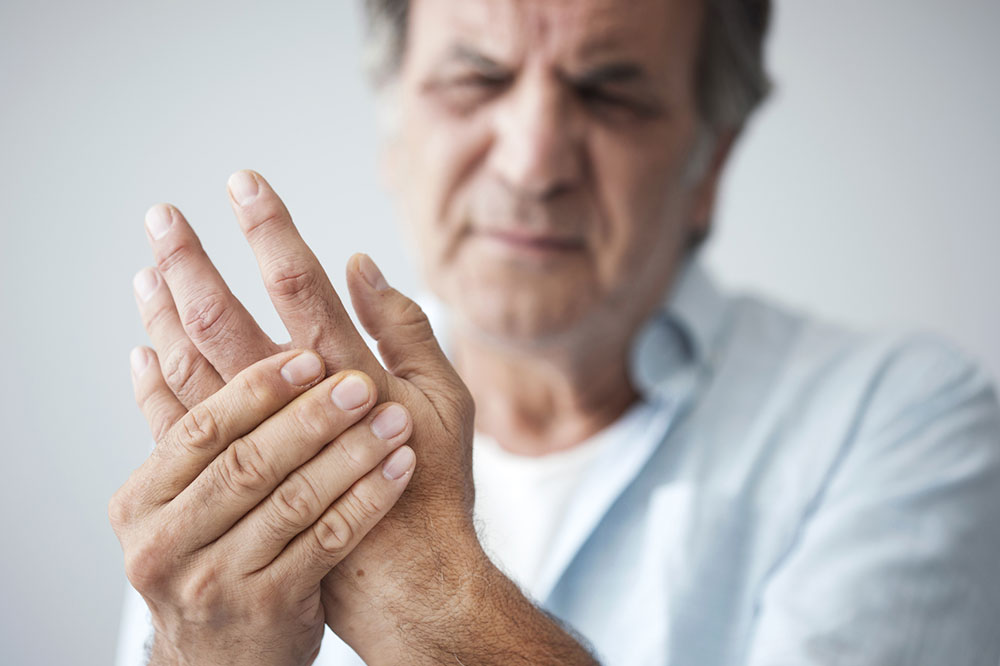
Arthritis refers to joint inflammation and includes over 200 different conditions affecting joints and surrounding tissues. The most prevalent form is osteoarthritis, but other types include gout, fibromyalgia, and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Common symptoms involve pain, swelling, stiffness, and discomfort around joints. Symptoms can appear suddenly or develop gradually and, in some cases, may involve the immune system or internal organs.
Multiple organs and systemic symptoms are linked to certain types like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
Stages of Arthritis
The progression of arthritis varies by type. Focusing on osteoarthritis, the most common variant, the stages are:
Stage 0
Normal joint function with no signs of arthritis; no treatment needed.
Stage 1
Minor bone spur formation without significant symptoms.
Stage 2
Early stage where bone spurs grow more, but cartilage remains unaffected; lifestyle adjustments may be helpful.
Stage 3
Moderate damage with narrowing joint space, potential pain, and possible corticosteroid treatment.
Stage 4
Severe degeneration with nearly absent cartilage, joint space reduced significantly, causing walking difficulties; surgical intervention might be necessary.
Diagnosing Arthritis
If you notice symptoms, consult a healthcare professional. They will examine the joints for fluid buildup and might perform imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans for an accurate diagnosis. Severe cases may involve a rheumatologist for expedited care.
Preventing Arthritis
Preventative steps include maintaining a healthy weight, consuming omega-3-rich foods such as fatty fish to reduce inflammation, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding joint injuries. These measures can help delay or prevent the onset of arthritis.