Essential Guide to Recognizing Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms
Learn the key symptoms of pulmonary embolism, a serious condition caused by blood clots in the lungs. Early recognition and prompt medical diagnosis are crucial to prevent life-threatening outcomes. Symptoms include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid breathing, coughing blood, dizziness, irregular heartbeat, and leg swelling. Diagnosis involves specific tests such as angiography, blood tests, and scans. Treatment options range from medication to surgery, emphasizing the importance of timely intervention to avoid fatalities. Stay informed on symptoms for immediate medical attention.
Sponsored
Recognizing Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism
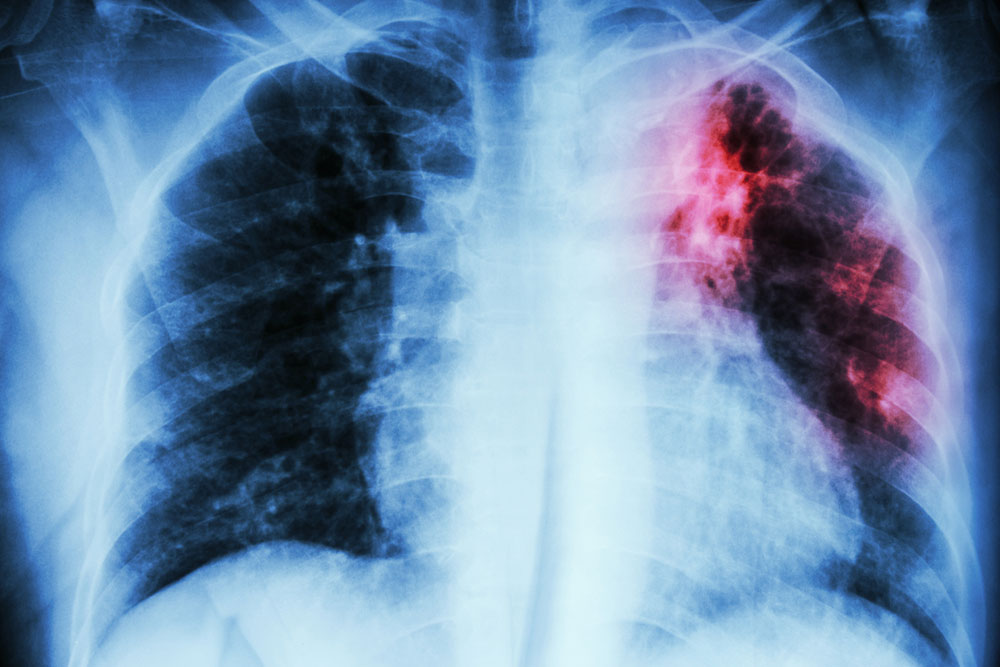
Pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot blocks arteries in the lungs. It usually originates elsewhere in the body and travels through the bloodstream, leading to partial or complete lung obstruction. Factors like cancer, obesity, aging, and genetics can increase risk. Often linked to deep vein thrombosis, where clots form in deep veins—particularly in the legs—these clots can dislodge and cause embolisms. If untreated, a large clot can deprive lungs of oxygen and be fatal.
Early detection is vital. Common warning signs include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain—ranging from mild to intense—and rapid breathing. Other symptoms encompass coughing blood, fainting episodes, irregular heartbeat, skin discoloration, confusion, leg swelling, and sometimes fever. Recognizing these signs helps in prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing pulmonary embolism involves various tests such as pulmonary angiography, blood tests like D-dimer, ECG, ventilation/perfusion scans, chest X-rays, and leg Doppler ultrasound. Treatment typically includes anticoagulants and thrombolytic therapy, with surgical options in severe cases. Managing underlying causes like deep vein thrombosis through regular leg exercises is crucial. Since untreated embolisms can be fatal, early detection and medical intervention are essential. Recognize symptoms early to prevent life-threatening complications.