Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis
This comprehensive guide explains atopic dermatitis, its various forms, symptoms, and management strategies. Recognizing the signs early, especially in children, can improve outcomes. Learn about causes, types like contact, seborrheic, allergic, nummular, and stasis dermatitis, and when to seek medical help to control this chronic skin condition effectively.
Sponsored
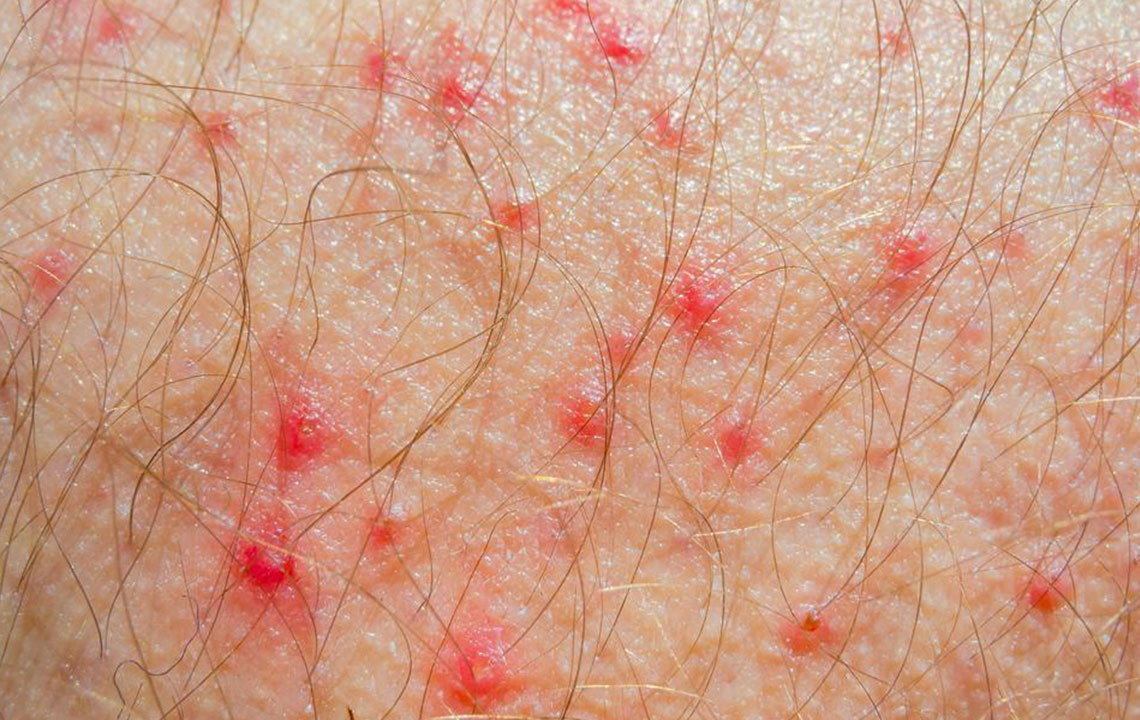
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Types, and Treatments
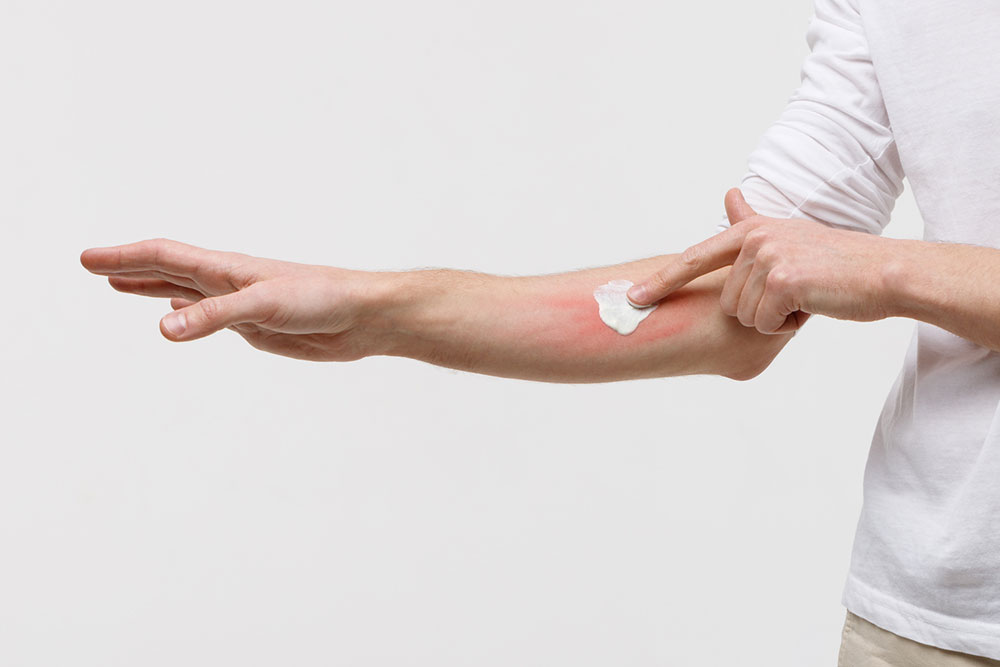
Atopic dermatitis, often called eczema, is a common skin condition primarily affecting children. It manifests as itchy, inflamed, and dry skin, frequently occurring in specific areas. While it cannot be cured completely, managing symptoms is possible through understanding its causes, types, and treatment options.
What is atopic dermatitis and its development?
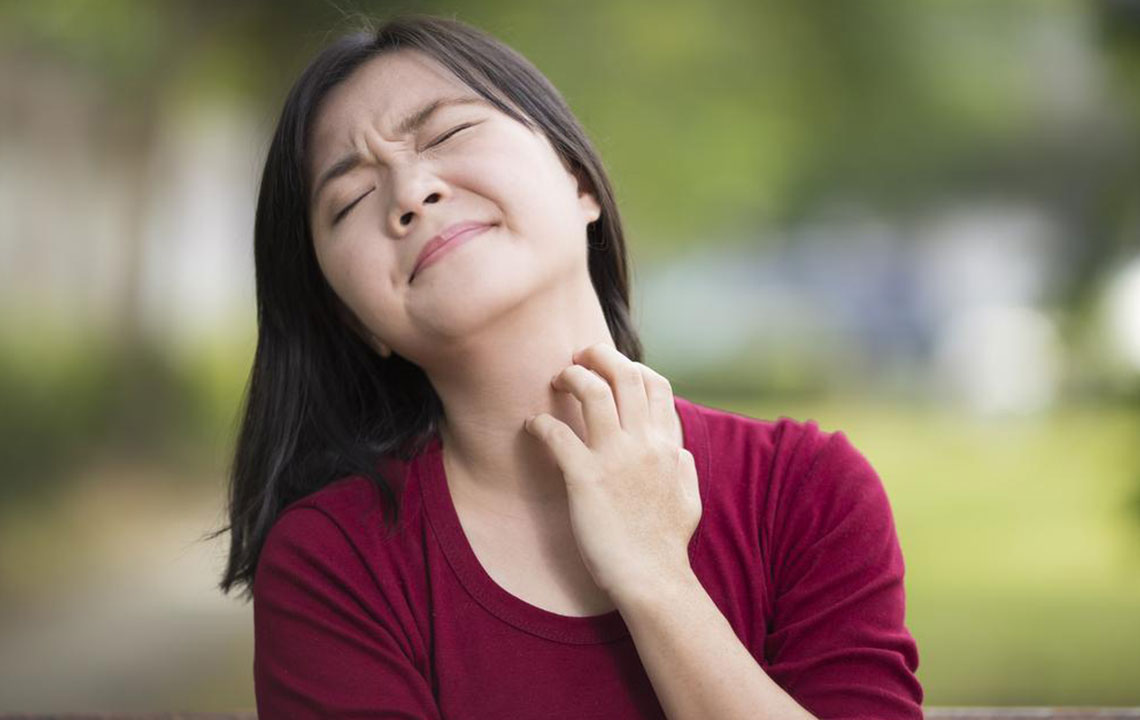
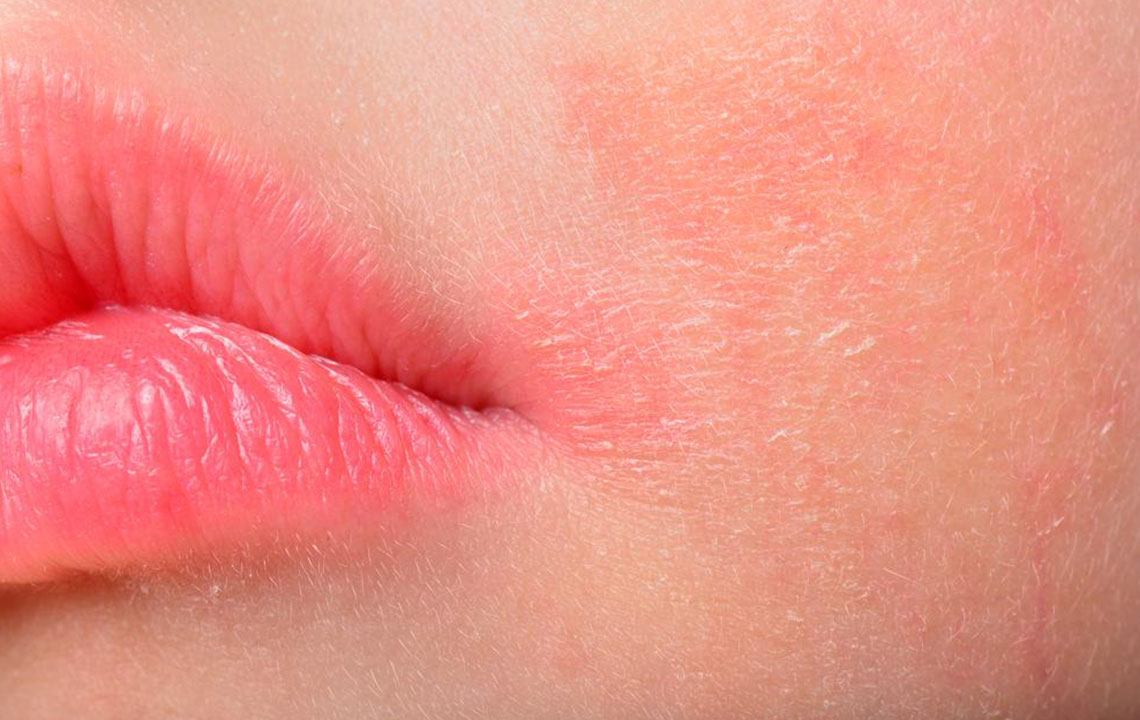
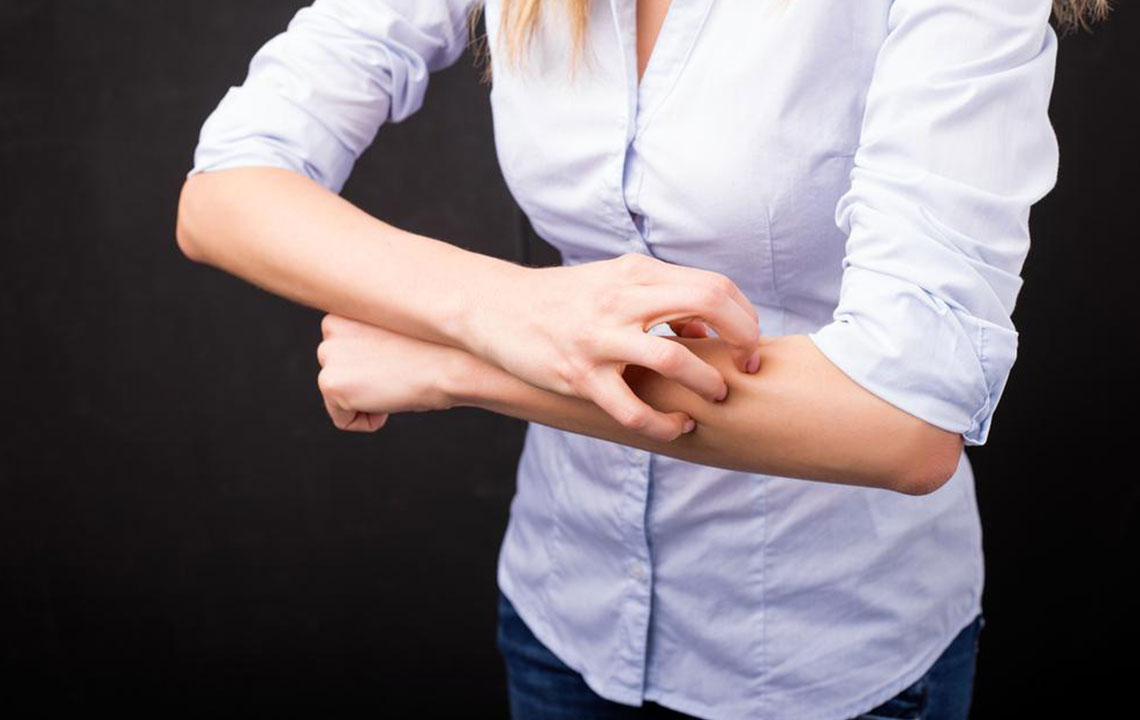
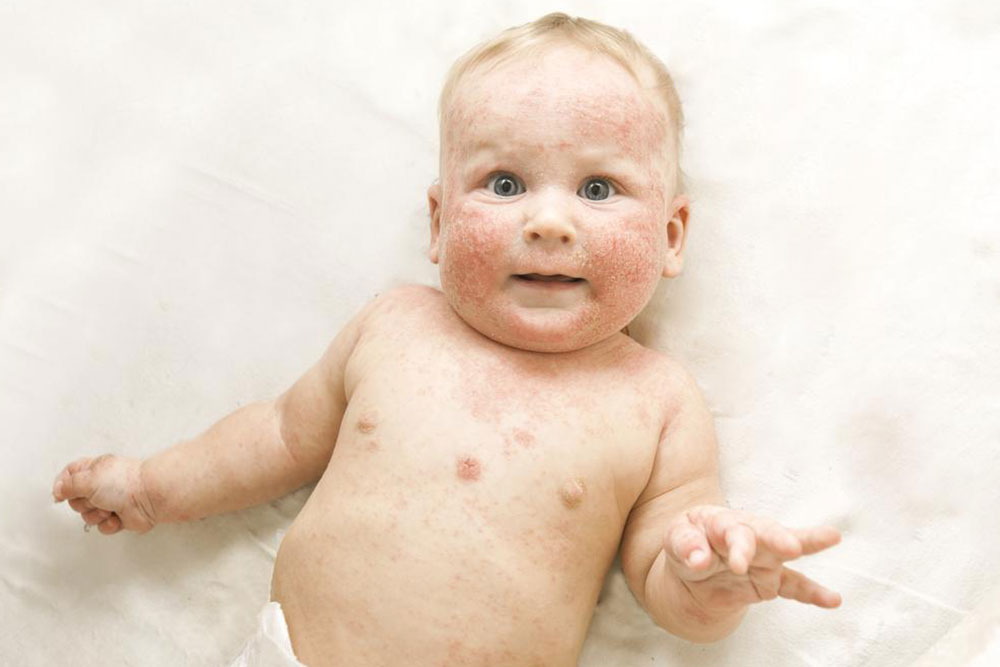
The skin develops extreme dryness, impairing its barrier function and ability to fight bacteria. This condition is linked to immune system irregularities, though its exact origin remains unknown. Symptoms include redness, itching, scaling, and cracking. Visual aids, like atopic dermatitis images, help in recognizing the disorder.
Different forms of atopic dermatitis include contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, nummular eczema, and stasis dermatitis. Contact dermatitis arises from skin contact with irritating or allergenic substances, causing flaky, leathery skin and painful blisters. Seborrheic dermatitis, possibly related to stress or genetics, appears as itchy, reddish patches on areas like the chest or behind the ears. Allergic atopic dermatitis results from specific allergies, such as poison ivy exposure, with corresponding rashes. Nummular eczema, characterized by coin-shaped lesions, is rare and tends to be chronic. Stasis dermatitis occurs mainly on the lower legs due to circulatory issues, showing dark spots and swelling. Recognizing these variations aids early diagnosis and management.
Symptoms typically start in early childhood, with most affected individuals experiencing issues before age five. Infants may exhibit widespread rashes, and a significant portion of children continue to show symptoms into adulthood. If symptoms worsen or cause sleep disruption, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Awareness and timely medical attention are crucial to controlling this condition.
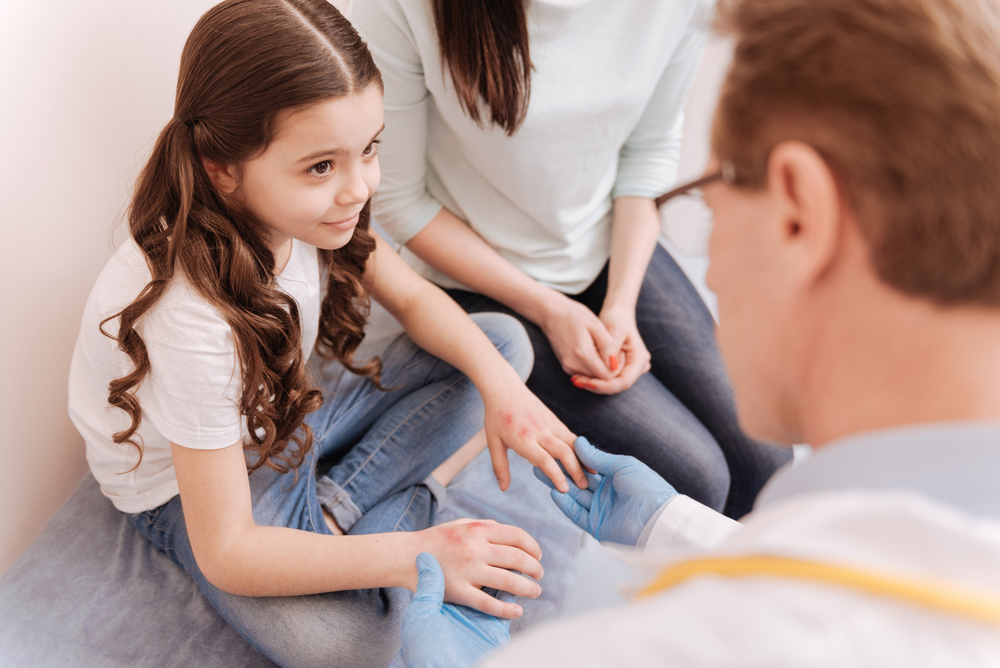
If your child develops a persistent rash, consult a doctor and compare symptoms with reliable images. About 10% of newborns are affected, and many carry symptoms into their adult years. With over 15 million Americans impacted, understanding atopic dermatitis helps in effective management and improved quality of life.