Understanding Atopic Dermatitis: Symptoms and Effective Management Strategies
This article explores typical symptoms of atopic dermatitis and offers practical treatment options. From infants to adults, it covers rash appearances, causes, and management tips to help control this chronic skin condition effectively and improve quality of life.
Sponsored

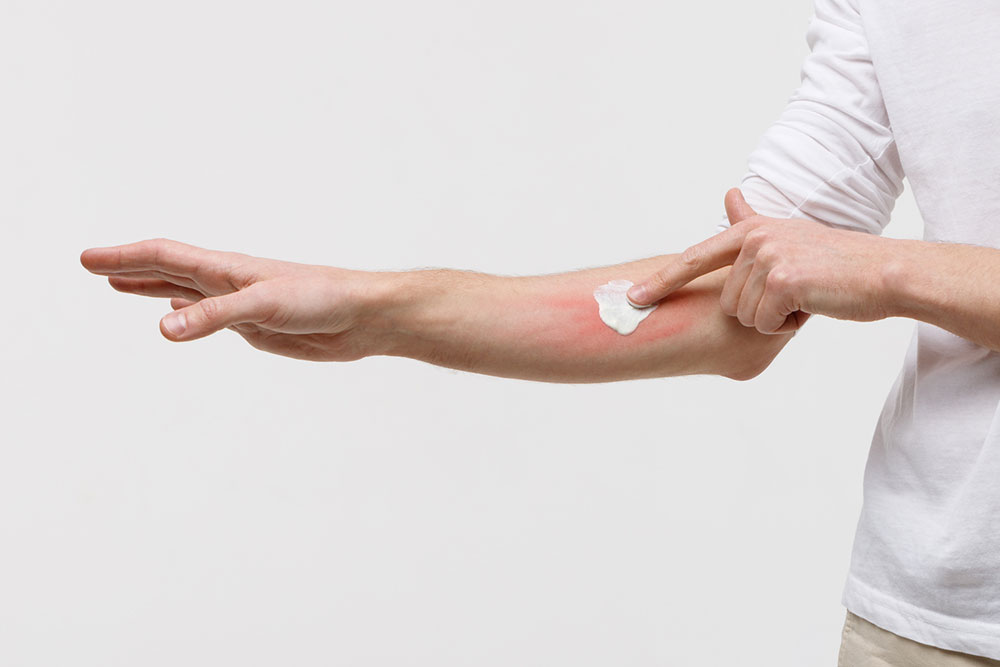
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition marked by red, inflamed, itchy, and swollen skin. It is often linked to genetic factors inherited from family members. Diagnosis typically involves considering personal or family history of allergies like asthma or hay fever, alongside visible rashes.
This condition primarily affects infants and young children but can occur at any age.
Common Symptoms
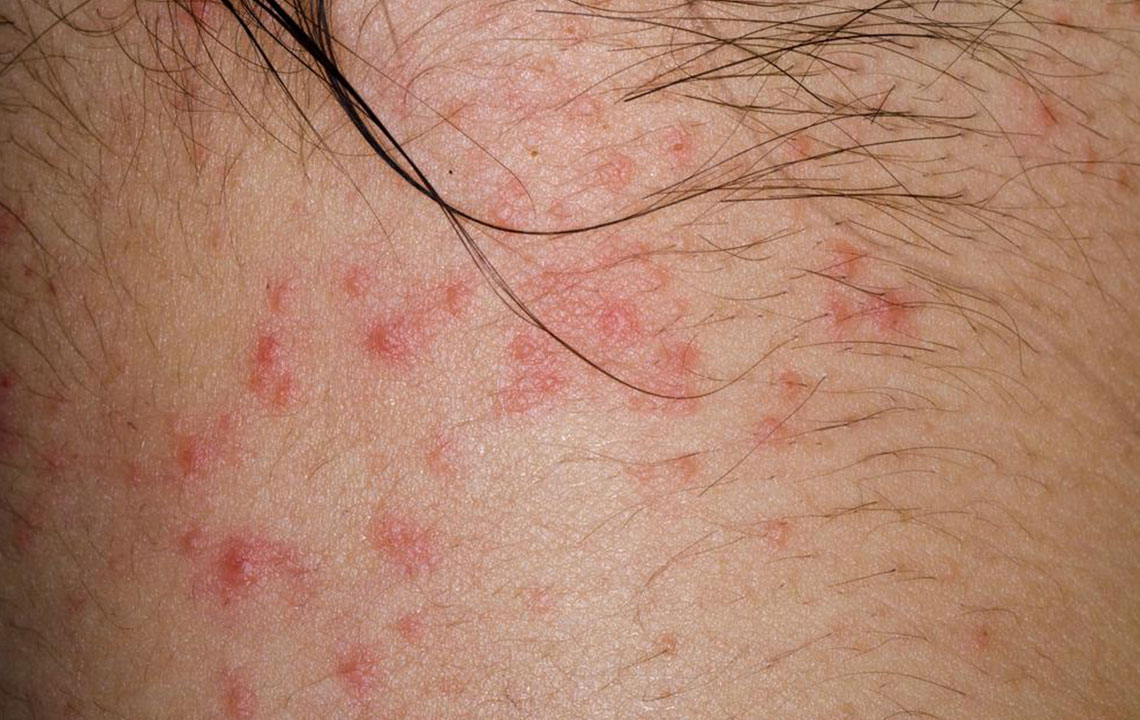
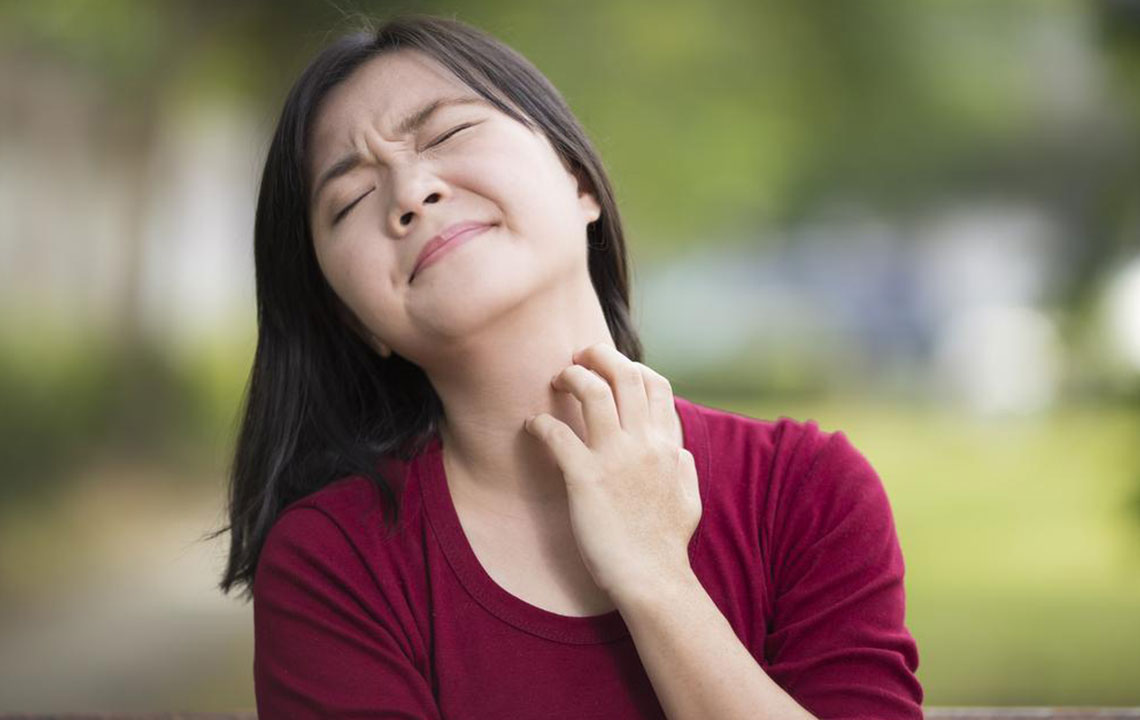
Dry, itchy, and uncomfortable skin
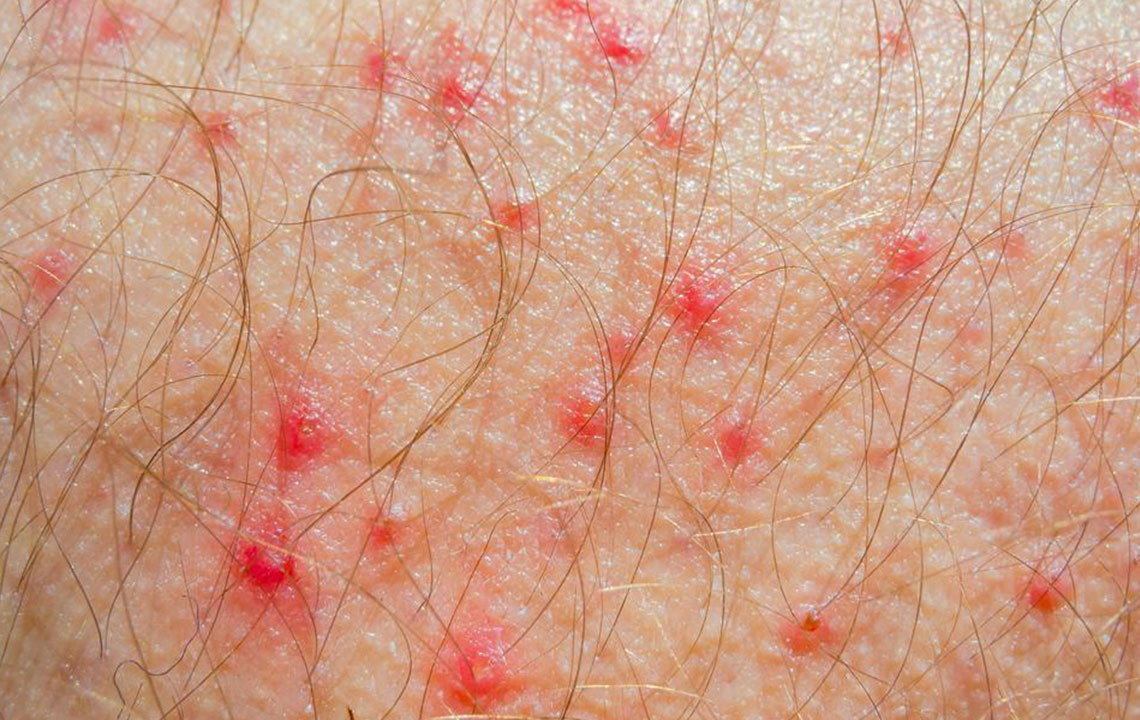
Formation of small blisters filled with clear fluid
Blisters may burst, forming crusts over time
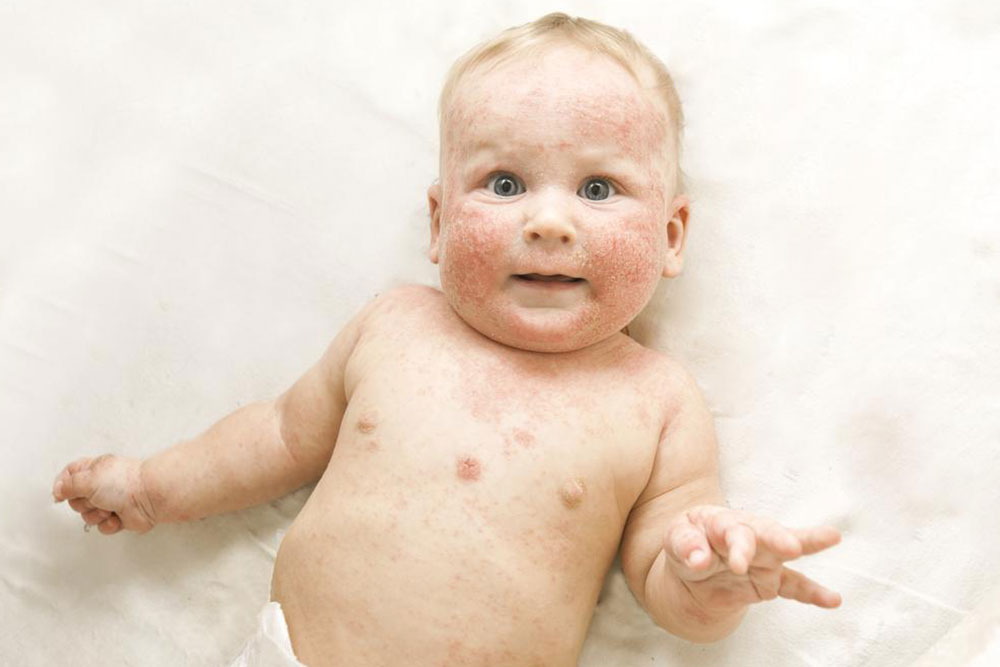
The rash's location and appearance vary with age.
In infants, rashes typically appear on the face and scalp. The discomfort often causes babies to scratch and have sleep disturbances.
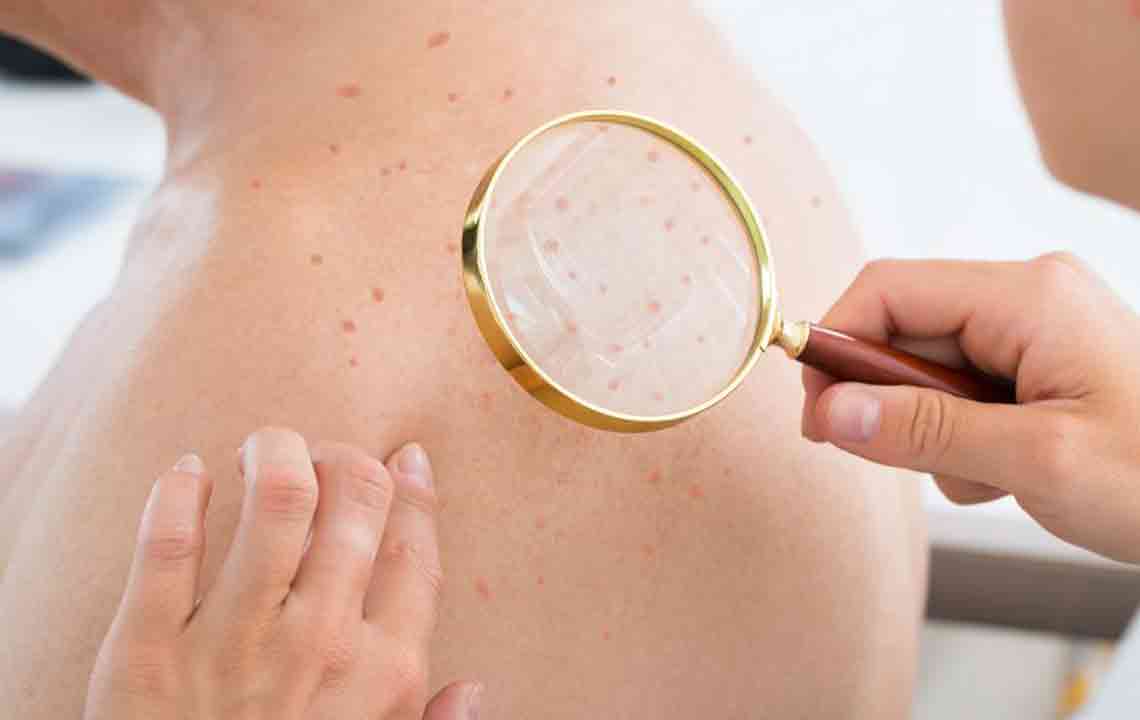
In children over two years, rashes may develop behind knees, elbows, neck, wrists, ankles, or around the buttocks. It begins as an itchy red patch, which may thicken and form nodules over time.
In adults, the rash commonly appears on the face and neck. The skin becomes dry, itchy, and may develop scales or discoloration.
Management and Treatment
Managing atopic dermatitis involves symptom relief and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some effective strategies:
Using barrier-repair moisturizers to soothe the skin and reduce scratching
Avoiding known triggers such as wool and pollen to prevent flare-ups
Taking lukewarm bleach baths lasting 10 minutes for oozing or thickened skin
Applying corticosteroids for severe cases
Antihistamines can help ease itchiness
Supplementing with vitamin D and probiotics may improve symptoms
Phototherapy using UV light may be considered if other treatments fail
The primary goals are symptom relief, preventing infections, and avoiding skin thickening over time.